Population pharmacokinetics of nintedanib, an inhibitor of tyrosine kinases, in patients with non-small cell lung cancer or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 29119292
- PMCID: PMC5754397
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-017-3452-0
Population pharmacokinetics of nintedanib, an inhibitor of tyrosine kinases, in patients with non-small cell lung cancer or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Purpose: A population pharmacokinetic model was developed for nintedanib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The effects of intrinsic and extrinsic patient factors on exposure of nintedanib and its main metabolite BIBF 1202 were studied.
Methods: Data from 1191 patients with NSCLC (n = 849) or IPF (n = 342) treated with oral nintedanib (once- or twice-daily, dose range 50-250 mg) in 4 Phase II or III studies were combined. Plasma concentrations of nintedanib (n = 5611) and BIBF 1202 (n = 5376) were analyzed using non-linear mixed-effects modeling.
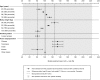
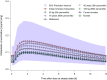
Results: Pharmacokinetics of nintedanib were described by a one-compartment model with linear elimination, first-order absorption, and absorption lag time. For a typical patient, the absorption rate was 0.0827 h-1, apparent total clearance was 897 L/h, apparent volume of distribution at steady state was 465 L, and lag time was 25 min. Age, weight, smoking, and Asian race were statistically significant covariates influencing nintedanib exposure, but no individual covariate at extreme values (5th and 95th percentiles of baseline values for continuous covariates) resulted in a change of more than 33% relative to a typical patient. Pharmacokinetics and covariate effects for BIBF 1202 were similar to nintedanib. Mild or moderate renal impairment and mild hepatic impairment (classified by transaminase or bilirubin increase above the upper limit of normal) or underlying disease had no significant effects on nintedanib pharmacokinetics.
Conclusions: This model adequately described the pharmacokinetic profile of nintedanib in NSCLC and IPF populations and can be used for simulations exploring covariate effects and exposure-response analyses.
Keywords: Covariates; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Nintedanib; Non-small cell lung cancer; Population pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
These studies were sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG, Germany.
Conflict of interest
All authors are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG. The authors declare that they have no other conflicts of interest directly related to the content of this analysis.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nintedanib.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Sep;58(9):1131-1147. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00766-0. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 31016670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population pharmacokinetics of nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Feb;48:136-143. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29133080
-
Pharmacokinetic Properties of Nintedanib in Healthy Volunteers and Patients With Advanced Cancer.J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Nov;56(11):1387-1394. doi: 10.1002/jcph.752. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27093880 Clinical Trial.
-
Exposure-efficacy analyses of nintedanib in patients with chronic fibrosing interstitial lung disease.Respir Med. 2021 Apr-May;180:106369. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106369. Epub 2021 Mar 14. Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 33798871
-
Nintedanib: a novel therapeutic approach for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Care. 2014 Sep;59(9):1450-5. doi: 10.4187/respcare.03023. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Respir Care. 2014. PMID: 24782550 Review.
Cited by
-
The landscape of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in sarcomas: looking beyond pazopanib.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2019 Nov;19(11):971-991. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1686979. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31665941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase 2 clinical trial of PBI-4050 in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Eur Respir J. 2019 Mar 18;53(3):1800663. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00663-2018. Print 2019 Mar. Eur Respir J. 2019. PMID: 30578394 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Ann Pharmacother. 2019 Dec;53(12):1238-1248. doi: 10.1177/1060028019862497. Epub 2019 Jul 7. Ann Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31280590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-analysis: clinical features and treatments of lung cancer in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2023 Dec 20;40(4):e2023045. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v40i4.14433. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2023. PMID: 38126502 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nintedanib.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Sep;58(9):1131-1147. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00766-0. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 31016670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hilberg F, Roth GJ, Krssak M, Kautschitsch S, Sommergruber W, Tontsch-Grunt U, Garin-Chesa P, Bader G, Zoephel A, Quant J, Heckel A, Rettig WJ. BIBF 1120: triple angiokinase inhibitor with sustained receptor blockade and good antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res. 2008;68(12):4774–4782. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6307. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bouquet C, Lamande N, Brand M, Gasc JM, Jullienne B, Faure G, Griscelli F, Opolon P, Connault E, Perricaudet M, Corvol P. Suppression of angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis by adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of human angiotensinogen. Mol Ther. 2006;14(2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2006.01.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Kaiser R, Mellemgaard A, Douillard JY, Orlov S, Krzakowski M, von Pawel J, Gottfried M, Bondarenko I, Liao M, Gann CN, Barrueco J, Gaschler-Markefski B, Novello S. Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): a phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(2):143–155. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70586-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

