A community detection algorithm using network topologies and rule-based hierarchical arc-merging strategies
- PMID: 29121100
- PMCID: PMC5679540
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187603
A community detection algorithm using network topologies and rule-based hierarchical arc-merging strategies
Abstract
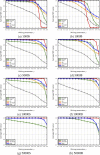
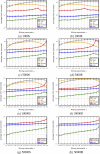
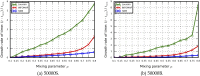
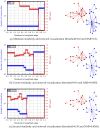
The authors use four criteria to examine a novel community detection algorithm: (a) effectiveness in terms of producing high values of normalized mutual information (NMI) and modularity, using well-known social networks for testing; (b) examination, meaning the ability to examine mitigating resolution limit problems using NMI values and synthetic networks; (c) correctness, meaning the ability to identify useful community structure results in terms of NMI values and Lancichinetti-Fortunato-Radicchi (LFR) benchmark networks; and (d) scalability, or the ability to produce comparable modularity values with fast execution times when working with large-scale real-world networks. In addition to describing a simple hierarchical arc-merging (HAM) algorithm that uses network topology information, we introduce rule-based arc-merging strategies for identifying community structures. Five well-studied social network datasets and eight sets of LFR benchmark networks were employed to validate the correctness of a ground-truth community, eight large-scale real-world complex networks were used to measure its efficiency, and two synthetic networks were used to determine its susceptibility to two resolution limit problems. Our experimental results indicate that the proposed HAM algorithm exhibited satisfactory performance efficiency, and that HAM-identified and ground-truth communities were comparable in terms of social and LFR benchmark networks, while mitigating resolution limit problems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hierarchical benchmark graphs for testing community detection algorithms.Phys Rev E. 2017 Nov;96(5-1):052311. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.96.052311. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Phys Rev E. 2017. PMID: 29347723
-
Detecting Community Structure by Using a Constrained Label Propagation Algorithm.PLoS One. 2016 May 13;11(5):e0155320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155320. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27176470 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping Structures Detection in Protein-Protein Interaction Networks Using Community Detection Algorithm Based on Neighbor Clustering Coefficient.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 23;12:689515. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.689515. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34249104 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping Community Detection Based on Membership Degree Propagation.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Dec 24;23(1):15. doi: 10.3390/e23010015. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33374305 Free PMC article.
-
Community Detection in Large-Scale Bipartite Biological Networks.Front Genet. 2021 Apr 21;12:649440. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.649440. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33968132 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Detecting multiple communities using quantum annealing on the D-Wave system.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 13;15(2):e0227538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227538. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32053622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Newman M. Networks: An introduction. Oxford University Press; 2010.
-
- Fu YH, Huang CY, Sun CT. Using global diversity and local topology features to identify influential network spreaders. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications. 2015; 433: 344–355.
-
- Watts DJ, Strogatz SH. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’networks. Nature. 1998; 393(6684): 440–442. doi: 10.1038/30918 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barabási AL, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science. 1999; 286(5439): 509–512. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

