Ultrasensitive High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Analysis of a DNA Adduct of the Carcinogen Benzo[a]pyrene in Human Lung
- PMID: 29111668
- PMCID: PMC6027747
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02856
Ultrasensitive High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Analysis of a DNA Adduct of the Carcinogen Benzo[a]pyrene in Human Lung
Abstract
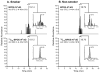
Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP), an archetypical polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, is classified as "carcinogenic to humans" and is ubiquitous in the environment, as evident by the measurable levels of BaP metabolites in virtually all human urine samples examined. BaP carcinogenicity is believed to occur mainly through its covalent modification of DNA, resulting in the formation of BPDE-N2-dG, an adduct formed between deoxyguanosine and a diol epoxide metabolite of BaP, with subsequent mutation of critical growth control genes. In spite of the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS)-based detection of BPDE-N2-dG in BaP-treated rodents, and indirectly through high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-fluorescence detection of BaP-7,8,9,10-tetraols released from human DNA upon acid hydrolysis, BPDE-N2-dG adducts have rarely if ever been observed directly in human samples using LC-MS techniques, even though sophisticated methodologies have been employed which should have had sufficient sensitivity. With this in mind, we developed a liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS) methodology employing high-resolution/accurate mass analysis for detecting ultratrace levels of these adducts. These efforts are directly translatable to the development of sensitive detection of other small molecules using trap-based LC-ESI-MS/MS detection. The developed methodology had a limit of detection (LOD) of 1 amol of BPDE-N2-dG on-column, corresponding to 1 BPDE-N2-dG adduct per 1011 nucleotides (1 adduct per 10 human lung cells) using 40 μg of human lung DNA. To our knowledge, this is the most sensitive DNA adduct quantitation method yet reported, exceeding the sensitivity of the 32P-postlabeling assay (∼1 adduct per 1010 nucleotides). Twenty-nine human lung DNA samples resulted in 20 positive measurements above the LOD, with smoker and nonsmoker DNA containing 3.1 and 1.3 BPDE-N2-dG adducts per 1011 nucleotides, respectively.
Figures

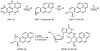
Similar articles
-
High-performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry for the detection and quantitation of benzo[a]pyrene-DNA adducts.Chem Res Toxicol. 2005 Aug;18(8):1306-15. doi: 10.1021/tx050068y. Chem Res Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 16097804
-
Preparation, identification and analysis of stereoisomeric anti-benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-deoxyguanosine adducts using phenyl liquid chromatography with diode array, fluorescence and tandem mass spectrometry detection.J Chromatogr A. 2008 Mar 7;1183(1-2):119-28. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.01.018. Epub 2008 Jan 16. J Chromatogr A. 2008. PMID: 18243229
-
Formation of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-DNA adducts at specific guanines within K-ras and p53 gene sequences: stable isotope-labeling mass spectrometry approach.Biochemistry. 2002 Jul 30;41(30):9535-44. doi: 10.1021/bi025540i. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12135376
-
Analysis of DNA and protein adducts of benzo[a]pyrene in human tissues using structure-specific methods.Mutat Res. 2003 Jan;543(1):17-30. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(02)00068-6. Mutat Res. 2003. PMID: 12510015 Review.
-
The dual effects of Benzo(a)pyrene/Benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide on DNA Methylation.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Nov 10;950:175042. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175042. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 39084379 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Analysis of DNA Adducts Using Data-Independent wSIM/MS2 Acquisition and wSIM-City.Anal Chem. 2021 Apr 27;93(16):6491-6500. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00362. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33844920 Free PMC article.
-
Smokeless tobacco and cigarette smoking: chemical mechanisms and cancer prevention.Nat Rev Cancer. 2022 Mar;22(3):143-155. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00423-4. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34980891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methyl DNA phosphate adduct formation in lung tumor tissue and adjacent normal tissue of lung cancer patients.Carcinogenesis. 2019 Nov 25;40(11):1387-1394. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz053. Carcinogenesis. 2019. PMID: 30873516 Free PMC article.
-
Benzo[a]pyrene toxicokinetics in humans following dietary supplementation with 3,3'-diindolylmethane (DIM) or Brussels sprouts.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 1;460:116377. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2023.116377. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36642108 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Toxicokinetics of benzo[a]pyrene in humans: Extensive metabolism as determined by UPLC-accelerator mass spectrometry following oral micro-dosing.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 1;364:97-105. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.12.010. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30582946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phillips DH. Nature. 1983;303:468–472. - PubMed
-
- Grainger J, Huang W, Patterson DG, Jr, Turner WE, Pirkle J, Caudill SP, Wang RY, Needham LL, Sampson EJ. Environ Res. 2006;100:394–423. - PubMed
-
- Huang W, Grainger J, Patterson DG, Jr, Turner WE, Caudill SP, Needham LL, Pirkle JL, Sampson EJ. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2004;77:491–498. - PubMed
-
- Suwan-ampai P, Navas-Acien A, Strickland PT, Agnew J. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:884–893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

