Dense and accurate whole-chromosome haplotyping of individual genomes
- PMID: 29101320
- PMCID: PMC5670131
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01389-4
Dense and accurate whole-chromosome haplotyping of individual genomes
Abstract
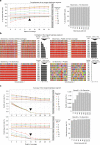
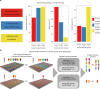
The diploid nature of the human genome is neglected in many analyses done today, where a genome is perceived as a set of unphased variants with respect to a reference genome. This lack of haplotype-level analyses can be explained by a lack of methods that can produce dense and accurate chromosome-length haplotypes at reasonable costs. Here we introduce an integrative phasing strategy that combines global, but sparse haplotypes obtained from strand-specific single-cell sequencing (Strand-seq) with dense, yet local, haplotype information available through long-read or linked-read sequencing. We provide comprehensive guidance on the required sequencing depths and reliably assign more than 95% of alleles (NA12878) to their parental haplotypes using as few as 10 Strand-seq libraries in combination with 10-fold coverage PacBio data or, alternatively, 10X Genomics linked-read sequencing data. We conclude that the combination of Strand-seq with different technologies represents an attractive solution to chart the genetic variation of diploid genomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Semi-automated assembly of high-quality diploid human reference genomes.Nature. 2022 Nov;611(7936):519-531. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05325-5. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36261518 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating read-based and population-based phasing for dense and accurate haplotyping of individual genomes.Bioinformatics. 2019 Jul 15;35(14):i242-i248. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz329. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31510646 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-Length Haplotypes with StrandPhaseR and Strand-seq.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2590:183-200. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2819-5_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36335500
-
Haplotyping-Assisted Diploid Assembly and Variant Detection with Linked Reads.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2590:161-182. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2819-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36335499 Review.
-
Computational methods for chromosome-scale haplotype reconstruction.Genome Biol. 2021 Apr 12;22(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02328-9. Genome Biol. 2021. PMID: 33845884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toward the functional interpretation of somatic structural variations: bulk- and single-cell approaches.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Sep 20;24(5):bbad297. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad297. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37587831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dominance vs epistasis: the biophysical origins and plasticity of genetic interactions within and between alleles.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 9;14(1):5551. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41188-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37689712 Free PMC article.
-
Variant calling: Considerations, practices, and developments.Hum Mutat. 2022 Aug;43(8):976-985. doi: 10.1002/humu.24311. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Hum Mutat. 2022. PMID: 34882898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-platform discovery of haplotype-resolved structural variation in human genomes.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 16;10(1):1784. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08148-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30992455 Free PMC article.
-
Minimum error correction-based haplotype assembly: Considerations for long read data.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 12;15(6):e0234470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234470. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32530974 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

