IL-10 promoter transactivation by the viral K-RTA protein involves the host-cell transcription factors, specificity proteins 1 and 3
- PMID: 29184003
- PMCID: PMC5767870
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.802900
IL-10 promoter transactivation by the viral K-RTA protein involves the host-cell transcription factors, specificity proteins 1 and 3
Abstract
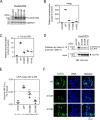
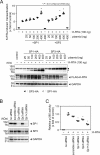
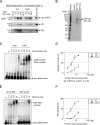
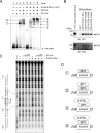
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)/human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) causes a persistent infection, presenting latent and lytic replication phases during its life cycle. KSHV-related diseases are associated with deregulated expression of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6 and IL-10, but the mechanisms underlying this dysregulation are unclear. Herein, we report a molecular mechanism for KSHV-induced IL-10 gene expression. KSHV replication and transcription activator (K-RTA) is a molecular switch for the initiation of expression of viral lytic genes, and we describe, for the first time, that K-RTA significantly activates the promoter of the human IL-10 gene. Of note, mutations involving a basic region of K-RTA reduced the association of K-RTA with the IL-10 promoter. Moreover, the host-cell transcription factors, specificity proteins (SP) 1 and 3, play a pivotal cooperative role in K-RTA-mediated transactivation of the IL-10 promoter. K-RTA can interact with SP1 and SP3 directly in vitro, and electrophoresis mobility shift assays (EMSAs) revealed co-operative interaction involving K-RTA, SP1, and SP3 in binding to the IL-10 promoter. As DNase I footprinting assays indicated that K-RTA did not affect SP3 binding to the IL-10 promoter, SP3 can function to recruit K-RTA to the IL-10 promoter. These findings indicate that K-RTA can directly contribute to IL-10 up-regulation via a functional interplay with the cellular transcription factors SP1 and SP3.
Keywords: IL-10; SP3; herpesvirus; interleukin; specificity protein 1 (Sp1); transactivation; transcription; viral transcription.
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sp3 Transcription Factor Cooperates with the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF50 Protein To Synergistically Activate Specific Viral and Cellular Gene Promoters.J Virol. 2020 Aug 31;94(18):e01143-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01143-20. Print 2020 Aug 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32641483 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha is induced during the early stages of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic cycle reactivation and together with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) cooperatively stimulates the viral RTA, MTA, and PAN promoters.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9590-612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9590-9612.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915572 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) in activation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic-cycle replication-associated protein (RAP) promoter in cooperation with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) and RAP.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(1):600-23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.1.600-623.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12477864 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus-8 regulator of transcription activation (RTA) in control of gene expression.Oncogene. 2003 Aug 11;22(33):5150-63. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206555. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12910252 Review.
-
Reactivation and Lytic Replication of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus: An Update.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 20;8:613. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00613. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28473805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Chromatin Accessibility Changes Induced by BMMC Recognition of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus-like Particles through ATAC-seq.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 1;24(23):17044. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317044. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069369 Free PMC article.
-
Induced dual-target rebalance simultaneously enhances efficient therapeutical efficacy in tumors.Cell Death Discov. 2024 May 23;10(1):249. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02018-y. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38782895 Free PMC article.
-
Human Virus Transcriptional Regulators.Cell. 2020 Jul 9;182(1):24-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.023. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32649876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus replication and transcription activator protein activates CD274/PD-L1 gene promoter.Cancer Sci. 2023 Apr;114(4):1718-1728. doi: 10.1111/cas.15673. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36411531 Free PMC article.
-
Viral, immunologic, and clinical features of primary effusion lymphoma.Blood. 2019 Apr 18;133(16):1753-1761. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-01-893339. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Blood. 2019. PMID: 30782610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deng H., Liang Y., and Sun R. (2007) Regulation of KSHV lytic gene expression. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 312, 157–183 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

