Melatonin as a potential inhibitory agent in head and neck cancer
- PMID: 29163852
- PMCID: PMC5685773
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20079
Melatonin as a potential inhibitory agent in head and neck cancer
Abstract
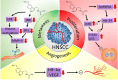
Melatonin is a molecule secreted by the pineal gland; it is an important regulator of sleep and circadian rhythms. Through multiple interrelated mechanisms, melatonin exhibits various inhibitory properties at different stages of tumor progression. Many studies have explored the oncostatic effects of melatonin on hormone-dependent tumors. In this review, we highlight recent advances in understanding the effects of melatonin on the development of head and neck cancers, including molecular mechanisms identified through experimental and clinical observations. Because melatonin exerts a wide range of effects, melatonin may influence many mechanisms that influence the development of cancer. These include cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, extracellular matrix remodeling through matrix metalloproteinases, and genetic polymorphism. Thus, the evidence discussed in this article will serve as a basis for basic and clinical research to promote the use of melatonin for understanding and controlling the development of head and neck cancers.
Keywords: head and neck cancers; matrix metalloproteinase; melatonin; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer metastasis: Mechanisms of inhibition by melatonin.J Pineal Res. 2017 Jan;62(1). doi: 10.1111/jpi.12370. Epub 2016 Nov 25. J Pineal Res. 2017. PMID: 27706852 Review.
-
Pineal gland, melatonin and cancer. NEL Review.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 1999;20(3-4):139-144. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 1999. PMID: 11462104
-
Human pineal physiology and functional significance of melatonin.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2004 Sep-Dec;25(3-4):177-95. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2004.08.001. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15589268 Review.
-
Melatonin: An Anti-Tumor Agent in Hormone-Dependent Cancers.Int J Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 2;2018:3271948. doi: 10.1155/2018/3271948. eCollection 2018. Int J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30386380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pineal gland hormone and idiopathic scoliosis: possible effect of melatonin on sleep-related postural mechanisms.Arch Ital Biol. 2002 Apr;140(2):129-58. Arch Ital Biol. 2002. PMID: 12004644 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin and non-small cell lung cancer: new insights into signaling pathways.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 May 16;19:131. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0853-7. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31123430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALKBH5 suppresses tumor progression via an m6A-dependent epigenetic silencing of pre-miR-181b-1/YAP signaling axis in osteosarcoma.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jan 11;12(1):60. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03315-x. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33431791 Free PMC article.
-
Serum melatonin is inversely associated with matrix metalloproteinase-9 in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2020 Apr;19(4):3011-3020. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11392. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32218858 Free PMC article.
-
Deoxyshikonin Mediates Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction and Apoptotic Response via p38 Signaling in Tongue Cancer Cell Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 26;23(13):7115. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137115. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806120 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Use after Diagnosis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC): A Systematic Review of Application during Radiotherapy and in Second Primary Cancer Prevention.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Sep 12;12(9):1753. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091753. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Boyle P, Levin B. World Cancer Report 2008. Lyon: IARC Press, International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008.
-
- Hashibe M, Brennan P, Chuang SC, Boccia S, Castellsague X, Chen C, Curado MP, Dal Maso L, Daudt AW, Fabianova E, Fernandez L, Wunsch-Filho V, Franceschi S, et al. Interaction between tobacco and alcohol use and the risk of head and neck cancer: pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:541–550. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury N, Alvi S, Kimura K, Tawfik O, Manna P, Beahm D, Robinson A, Kerley S, Hoover L. Outcomes of HPV-related nasal squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

