Identification of tRNA nucleoside modification genes critical for stress response and development in rice and Arabidopsis
- PMID: 29268705
- PMCID: PMC5740945
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-017-1206-0
Identification of tRNA nucleoside modification genes critical for stress response and development in rice and Arabidopsis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Identification of tRNA nucleoside modification genes critical for stress response and development in rice and Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Feb 19;18(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1247-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 29458331 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Modification of nucleosides on transfer RNA (tRNA) is important either for correct mRNA decoding process or for tRNA structural stabilization. Nucleoside methylations catalyzed by MTase (methyltransferase) are the most common type among all tRNA nucleoside modifications. Although tRNA modified nucleosides and modification enzymes have been extensively studied in prokaryotic systems, similar research remains preliminary in higher plants, especially in crop species, such as rice (Oryza sativa). Rice is a monocot model plant as well as an important cereal crop, and stress tolerance and yield are of great importance for rice breeding.
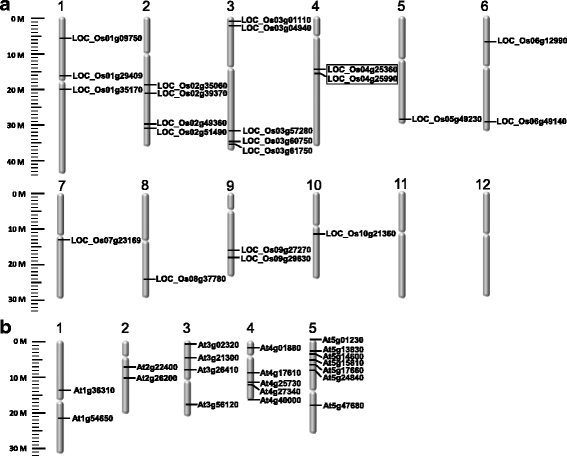
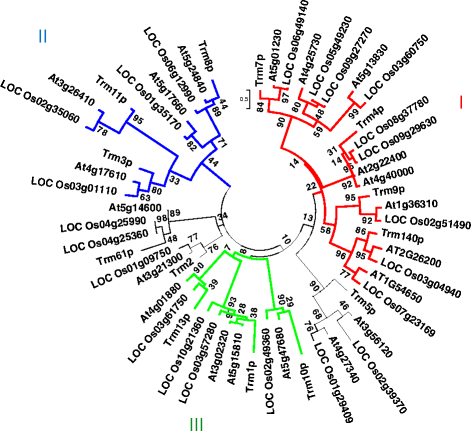
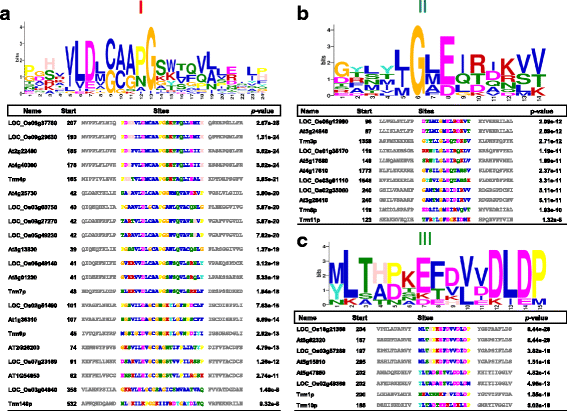
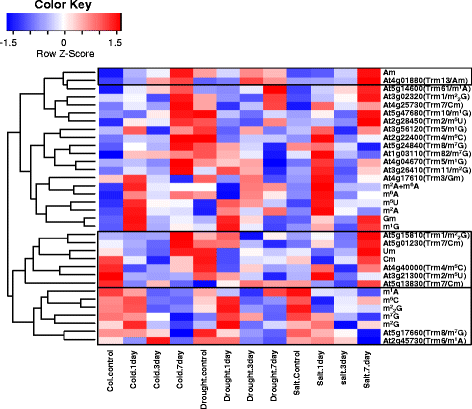
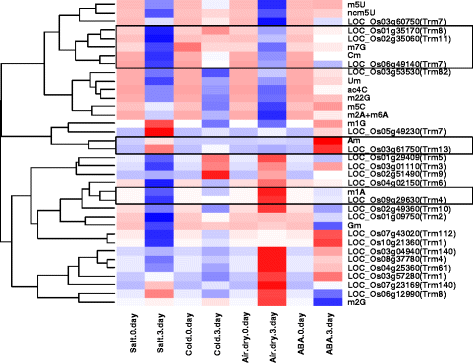
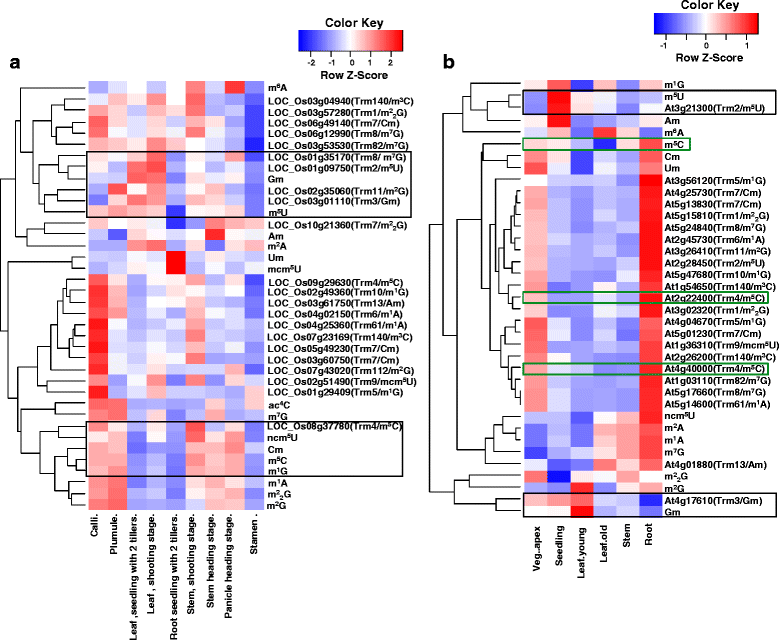
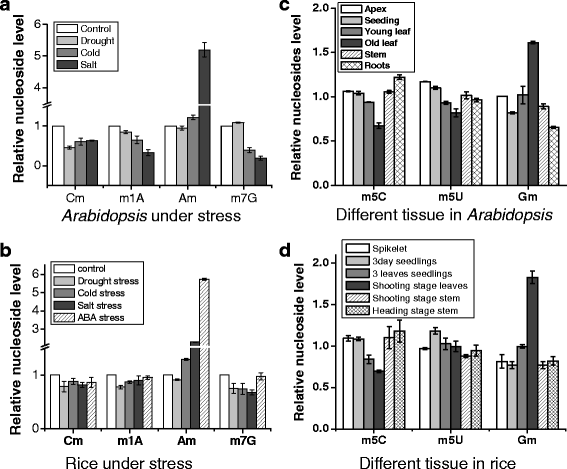
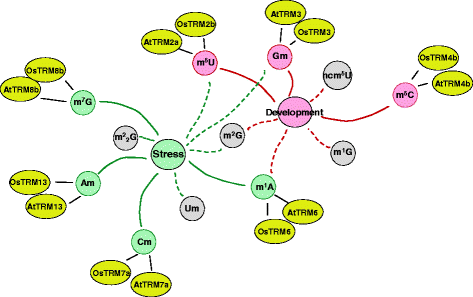
Results: In this study, we investigated how the composition and abundance of tRNA modified nucleosides could change in response to drought, salt and cold stress, as well as in different tissues during the whole growth season in two model plants-O. sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana. Twenty two and 20 MTase candidate genes were identified in rice and Arabidopsis, respectively, by protein sequence homology and conserved domain analysis. Four methylated nucleosides, Am, Cm, m1A and m7G, were found to be very important in stress response both in rice and Arabidopsis. Additionally, three nucleosides,Gm, m5U and m5C, were involved in plant development. Hierarchical clustering analysis revealed consistency on Am, Cm, m1A and m7G MTase candidate genes, and the abundance of the corresponding nucleoside under stress conditions. The same is true for Gm, m5U and m5C modifications and corresponding methylation genes in different tissues during different developmental stages.
Conclusions: We identified candidate genes for various tRNA modified nucleosides in rice and Arabidopsis, especially on MTases for methylated nucleosides. Based on bioinformatics analysis, nucleoside abundance assessments and gene expression profiling, we propose four methylated nucleosides (Am, Cm, m1A and m7G) that are critical for stress response in rice and Arabidopsis, and three methylated nucleosides (Gm, m5U and m5C) that might be important during development.
Keywords: Development; Methyltransferase; Modified nucleoside; Stress; tRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Nipponbare rice (
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The 2'-O-methyladenosine nucleoside modification gene OsTRM13 positively regulates salt stress tolerance in rice.J Exp Bot. 2017 Mar 1;68(7):1479-1491. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx061. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 28369540 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer RNA modifications and genes for modifying enzymes in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Sep 14;10:201. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-201. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20836892 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Arabidopsis glycine-rich RNA-binding protein AtGRP2 or AtGRP7 improves grain yield of rice (Oryza sativa) under drought stress conditions.Plant Sci. 2014 Jan;214:106-12. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Oct 20. Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24268168
-
The control of flowering time by environmental factors.Plant J. 2017 May;90(4):708-719. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13461. Epub 2017 Feb 11. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 27995671 Review.
-
Rice SUMOs and unification of their names.Genes Genet Syst. 2023 Jun 23;98(1):1-7. doi: 10.1266/ggs.22-00097. Epub 2023 May 2. Genes Genet Syst. 2023. PMID: 37150617 Review.
Cited by
-
Transfer RNA-derived non-coding RNAs (tncRNAs): Hidden regulation of plants' transcriptional regulatory circuits.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Sep 22;19:5278-5291. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.09.021. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34630945 Free PMC article.
-
m5UPred: A Web Server for the Prediction of RNA 5-Methyluridine Sites from Sequences.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Sep 30;22:742-747. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.031. eCollection 2020 Dec 4. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 33230471 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-Tuning of Gene Expression by tRNA-Derived Fragments during Abiotic Stress Signal Transduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 8;19(2):518. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020518. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29419808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Arabidopsis TRM61/TRM6 complex is a bona fide tRNA N1-methyladenosine methyltransferase.J Exp Bot. 2020 May 30;71(10):3024-3036. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa100. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 32095811 Free PMC article.
-
RNA methylation in chloroplasts or mitochondria in plants.RNA Biol. 2021 Dec;18(12):2127-2135. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1909321. Epub 2021 Apr 5. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33779501 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

