Development of phospho-specific Rab protein antibodies to monitor in vivo activity of the LRRK2 Parkinson's disease kinase
- PMID: 29127256
- PMCID: PMC5748839
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20170802
Development of phospho-specific Rab protein antibodies to monitor in vivo activity of the LRRK2 Parkinson's disease kinase
Abstract
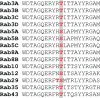
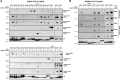
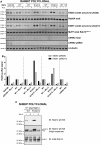
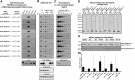
Mutations that activate the LRRK2 (leucine-rich repeat protein kinase 2) protein kinase predispose to Parkinson's disease, suggesting that LRRK2 inhibitors might have therapeutic benefit. Recent work has revealed that LRRK2 phosphorylates a subgroup of 14 Rab proteins, including Rab10, at a specific residue located at the centre of its effector-binding switch-II motif. In the present study, we analyse the selectivity and sensitivity of polyclonal and monoclonal phospho-specific antibodies raised against nine different LRRK2-phosphorylated Rab proteins (Rab3A/3B/3C/3D, Rab5A/5B/5C, Rab8A/8B, Rab10, Rab12, Rab29[T71], Rab29[S72], Rab35 and Rab43). We identify rabbit monoclonal phospho-specific antibodies (MJFF-pRAB10) that are exquisitely selective for LRRK2-phosphorylated Rab10, detecting endogenous phosphorylated Rab10 in all analysed cell lines and tissues, including human brain cingulate cortex. We demonstrate that the MJFF-pRAB10 antibodies can be deployed to assess enhanced Rab10 phosphorylation resulting from pathogenic (R1441C/G or G2019S) LRRK2 knock-in mutations as well as the impact of LRRK2 inhibitor treatment. We also identify rabbit monoclonal antibodies displaying broad specificity (MJFF-pRAB8) that can be utilised to assess LRRK2-controlled phosphorylation of a range of endogenous Rab proteins, including Rab8A, Rab10 and Rab35. The antibodies described in the present study will help with the assessment of LRRK2 activity and examination of which Rab proteins are phosphorylated in vivo These antibodies could also be used to assess the impact of LRRK2 inhibitors in future clinical trials.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; Rab GTPases; Rab10; antibodies; leucine-rich repeat kinase; protein kinase.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.-Y.C. is an employee of Abcam, a global antibody company that may benefit financially through future sales of antibodies resulting from this publication. The other authors of the present paper declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
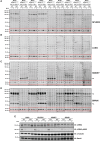
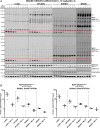
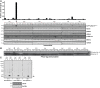
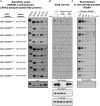
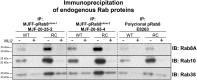
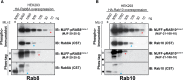
Comment in
-
Back to the future: new target-validated Rab antibodies for evaluating LRRK2 signalling in cell biology and Parkinson's disease.Biochem J. 2018 Jan 5;475(1):185-189. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170870. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29305429 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Interrogating Parkinson's disease LRRK2 kinase pathway activity by assessing Rab10 phosphorylation in human neutrophils.Biochem J. 2018 Jan 2;475(1):23-44. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170803. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29127255 Free PMC article.
-
The Parkinson's disease VPS35[D620N] mutation enhances LRRK2-mediated Rab protein phosphorylation in mouse and human.Biochem J. 2018 Jun 6;475(11):1861-1883. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180248. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29743203 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous Rab29 does not impact basal or stimulated LRRK2 pathway activity.Biochem J. 2020 Nov 27;477(22):4397-4423. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200458. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 33135724 Free PMC article.
-
Rab GTPases as Physiological Substrates of LRRK2 Kinase.Exp Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;28(2):134-145. doi: 10.5607/en.2019.28.2.134. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Exp Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31138985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LRRK2 and Rab GTPases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Dec 17;46(6):1707-1712. doi: 10.1042/BST20180470. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 30467121 Review.
Cited by
-
Accurate MS-based Rab10 Phosphorylation Stoichiometry Determination as Readout for LRRK2 Activity in Parkinson's Disease.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Sep;19(9):1546-1560. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.002055. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32601174 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy defects in LRRK2-R1441C Parkinson's disease models.Hum Mol Genet. 2023 Sep 5;32(18):2808-2821. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddad102. Hum Mol Genet. 2023. PMID: 37384414 Free PMC article.
-
Rab29 activation of the Parkinson's disease-associated LRRK2 kinase.EMBO J. 2018 Jan 4;37(1):1-18. doi: 10.15252/embj.201798099. Epub 2017 Dec 6. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 29212815 Free PMC article.
-
A leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) pathway biomarker characterization study in patients with Parkinson's disease with and without LRRK2 mutations and healthy controls.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Aug;16(8):1408-1420. doi: 10.1111/cts.13541. Epub 2023 May 15. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37177855 Free PMC article.
-
Dopaminergic neurodegeneration induced by Parkinson's disease-linked G2019S LRRK2 is dependent on kinase and GTPase activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 21;117(29):17296-17307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922184117. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32631998 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

