Effect of Oral Insulin on Prevention of Diabetes in Relatives of Patients With Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 29164254
- PMCID: PMC5798455
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.17070
Effect of Oral Insulin on Prevention of Diabetes in Relatives of Patients With Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Type 1 diabetes requires major lifestyle changes and carries increased morbidity and mortality. Prevention or delay of diabetes would have major clinical effect.
Objective: To determine whether oral insulin delays onset of type 1 diabetes in autoantibody-positive relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes.
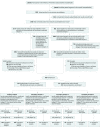
Design, setting, and participants: Between March 2, 2007, and December 21, 2015, relatives with at least 2 autoantibodies, including insulin autoantibodies and normal glucose tolerance, were enrolled in Canada, the United States, Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Italy, Sweden, Finland, and Germany. The main study group (n = 389) had first-phase insulin release on an intravenous glucose tolerance test that was higher than the threshold. The 55 patients in the secondary stratum 1 had an identical antibody profile as the main study group except they had first-phase insulin release that was lower than the threshold. Secondary strata 2 (n = 114) and strata 3 (n = 3) had different autoantibody profiles and first-phase insulin release threshold combinations. Follow-up continued through December 31, 2016.
Interventions: Randomization to receive 7.5 mg/d of oral insulin (n = 283) or placebo (n = 277), including participants in the main study group who received oral insulin (n = 203) or placebo (n = 186).
Main outcome and measures: The primary outcome was time to diabetes in the main study group. Significance was based on a 1-sided threshold of .05, and 1-sided 95% CIs are reported.
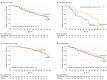
Results: Of a total of 560 randomized participants (median enrollment age, 8.2 years; interquartile range [IQR], 5.7-12.1 years; 170 boys [60%]; 90.7% white non-Hispanic; 57.6% with a sibling with type 1 diabetes), 550 completed the trial including 389 participants (median age, 8.4 years; 245 boys [63%]), 382 (96%) in the main study group. During a median follow-up of 2.7 years (IQR, 1.5-4.6 years) in the main study group, diabetes was diagnosed in 58 participants (28.5%) in the oral insulin group and 62 (33%) in the placebo group. Time to diabetes was not significantly different between the 2 groups (hazard ratio [HR], 0.87; 95% CI, 0-1.2; P = .21). In secondary stratum 1 (n = 55), diabetes was diagnosed in 13 participants (48.1%) in the oral insulin group and in 19 participants (70.3%) in the placebo group. The time to diabetes was significantly longer with oral insulin (HR, 0.45; 95% CI, 0-0.82; P = .006). The HR for time to diabetes for the between-group comparisons for the 116 participants in the other secondary stratum was 1.03 (95% CI, 0-2.11; P = .53) and for the entire cohort of 560 participants was 0.83 (95% CI, 0-1.07; P = .11), which were not significantly different. The most common adverse event was infection (n = 254), with 134 events in the oral insulin group and 120 events in the placebo group, but no significant study-related adverse events occurred.
Conclusions and relevance: Among autoantibody-positive relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes, oral insulin at a dose of 7.5 mg/d, compared with placebo, did not delay or prevent the development of type 1 diabetes over 2.7 years. These findings do not support oral insulin as used in this study for diabetes prevention.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT00419562.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of high-dose oral insulin on immune responses in children at high risk for type 1 diabetes: the Pre-POINT randomized clinical trial.JAMA. 2015 Apr 21;313(15):1541-9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.2928. JAMA. 2015. PMID: 25898052 Clinical Trial.
-
Delay of type I diabetes in high risk, first degree relatives by parenteral antigen administration: the Schwabing Insulin Prophylaxis Pilot Trial.Diabetologia. 1998 May;41(5):536-41. doi: 10.1007/s001250050943. Diabetologia. 1998. PMID: 9628270 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of oral insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes: The Diabetes Prevention Trial--Type 1.Diabetes Care. 2005 May;28(5):1068-76. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.5.1068. Diabetes Care. 2005. PMID: 15855569 Clinical Trial.
-
Repaglinide : a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(6):389-411. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200422060-00005. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004. PMID: 15099124 Review.
-
Behavioral and Pharmacotherapy Weight Loss Interventions to Prevent Obesity-Related Morbidity and Mortality in Adults: An Updated Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Sep. Report No.: 18-05239-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Sep. Report No.: 18-05239-EF-1. PMID: 30354042 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin is necessary but not sufficient: changing the therapeutic paradigm in type 1 diabetes.F1000Res. 2020 Jul 30;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-827. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.21801.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32789003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Insulin Delay of Stage 3 Type 1 Diabetes Revisited in HLA DR4-DQ8 Participants in the TrialNet Oral Insulin Prevention Trial (TN07).Diabetes Care. 2024 Sep 1;47(9):1608-1616. doi: 10.2337/dc24-0573. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 38949847
-
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Measures of First-phase Insulin Response and Their Predictive Ability for Type 1 Diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jul 14;107(8):e3273-e3280. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac285. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35524749 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Medicine in Type 1 Diabetes.J Indian Inst Sci. 2023;103(1):335-351. doi: 10.1007/s41745-023-00356-x. Epub 2023 Mar 7. J Indian Inst Sci. 2023. PMID: 37538198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus and its oral tolerance therapy.World J Diabetes. 2020 Oct 15;11(10):400-415. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i10.400. World J Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 33133388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diabetes Prevention Trial—Type 1 Diabetes Study Group Effects of insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(22):1685-1691. - PubMed
-
- Skyler JS, Krischer JP, Wolfsdorf J, et al. . Effects of oral insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes: the Diabetes Prevention Trial—Type 1. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(5):1068-1076. - PubMed
-
- Williams AJK, Bingley PJ, Bonifacio E, Palmer JP, Gale EAM. A novel micro-assay for insulin autoantibodies. J Autoimmun. 1997;10(5):473-478. - PubMed
-
- Bingley PJ. Clinical applications of diabetes antibody testing. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(1):25-33. - PubMed
-
- Mahon JL, Sosenko JM, Rafkin-Mervis L, et al. ; TrialNet Natural History Committee; Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Study Group . The TrialNet Natural History Study of the Development of Type 1 Diabetes: objectives, design, and initial results. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009;10(2):97-104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK084565/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029890/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061035/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060782/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103282/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106994/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001855/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061029/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060916/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061037/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK117009/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK097835/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061030/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

