Vacuole-mediated selective regulation of TORC1-Sch9 signaling following oxidative stress
- PMID: 29237820
- PMCID: PMC6014174
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E17-09-0553
Vacuole-mediated selective regulation of TORC1-Sch9 signaling following oxidative stress
Abstract
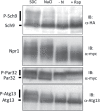
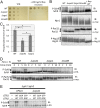
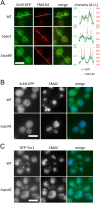
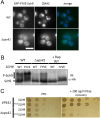
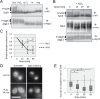
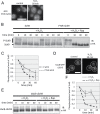
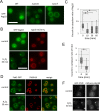
Target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1) is a central cellular signaling coordinator that allows eukaryotic cells to adapt to the environment. In the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, TORC1 senses nitrogen and various stressors and modulates proteosynthesis, nitrogen uptake and metabolism, stress responses, and autophagy. There is some indication that TORC1 may regulate these downstream pathways individually. However, the potential mechanisms for such differential regulation are unknown. Here we show that the serine/threonine protein kinase Sch9 branch of TORC1 signaling depends specifically on the integrity of the vacuolar membrane, and this dependency originates in changes in Sch9 localization reflected by phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate. Moreover, oxidative stress induces the delocalization of Sch9 from vacuoles, contributing to the persistent inhibition of the Sch9 branch after stress. Thus, our results establish that regulation of the vacuolar localization of Sch9 serves as a selective switch for the Sch9 branch in divergent TORC1 signaling. We propose that the Sch9 branch integrates the intrinsic activity of TORC1 kinase and vacuolar status, which is monitored by the phospholipids of the vacuolar membrane, into the regulation of macromolecular synthesis.
© 2018 Takeda et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vacuolar Localization via the N-terminal Domain of Sch9 is Required for TORC1-dependent Phosphorylation and Downstream Signal Transduction.J Mol Biol. 2021 Dec 3;433(24):167326. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167326. Epub 2021 Oct 22. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34695378
-
State transitions in the TORC1 signaling pathway and information processing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2014 Oct;198(2):773-86. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.168369. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 25085507 Free PMC article.
-
Sch9 partially mediates TORC1 signaling to control ribosomal RNA synthesis.Cell Cycle. 2009 Dec 15;8(24):4085-90. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.24.10170. Epub 2009 Dec 25. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19823048 Free PMC article.
-
The TORC1-Sch9 pathway as a crucial mediator of chronological lifespan in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Yeast Res. 2018 Aug 1;18(5). doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foy048. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018. PMID: 29788208 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms linking the evolutionary conserved TORC1-Sch9 nutrient signalling branch to lifespan regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Yeast Res. 2014 Feb;14(1):17-32. doi: 10.1111/1567-1364.12097. Epub 2013 Oct 11. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014. PMID: 24102693 Review.
Cited by
-
Sphingolipid/Pkh1/2-TORC1/Sch9 Signaling Regulates Ribosome Biogenesis in Tunicamycin-Induced Stress Response in Yeast.Genetics. 2019 May;212(1):175-186. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301874. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30824472 Free PMC article.
-
Human gasdermin D and MLKL disrupt mitochondria, endocytic traffic and TORC1 signalling in budding yeast.Open Biol. 2023 May;13(5):220366. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220366. Epub 2023 May 24. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37220793 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrient transceptors physically interact with the yeast S6/protein kinase B homolog, Sch9, a TOR kinase target.Biochem J. 2021 Jan 29;478(2):357-375. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200722. Biochem J. 2021. PMID: 33394033 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct TORC1 signalling branches regulate Adc17 proteasome assembly chaperone expression.J Cell Sci. 2024 Jul 15;137(14):jcs261892. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261892. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 38949052 Free PMC article.
-
A substrate localization model for the selective regulation of TORC1 downstream pathways.Commun Integr Biol. 2018 Jun 18;11(2):1-4. doi: 10.1080/19420889.2018.1475830. eCollection 2018. Commun Integr Biol. 2018. PMID: 30083287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bae GU, Seo DW, Kwon HK, Lee HY, Hong S, Lee ZW, Ha KS, Lee HW, Han JW. Hydrogen peroxide activates p70(S6k) signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1999:32596–32602. - PubMed
-
- Balderhaar HJ, Ungermann C. CORVET and HOPS tethering complexes—coordinators of endosome and lysosome fusion. J Cell Sci. 2013:1307–1316. - PubMed
-
- Beck T, Hall MN. The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient-regulated transcription factors. Nature. 1999:689–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

