Experimental design for single-cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 29126257
- PMCID: PMC6063265
- DOI: 10.1093/bfgp/elx035
Experimental design for single-cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
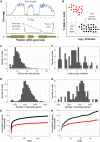
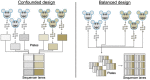
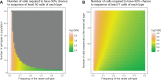
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has opened new avenues for the characterization of heterogeneity in a large variety of cellular systems. As this is a relatively new technique, the field is fast evolving. Here, we discuss general considerations in experimental design and the two most popular approaches, plate-based Smart-Seq2 and microdroplet-based scRNA-seq at the example of 10x Chromium. We discuss advantages and disadvantages of both methods and point out major factors to consider in designing successful experiments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct Comparative Analyses of 10X Genomics Chromium and Smart-seq2.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2021 Apr;19(2):253-266. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2020.02.005. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33662621 Free PMC article.
-
Full-Length Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing with FLASH-seq.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2584:123-164. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2756-3_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36495447
-
TAS-Seq is a robust and sensitive amplification method for bead-based scRNA-seq.Commun Biol. 2022 Jun 27;5(1):602. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03536-0. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35760847 Free PMC article.
-
A Single-Cell Sequencing Guide for Immunologists.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 23;9:2425. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02425. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30405621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative single-cell transcriptomics.Brief Funct Genomics. 2018 Jul 1;17(4):220-232. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ely009. Brief Funct Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29579145 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-bias training for (sc)RNA-seq: experimental and computational approaches to improve precision.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Nov 5;22(6):bbab148. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab148. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33959753 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing and Its Applications in Pituitary Research.Neuroendocrinology. 2024;114(10):875-893. doi: 10.1159/000540352. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Neuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39053437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Platforms and Methods.J Biomol Tech. 2021 Dec 15;32(4):3fc1f5fe.3eccea01. doi: 10.7171/3fc1f5fe.3eccea01. J Biomol Tech. 2021. PMID: 35837267 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of glycan and RNA in single cells.iScience. 2021 Jul 17;24(8):102882. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102882. eCollection 2021 Aug 20. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34401666 Free PMC article.
-
Long read single cell RNA sequencing reveals the isoform diversity of Plasmodium vivax transcripts.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Dec 16;16(12):e0010991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010991. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 36525464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Picelli S, Faridani OR, Björklund ÅK, et al.Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Nat Protoc 2014;9(1):171–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

