Insights from resolving protein-DNA interactions at near base-pair resolution
- PMID: 29211822
- PMCID: PMC5889022
- DOI: 10.1093/bfgp/elx043
Insights from resolving protein-DNA interactions at near base-pair resolution
Abstract
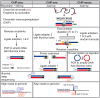
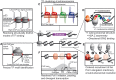
One of the central goals in molecular biology is to understand how cell-type-specific expression patterns arise through selective recruitment of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) to a subset of gene promoters. Pol II needs to be recruited to a precise genomic position at the proper time to produce messenger RNA from a DNA template. Ostensibly, transcription is a relatively simple cellular process; yet, experimentally measuring and then understanding the combinatorial possibilities of transcriptional regulators remain a daunting task. Since its introduction in 1985, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) has remained a key tool for investigating protein-DNA contacts in vivo. Over 30 years of intensive research using ChIP have provided numerous insights into mechanisms of gene regulation. As functional genomic technologies improve, they present new opportunities to address key biological questions. ChIP-exo is a refined version of ChIP-seq that significantly reduces background signal, while providing near base-pair mapping resolution for protein-DNA interactions. This review discusses the evolution of the ChIP assay over the years; the methodological differences between ChIP-seq, ChIP-exo and ChIP-nexus; and highlight new insights into epigenetic and transcriptional mechanisms that were uniquely enabled with the near base-pair resolution of ChIP-exo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The ChIP-exo Method: Identifying Protein-DNA Interactions with Near Base Pair Precision.J Vis Exp. 2016 Dec 23;(118):55016. doi: 10.3791/55016. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 28060339 Free PMC article.
-
A simple method for generating high-resolution maps of genome-wide protein binding.Elife. 2015 Jun 16;4:e09225. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09225. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26079792 Free PMC article.
-
Precise Identification of DNA-Binding Proteins Genomic Location by Exonuclease Coupled Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP-exo).Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1334:173-93. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2877-4_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26404150
-
[Finding targets of transcriptional regulators--chromatin immunoprecipitation assay (ChIP)].Postepy Biochem. 2011;57(4):418-24. Postepy Biochem. 2011. PMID: 22568174 Review. Polish.
-
Genome Wide Approaches to Identify Protein-DNA Interactions.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(42):7641-7654. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180530115711. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29848263 Review.
Cited by
-
Single cell imaging reveals cisplatin regulating interactions between transcription (co)factors and DNA.Chem Sci. 2021 Feb 25;12(15):5419-5429. doi: 10.1039/d0sc06760a. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34163767 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characteristics of the chondrocyte-enriched SNORC protein and its transcriptional regulation by SOX9.Sci Rep. 2020 May 8;10(1):7790. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64640-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32385306 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of ChIP-exo peak-callers: impact of data quality, read duplication and binding subtypes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Feb 21;21(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3403-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32085702 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic and transcriptional profiling of triple negative breast cancer.Sci Data. 2019 Mar 5;6:190033. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2019.33. Sci Data. 2019. PMID: 30835260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li W, Notani D, Rosenfeld MG.. Enhancers as non-coding RNA transcription units: recent insights and future perspectives. Nat Rev Genet 2016;17(4):207–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

