Toll-Like Receptor 4, but Not Neutrophil Extracellular Traps, Promote IFN Type I Expression to Enhance Th2 Responses to Nippostrongylus brasiliensis
- PMID: 29201030
- PMCID: PMC5696323
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01575
Toll-Like Receptor 4, but Not Neutrophil Extracellular Traps, Promote IFN Type I Expression to Enhance Th2 Responses to Nippostrongylus brasiliensis
Abstract
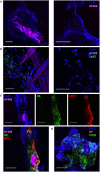
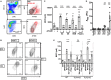
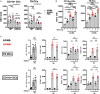
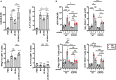
The induction of Th2 responses is thought to be multifactorial, and emerge from specific pathways distinct from those associated with antagonistic antibacterial or antiviral Th1 responses. Here, we show that the recognition of non-viable Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nb) in the skin induces a strong recruitment of monocytes and neutrophils and the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Nb also activates toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling with expression of Ifnb transcripts in the skin and the development of an IFN type I signature on helminth antigen-bearing dendritic cells in draining lymph nodes. Co-injection of Nb together with about 10,000 Gram-negative bacteria amplified this TLR4-dependent but NET-independent IFN type I response and enhanced the development of Th2 responses. Thus, a limited activation of antibacterial signaling pathways is able to boost antihelminthic responses, suggesting a role for bacterial sensing in the optimal induction of Th2 immunity.
Keywords: IFN-I; Nippostrongylus brasiliensis; Th2 response; dendritic cells; helminth; neutrophil extracellular traps; skin immunity; toll-like receptor 4.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Th2 responses are primed by skin dendritic cells with distinct transcriptional profiles.J Exp Med. 2017 Jan;214(1):125-142. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160470. Epub 2016 Dec 2. J Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 27913566 Free PMC article.
-
Infection with Toxoplasma gondii reduces established and developing Th2 responses induced by Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection.Infect Immun. 2004 Jul;72(7):3812-22. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.3812-3822.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15213122 Free PMC article.
-
Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: cytokine responses and nematode expulsion in normal and IL-4-deficient mice.Exp Parasitol. 1996 Oct;84(1):65-73. doi: 10.1006/expr.1996.0090. Exp Parasitol. 1996. PMID: 8888733
-
Hookworms Evade Host Immunity by Secreting a Deoxyribonuclease to Degrade Neutrophil Extracellular Traps.Cell Host Microbe. 2020 Feb 12;27(2):277-289.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.01.011. Cell Host Microbe. 2020. PMID: 32053791
-
Inhibitors of Serine Proteases in Regulating the Production and Function of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps.Front Immunol. 2016 Jun 30;7:261. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00261. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27446090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short-Chain Fatty Acids Calibrate RARα Activity Regulating Food Sensitization.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 14;12:737658. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.737658. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34721398 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse innate stimuli activate basophils through pathways involving Syk and IκB kinases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 23;118(12):e2019524118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2019524118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33727419 Free PMC article.
-
CRFB5a, a Subtype of Japanese Eel (Anguilla japonica) Type I IFN Receptor, Regulates Host Antiviral and Antimicrobial Functions through Activation of IRF3/IRF7 and LEAP2.Animals (Basel). 2023 Oct 9;13(19):3157. doi: 10.3390/ani13193157. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835763 Free PMC article.
-
Hookworm infections: Reappraising the evidence for a role of neutrophils in light of NETosis.Parasite Immunol. 2022 Jun;44(6):e12911. doi: 10.1111/pim.12911. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Parasite Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35124825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homeostatic IL-13 in healthy skin directs dendritic cell differentiation to promote TH2 and inhibit TH17 cell polarization.Nat Immunol. 2021 Dec;22(12):1538-1550. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-01067-0. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Nat Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34795444
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

