Cryo-EM structures reveal specialization at the myosin VI-actin interface and a mechanism of force sensitivity
- PMID: 29199952
- PMCID: PMC5762158
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.31125
Cryo-EM structures reveal specialization at the myosin VI-actin interface and a mechanism of force sensitivity
Abstract
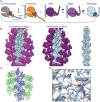
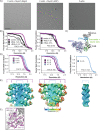
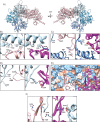
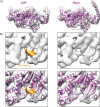
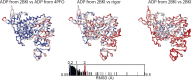
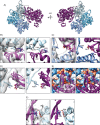
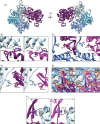
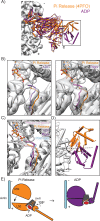
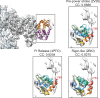
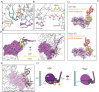
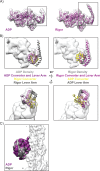
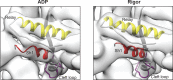
Despite extensive scrutiny of the myosin superfamily, the lack of high-resolution structures of actin-bound states has prevented a complete description of its mechanochemical cycle and limited insight into how sequence and structural diversification of the motor domain gives rise to specialized functional properties. Here we present cryo-EM structures of the unique minus-end directed myosin VI motor domain in rigor (4.6 Å) and Mg-ADP (5.5 Å) states bound to F-actin. Comparison to the myosin IIC-F-actin rigor complex reveals an almost complete lack of conservation of residues at the actin-myosin interface despite preservation of the primary sequence regions composing it, suggesting an evolutionary path for motor specialization. Additionally, analysis of the transition from ADP to rigor provides a structural rationale for force sensitivity in this step of the mechanochemical cycle. Finally, we observe reciprocal rearrangements in actin and myosin accompanying the transition between these states, supporting a role for actin structural plasticity during force generation by myosin VI.
Keywords: Cryo-EM; actin; biophysics; cytoskeleton; molecular motors; myosin; none; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
High-resolution structures of the actomyosin-V complex in three nucleotide states provide insights into the force generation mechanism.Elife. 2021 Nov 23;10:e73724. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73724. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34812732 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution cryo-EM structures of actin-bound myosin states reveal the mechanism of myosin force sensing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 6;115(6):1292-1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1718316115. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29358376 Free PMC article.
-
Autoinhibition and activation of myosin VI revealed by its cryo-EM structure.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 8;15(1):1187. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45424-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38331992 Free PMC article.
-
[Myosin VI: the unique motor protein of the actin cytoskeleton].Postepy Biochem. 2011;57(1):63-73. Postepy Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21735821 Review. Polish.
-
Myosin VI rewrites the rules for myosin motors.Cell. 2010 May 14;141(4):573-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.028. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20478251 Review.
Cited by
-
The Central Role of the F-Actin Surface in Myosin Force Generation.Biology (Basel). 2021 Nov 23;10(12):1221. doi: 10.3390/biology10121221. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and Computational Insights into a Blebbistatin-Bound Myosin•ADP Complex with Characteristics of an ADP-Release Conformation along the Two-Step Myosin Power Stoke.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 8;21(19):7417. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197417. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33049993 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution structures of the actomyosin-V complex in three nucleotide states provide insights into the force generation mechanism.Elife. 2021 Nov 23;10:e73724. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73724. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34812732 Free PMC article.
-
Greg Alushin: The shape of things to come.J Cell Biol. 2019 Jul 1;218(7):2073-2074. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201906042. Epub 2019 Jun 20. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31221629 Free PMC article.
-
Processivity and Velocity for Motors Stepping on Periodic Tracks.Biophys J. 2020 Apr 7;118(7):1537-1551. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.01.047. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32367805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed ZM, Morell RJ, Riazuddin S, Gropman A, Shaukat S, Ahmad MM, Mohiddin SA, Fananapazir L, Caruso RC, Husnain T, Khan SN, Riazuddin S, Griffith AJ, Friedman TB, Wilcox ER. Mutations of MYO6 are associated with recessive deafness, DFNB37. The American Journal of Human Genetics. 2003;72:1315–1322. doi: 10.1086/375122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

