A Novel Sterol-Signaling Pathway Governs Azole Antifungal Drug Resistance and Hypoxic Gene Repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 29263028
- PMCID: PMC5844321
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.117.300554
A Novel Sterol-Signaling Pathway Governs Azole Antifungal Drug Resistance and Hypoxic Gene Repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
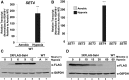
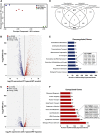
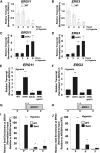
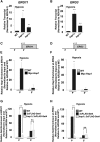
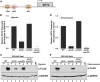
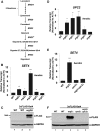
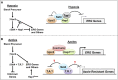
During antifungal drug treatment and hypoxia, genetic and epigenetic changes occur to maintain sterol homeostasis and cellular function. In this study, we show that SET domain-containing epigenetic factors govern drug efficacy to the medically relevant azole class of antifungal drugs. Upon this discovery, we determined that Set4 is induced when Saccharomyces cerevisiae are treated with azole drugs or grown under hypoxic conditions; two conditions that deplete cellular ergosterol and increase sterol precursors. Interestingly, Set4 induction is controlled by the sterol-sensing transcription factors, Upc2 and Ecm22 To determine the role of Set4 on gene expression under hypoxic conditions, we performed RNA-sequencing analysis and showed that Set4 is required for global changes in gene expression. Specifically, loss of Set4 led to an upregulation of nearly all ergosterol genes, including ERG11 and ERG3, suggesting that Set4 functions in gene repression. Furthermore, mass spectrometry analysis revealed that Set4 interacts with the hypoxic-specific transcriptional repressor, Hap1, where this interaction is necessary for Set4 recruitment to ergosterol gene promoters under hypoxia. Finally, an erg3Δ strain, which produces precursor sterols but lacks ergosterol, expresses Set4 under untreated aerobic conditions. Together, our data suggest that sterol precursors are needed for Set4 induction through an Upc2-mediated mechanism. Overall, this new sterol-signaling pathway governs azole antifungal drug resistance and mediates repression of sterol genes under hypoxic conditions.
Keywords: SET4; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; antifungal drugs; chromatin; epigenetics; gene expression; hypoxia; sterol.
Copyright © 2018 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Candida glabrata maintains two HAP1 ohnologs, HAP1A and HAP1B, for distinct roles in ergosterol gene regulation to mediate sterol homeostasis under azole and hypoxic conditions.mSphere. 2024 Nov 21;9(11):e0052424. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00524-24. Epub 2024 Oct 23. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39440948 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast anaerobic response element AR1b regulates aerobic antifungal drug-dependent sterol gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 6;288(49):35466-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526087. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24163365 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans zinc cluster protein Upc2p confers resistance to antifungal drugs and is an activator of ergosterol biosynthetic genes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 May;49(5):1745-52. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.5.1745-1752.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15855491 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Ergosterol Biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 15;11(7):795. doi: 10.3390/genes11070795. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32679672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The synthesis, regulation, and functions of sterols in Candida albicans: Well-known but still lots to learn.Virulence. 2016 Aug 17;7(6):649-59. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1188236. Epub 2016 May 24. Virulence. 2016. PMID: 27221657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
yEvo: experimental evolution in high school classrooms selects for novel mutations that impact clotrimazole resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Nov 4;12(11):jkac246. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac246. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 36173330 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive local false discovery rate procedures for highly spiky data and their application RNA sequencing data of yeast SET4 deletion mutants.Biom J. 2021 Dec;63(8):1729-1744. doi: 10.1002/bimj.202000256. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Biom J. 2021. PMID: 34320248 Free PMC article.
-
Novel sterol binding domains in bacteria.Elife. 2024 Feb 8;12:RP90696. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90696. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38329015 Free PMC article.
-
Set4 is a chromatin-associated protein, promotes survival during oxidative stress, and regulates stress response genes in yeast.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 14;293(37):14429-14443. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003078. Epub 2018 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30082318 Free PMC article.
-
The Lysine Demethylases KdmA and KdmB Differently Regulate Asexual Development, Stress Response, and Virulence in Aspergillus fumigatus.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 May 31;8(6):590. doi: 10.3390/jof8060590. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal A. K., Rogers P. D., Baerson S. R., Jacob M. R., Barker K. S., et al. , 2003. Genome-wide expression profiling of the response to polyene, pyrimidine, azole, and echinocandin antifungal agents in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 34998–35015. - PubMed
-
- Bard M., Lees N. D., Turi T., Craft D., Cofrin L., et al. , 1993. Sterol synthesis and viability of erg11 (cytochrome P450 lanosterol demethylase) mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. Lipids 28: 963–967. - PubMed
-
- Becerra M., Lombardia-Ferreira L. J., Hauser N. C., Hoheisel J. D., Tizon B., et al. , 2002. The yeast transcriptome in aerobic and hypoxic conditions: effects of hap1, rox1, rox3 and srb10 deletions. Mol. Microbiol. 43: 545–555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

