Continuous-Flow Production of Injectable Liposomes via a Microfluidic Approach
- PMID: 29232873
- PMCID: PMC5744346
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10121411
Continuous-Flow Production of Injectable Liposomes via a Microfluidic Approach
Abstract
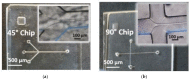
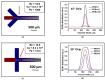
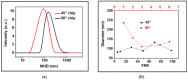
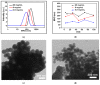
Injectable liposomes are characterized by a suitable size and unique lipid mixtures, which require time-consuming and nonstraightforward production processes. The complexity of the manufacturing methods may affect liposome solubility, the phase transition temperatures of the membranes, the average particle size, and the associated particle size distribution, with a possible impact on the drug encapsulation and release. By leveraging the precise steady-state control over the mixing of miscible liquids and a highly efficient heat transfer, microfluidic technology has proved to be an effective and direct methodology to produce liposomes. This approach results particularly efficient in reducing the number of the sizing steps, when compared to standard industrial methods. Here, Microfluidic Hydrodynamic Focusing chips were produced and used to form liposomes upon tuning experimental parameters such as lipids concentration and Flow-Rate-Ratios (FRRs). Although modelling evidenced the dependence of the laminar flow on the geometric constraints and the FRR conditions, for the specific formulation investigated in this study, the lipids concentration was identified as the primary factor influencing the size of the liposomes and their polydispersity index. This was attributed to a predominance of the bending elasticity modulus over the vesiculation index in the lipid mixture used. Eventually, liposomes of injectable size were produced using microfluidic one-pot synthesis in continuous flow.
Keywords: liposomes; microfluidics; microreactors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid and scale-independent microfluidic manufacture of liposomes entrapping protein incorporating in-line purification and at-line size monitoring.Int J Pharm. 2019 Feb 10;556:68-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.11.060. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30503269
-
Characterization of Nanoscale Loaded Liposomes Produced by 2D Hydrodynamic Flow Focusing.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018 Feb 12;4(2):502-513. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00572. Epub 2018 Jan 23. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018. PMID: 33418740
-
High-throughput continuous production of liposomes using hydrodynamic flow-focusing microfluidic devices.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017 Aug 1;156:349-357. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.05.033. Epub 2017 May 11. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017. PMID: 28549322
-
Microfluidic synthesis of lipid-based nanoparticles for drug delivery: recent advances and opportunities.Lab Chip. 2024 Feb 27;24(5):1154-1174. doi: 10.1039/d3lc00821e. Lab Chip. 2024. PMID: 38165786 Review.
-
Liposome production by microfluidics: potential and limiting factors.Sci Rep. 2016 May 19;6:25876. doi: 10.1038/srep25876. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27194474 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leveraging Numerical Simulation Technology to Advance Drug Preparation: A Comprehensive Review of Application Scenarios and Cases.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 7;16(10):1304. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101304. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Solvent Selection: Strategies to Guide the Manufacturing of Liposomes Using Microfluidics.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Dec 4;11(12):653. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11120653. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31817217 Free PMC article.
-
High Manganese Content of Lipid NanoMn (LNM) by Microfluidic Technology for Enhancing Anti-Tumor Immunity.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 19;16(4):556. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040556. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675217 Free PMC article.
-
Precise control of liposome size using characteristic time depends on solvent type and membrane properties.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 23;13(1):4728. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31895-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36959258 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Liposomal-Based Anti-Inflammatory Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 1;13(7):1004. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13071004. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34371695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

