Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Targeting Can Protect against Arthritis with Low Sensitization to Infection
- PMID: 29184553
- PMCID: PMC5694445
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01533
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Targeting Can Protect against Arthritis with Low Sensitization to Infection
Abstract
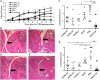
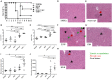
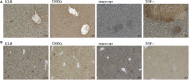
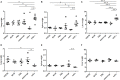
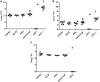
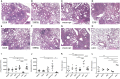
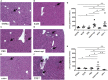
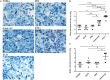
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) blockade is an effective treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other inflammatory diseases, but in patients, it is associated with reduced resistance to the infectious agents Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Listeria monocytogenes, among others. Our goal was to model infection and arthritis in mice and to compare etanercept, a currently used anti-TNF-α inhibitor, to an anti-TNF-α vaccine. We developed a murine surrogate of the TNF-α kinoid and produced an anti-murine TNF-α vaccine (TNFKi) composed of keyhole limpet hemocyanin conjugated to TNF-α, which resulted in anti-TNF-α antibody production in mice. We also used etanercept (a soluble receptor of TNF commonly used to treat RA) as a control of TNF neutralization. In a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis, TNFKi protected against inflammation similar to etanercept. In a mouse model of acute L. monocytogenes infection, all TNFKi-treated mice showed cleared bacterial infection and survived, whereas etanercept-treated mice showed large liver granulomas and quickly died. Moreover, TNFKi mice infected with the virulent H37Rv M. tuberculosis showed resistance to infection, in contrast with etanercept-treated mice or controls. Depending on the TNF-α blockade strategy, treating arthritis with a TNF-α inhibitor could result in a different profile of infection suceptibility. Our TNFKi vaccine allowed for a better remaining host defense than did etanercept.
Keywords: host-defense; infection; rheumatoid arthritis; tumor necrosis factor; vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dominant-negative tumor necrosis factor protects from Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette Guérin (BCG) and endotoxin-induced liver injury without compromising host immunity to BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Infect Dis. 2009 Apr 1;199(7):1053-63. doi: 10.1086/597204. J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19222369
-
The infectious profiles of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in a Thai population: a retrospective study a the university-based hospital.Int J Rheum Dis. 2009 Jul;12(2):118-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2009.01393.x. Int J Rheum Dis. 2009. PMID: 20374328
-
A virus-like particle-based vaccine selectively targeting soluble TNF-alpha protects from arthritis without inducing reactivation of latent tuberculosis.J Immunol. 2007 Jun 1;178(11):7450-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.11.7450. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17513796
-
Update on the Japanese guidelines for the use of infliximab and etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis.Mod Rheumatol. 2007;17(6):451-8. doi: 10.1007/s10165-007-0626-3. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Mod Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 18084695 Review.
-
Reactivation of latent tuberculosis by TNF blockade: the role of interferon gamma.J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2007 May;12(1):16-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.jidsymp.5650031. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2007. PMID: 17502864 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of nSMOL coupled with LC-MS bioanalysis for monitoring the Fc-fusion biopharmaceuticals Etanercept and Abatacept in human serum.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2018 Jul 24;6(4):e00422. doi: 10.1002/prp2.422. eCollection 2018 Jul. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2018. PMID: 30062014 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide-Based Vaccination Therapy for Rheumatic Diseases.J Immunol Res. 2020 Mar 18;2020:8060375. doi: 10.1155/2020/8060375. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32258176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ontology and Function of Fibroblast-Like and Macrophage-Like Synoviocytes: How Do They Talk to Each Other and Can They Be Targeted for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy?Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 26;9:1467. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01467. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29997624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

