Involvement of Adapter Protein Complex 4 in Hypersensitive Cell Death Induced by Avirulent Bacteria
- PMID: 29242374
- PMCID: PMC5813582
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.17.01610
Involvement of Adapter Protein Complex 4 in Hypersensitive Cell Death Induced by Avirulent Bacteria
Abstract
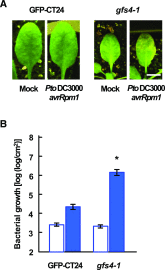
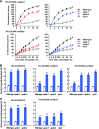
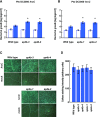
Plant immunity to avirulent bacterial pathogens is associated with subcellular membrane dynamics including fusion between the vacuolar and plasma membranes, resulting in hypersensitive cell death. Here, we report that ADAPTOR PROTEIN COMPLEX-4 (AP-4) subunits are involved in plant immunity associated with hypersensitive cell death. We isolated a mutant with a defect in resistance to an avirulent strain of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pto) DC3000 avrRpm1 from a vacuolar protein sorting mutant library of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). The mutant was identical to gfs4-1, which has a mutation in the gene encoding the AP-4 subunit AP4B. Thus, we focused on AP4B and another subunit, AP4E. All of the mutants (ap4b-3, ap4b-4, ap4e-1, and ap4e-2) were defective in hypersensitive cell death and resistance to Pto DC3000 with the type III effector AvrRpm1 or AvrRpt2, both of which are recognized on the plasma membrane, while they showed slightly enhanced susceptibility to the type-III-secretion-deficient P. syringae strain hrcC On the other hand, both ap4b-3 and ap4b-4 showed no defect in resistance to Pto DC3000 with the type III effector AvrRps4, which is recognized in the cytosol and does not induce hypersensitive cell death. Upon infection with Pto DC3000 avrRpt2, the ap4b-3 and ap4b-4 leaf cells did not show fusion between vacuolar and plasma membranes, whereas the wild-type leaf cells did. These results suggest that AP-4 contributes to cell death-associated immunity, possibly via membrane fusion, after type III effector-recognition on the plasma membrane.
© 2018 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A salicylic acid-induced lectin-like protein plays a positive role in the effector-triggered immunity response of Arabidopsis thaliana to Pseudomonas syringae Avr-Rpm1.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013 Dec;26(12):1395-406. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-13-0044-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013. PMID: 24006883
-
Arabidopsis thaliana serpins AtSRP4 and AtSRP5 negatively regulate stress-induced cell death and effector-triggered immunity induced by bacterial effector AvrRpt2.Physiol Plant. 2017 Mar;159(3):329-339. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12516. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Physiol Plant. 2017. PMID: 27709637
-
The Adaptor Complex AP-4 Regulates Vacuolar Protein Sorting at the trans-Golgi Network by Interacting with VACUOLAR SORTING RECEPTOR1.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jan;170(1):211-9. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00869. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26546666 Free PMC article.
-
The Erwinia amylovora avrRpt2EA gene contributes to virulence on pear and AvrRpt2EA is recognized by Arabidopsis RPS2 when expressed in pseudomonas syringae.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2006 Jun;19(6):644-54. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-0644. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2006. PMID: 16776298
-
Arabidopsis TAO1 is a TIR-NB-LRR protein that contributes to disease resistance induced by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 29;105(17):6475-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802157105. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18424557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Classification of adaptor proteins using recurrent neural networks and PSSM profiles.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 24;20(Suppl 9):966. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6335-4. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31874633 Free PMC article.
-
Two Liberibacter Proteins Combine to Suppress Critical Innate Immune Defenses in Citrus.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 2;13:869178. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.869178. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35586217 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into maydis leaf blight resistance in maize: a comprehensive genome-wide association study in sub-tropics of India.BMC Genomics. 2024 Aug 5;25(1):760. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10655-x. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39103778 Free PMC article.
-
Role of adaptin protein complexes in intracellular trafficking and their impact on diseases.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):8259-8278. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1982846. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34565296 Free PMC article.
-
The Effector AGLIP1 in Rhizoctonia solani AG1 IA Triggers Cell Death in Plants and Promotes Disease Development Through Inhibiting PAMP-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 26;10:2228. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02228. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31611861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam L, Somerville SC (1996) Genetic characterization of five powdery mildew disease resistance loci in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 9: 341–356 - PubMed
-
- Axtell MJ, Staskawicz BJ (2003) Initiation of RPS2-specified disease resistance in Arabidopsis is coupled to the AvrRpt2-directed elimination of RIN4. Cell 112: 369–377 - PubMed
-
- Bennett N, Letourneur F, Ragno M, Louwagie M (2008) Sorting of the v-SNARE VAMP7 in Dictyostelium discoideum: a role for more than one Adaptor Protein (AP) complex. Exp Cell Res 314: 2822–2833 - PubMed
-
- Bent AF, Kunkel BN, Dahlbeck D, Brown KL, Schmidt R, Giraudat J, Leung J, Staskawicz BJ (1994) RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265: 1856–1860 - PubMed
-
- Blott EJ, Griffiths GM (2002) Secretory lysosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 122–131 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

