Conserved noncoding transcription and core promoter regulatory code in early Drosophila development
- PMID: 29260710
- PMCID: PMC5754203
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.29005
Conserved noncoding transcription and core promoter regulatory code in early Drosophila development
Abstract
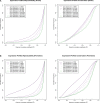
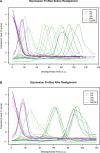
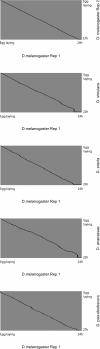
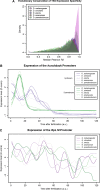
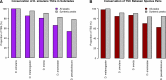
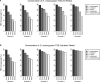
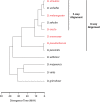
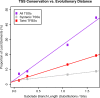
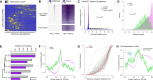
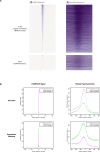
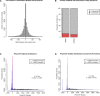
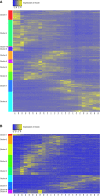
Multicellular development is driven by regulatory programs that orchestrate the transcription of protein-coding and noncoding genes. To decipher this genomic regulatory code, and to investigate the developmental relevance of noncoding transcription, we compared genome-wide promoter activity throughout embryogenesis in 5 Drosophila species. Core promoters, generally not thought to play a significant regulatory role, in fact impart restrictions on the developmental timing of gene expression on a global scale. We propose a hierarchical regulatory model in which core promoters define broad windows of opportunity for expression, by defining a range of transcription factors from which they can receive regulatory inputs. This two-tiered mechanism globally orchestrates developmental gene expression, including extremely widespread noncoding transcription. The sequence and expression specificity of noncoding RNA promoters are evolutionarily conserved, implying biological relevance. Overall, this work introduces a hierarchical model for developmental gene regulation, and reveals a major role for noncoding transcription in animal development.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Drosophila; Genome; Melanogaster; chromosomes; genes.
Conflict of interest statement
Reviewing editor,
No competing interests declared.
Figures
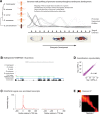
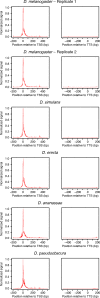
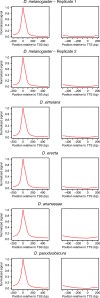
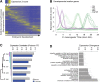


Similar articles
-
The degree of enhancer or promoter activity is reflected by the levels and directionality of eRNA transcription.Genes Dev. 2018 Jan 1;32(1):42-57. doi: 10.1101/gad.308619.117. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 29378788 Free PMC article.
-
High-fidelity promoter profiling reveals widespread alternative promoter usage and transposon-driven developmental gene expression.Genome Res. 2013 Jan;23(1):169-80. doi: 10.1101/gr.139618.112. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 22936248 Free PMC article.
-
cis-Acting sequences controlling the adult-specific transcription pattern of the Drosophila affinidisjuncta Adh gene.Dev Genet. 1998;23(2):119-27. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1998)23:2<119::AID-DVG4>3.0.CO;2-9. Dev Genet. 1998. PMID: 9770269
-
How does noncoding transcription regulate Hox genes?Bioessays. 2008 Feb;30(2):110-21. doi: 10.1002/bies.20704. Bioessays. 2008. PMID: 18200528 Review.
-
Unraveling cis-regulatory mechanisms at the abdominal-A and Abdominal-B genes in the Drosophila bithorax complex.Dev Biol. 2006 May 15;293(2):294-304. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.02.015. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16545794 Review.
Cited by
-
ElemeNT 2023: an enhanced tool for detection and curation of core promoter elements.Bioinformatics. 2024 Mar 4;40(3):btae110. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae110. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38407414 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter architecture of Drosophila genes regulated by Myocyte enhancer factor-2.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 21;17(7):e0271554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271554. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35862472 Free PMC article.
-
Two promoters integrate multiple enhancer inputs to drive wild-type knirps expression in the Drosophila melanogaster embryo.Genetics. 2021 Dec 10;219(4):iyab154. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab154. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 34849867 Free PMC article.
-
The Core Promoter Is a Regulatory Hub for Developmental Gene Expression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 10;9:666508. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.666508. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription initiation of distant core promoters in a large-sized genome of an insect.BMC Biol. 2021 Mar 30;19(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01004-5. BMC Biol. 2021. PMID: 33785021 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

