Structural and functional insights into sorting nexin 5/6 interaction with bacterial effector IncE
- PMID: 29263922
- PMCID: PMC5661634
- DOI: 10.1038/sigtrans.2017.30
Structural and functional insights into sorting nexin 5/6 interaction with bacterial effector IncE
Abstract
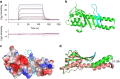
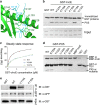
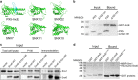
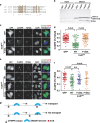
The endosomal trafficking pathways are essential for many cellular activities. They are also important targets by many intracellular pathogens. Key regulators of the endosomal trafficking include the retromer complex and sorting nexins (SNXs). Chlamydia trachomatis effector protein IncE directly targets the retromer components SNX5 and SNX6 and suppresses retromer-mediated transport, but the exact mechanism has remained unclear. We present the crystal structure of the PX domain of SNX5 in complex with IncE, showing that IncE binds to a highly conserved hydrophobic groove of SNX5. The unique helical hairpin of SNX5/6 is essential for binding, explaining the specificity of SNX5/6 for IncE. The SNX5/6-IncE interaction is required for cellular localization of IncE and its inhibitory function. Mechanistically, IncE inhibits the association of CI-MPR cargo with retromer-containing endosomal subdomains. Our study provides new insights into the regulation of retromer-mediated transport and illustrates the intricate competition between host and pathogens in controlling cellular trafficking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chlamydia interfere with an interaction between the mannose-6-phosphate receptor and sorting nexins to counteract host restriction.Elife. 2017 Mar 2;6:e22709. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22709. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28252385 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the hijacking of endosomal sorting nexin proteins by Chlamydia trachomatis.Elife. 2017 Feb 22;6:e22311. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22311. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28226239 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants specific for retromer protein sorting nexin 5 in regulating subcellular retrograde membrane trafficking.J Biomed Res. 2023 Nov 15;37(6):492-506. doi: 10.7555/JBR.37.20230112. J Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 37964759 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of Retromer in Modulating Pathogen Growth.Trends Microbiol. 2018 Sep;26(9):769-780. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Trends Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29703496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging roles of retromer and sorting nexins in the life cycle of viruses.Virol Sin. 2022 Jun;37(3):321-330. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.04.014. Epub 2022 May 2. Virol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35513271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and mechanistic insights into secretagogin-mediated exocytosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Mar 24;117(12):6559-6570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1919698117. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32156735 Free PMC article.
-
Out of the ESCPE room: Emerging roles of endosomal SNX-BARs in receptor transport and host-pathogen interaction.Traffic. 2023 Jun;24(6):234-250. doi: 10.1111/tra.12885. Epub 2023 Apr 23. Traffic. 2023. PMID: 37089068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hijacking host cell vesicular transport: New insights into the nutrient acquisition mechanism of Chlamydia.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2351234. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2351234. Epub 2024 May 21. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38773735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catch and arrest: exploiting the retromer by a Chlamydial effector.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017 Jun 30;2:17039. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2017.39. eCollection 2017. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017. PMID: 29263926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Temporal associations between leukocytes DNA methylation and blood lipids: a longitudinal study.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Oct 23;14(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01356-x. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 36274151 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

