Functional expression of CCL8 and its interaction with chemokine receptor CCR3
- PMID: 29281969
- PMCID: PMC5745793
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-017-0237-5
Functional expression of CCL8 and its interaction with chemokine receptor CCR3
Abstract
Background: Chemokines and their cognate receptors play important role in the control of leukocyte chemotaxis, HIV entry and other inflammatory diseases. Developing an effcient method to investigate the functional expression of chemokines and its interactions with specific receptors will be helpful to asses the structural and functional characteristics as well as the design of new approach to therapeutic intervention.
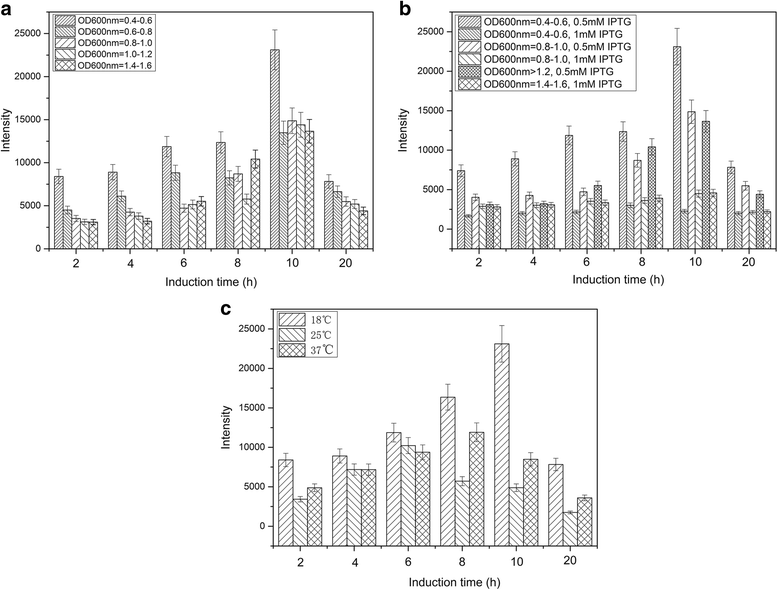
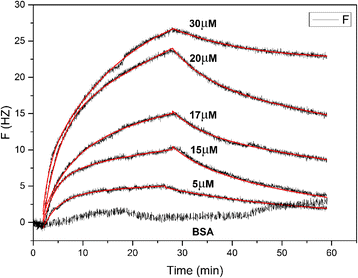
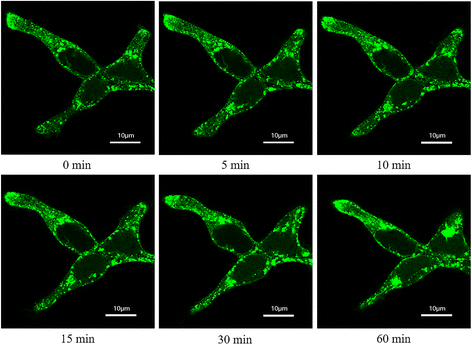
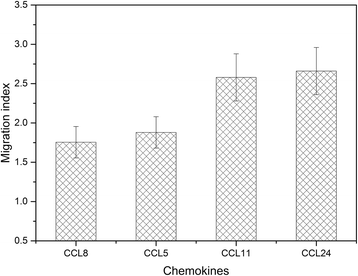
Results: By making systematic optimization study of expression conditions, soluble and functional production of chemokine C-C motif ligand 8 (CCL8) in Escherichia coli (E. coli) has been achieved with approx. 1.5 mg protein/l culture. Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) analysis exhibited that the purified CCL8 could bind with C-C chemokine receptor type 3 (CCR3) with dissociation equilibrium constant (K D) as 1.2 × 10-7 M in vitro. Obvious internalization of CCR3 in vivo could be detected in 1 h when exposed to 100 nM of CCL8. Compared with chemokine C-C motif ligand 11 (CCL11) and chemokine C-C motif ligand 24 (CCL24), a weaker chemotactic effect of CCR3 expressing cells was observed when induced by CCL8 with same concentration.
Conclusion: This study delivers a simple and applicable way to produce functional chemokines in E. coli. The results clearly confirms that CCL8 can interact with chemokine receptor CCR3, therefore, it is promising area to develop drugs for the treatment of related diseases.
Keywords: Agonist; CCL8; Chemokine; Chemokine receptor CCR3; Expression; Interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic up-regulation of MCP-2/CCL8 activity is counteracted by chemokine cleavage, limiting its inflammatory and anti-tumoral effects.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Mar;39(3):843-57. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838660. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19224633
-
Alanine scanning mutagenesis of the chemokine receptor CCR3 reveals distinct extracellular residues involved in recognition of the eotaxin family of chemokines.Mol Immunol. 2006 Mar;43(8):1221-31. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2005.07.015. Epub 2005 Aug 15. Mol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16102831
-
Cloning and characterization of the guinea pig eosinophil eotaxin receptor, C-C chemokine receptor-3: blockade using a monoclonal antibody in vivo.J Immunol. 1998 Dec 1;161(11):6139-47. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9834099
-
Chemokine receptor antagonists: a novel therapeutic approach in allergic diseases.Allergy. 2004 Dec;59(12):1243-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2004.00710.x. Allergy. 2004. PMID: 15507091 Review.
-
Regulation of chemokine receptor expression in eosinophils.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001;125 Suppl 1:29-32. doi: 10.1159/000053849. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11408769 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling of brain transcriptome of masked palm civet (Paguma larvata) with chronic infection of Toxoplasma gondii.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Jul 24;15(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05378-5. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35871661 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dissection of Chagas induced cardiomyopathy reveals central disease associated and druggable signaling pathways.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 May 20;14(5):e0007980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007980. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32433643 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus plantarum-derived extracellular vesicles induce anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage polarization in vitro.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Jul 17;9(1):1793514. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1793514. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 32944181 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of CCL8 inhibition at lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury.iScience. 2022 Dec 22;25(12):105520. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105520. Epub 2022 Nov 7. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36404927 Free PMC article.
-
Phagocytosis of Leptospira by leukocytes from mice with different susceptibility to leptospirosis and possible role of chemokines.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Jan 7;19(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1371-9. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30616505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martine J, SAL S, Leurs R. Fundamentals of chemokines and Chemokine receptors. Weinheim: Wiley; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

