miR-204 Controls Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Expression and Agonist Function
- PMID: 29101219
- PMCID: PMC5780066
- DOI: 10.2337/db17-0506
miR-204 Controls Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Expression and Agonist Function
Abstract
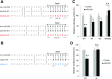
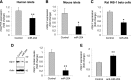
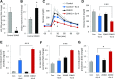
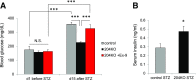
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R) agonists are widely used to treat diabetes. However, their function is dependent on adequate GLP1R expression, which is downregulated in diabetes. GLP1R is highly expressed on pancreatic β-cells, and activation by endogenous incretin or GLP1R agonists increases cAMP generation, which stimulates glucose-induced β-cell insulin secretion and helps maintain glucose homeostasis. We now have discovered that the highly β-cell-enriched microRNA, miR-204, directly targets the 3' UTR of GLP1R and thereby downregulates its expression in the β-cell-derived rat INS-1 cell line and primary mouse and human islets. Furthermore, in vivo deletion of miR-204 promoted islet GLP1R expression and enhanced responsiveness to GLP1R agonists, resulting in improved glucose tolerance, cAMP production, and insulin secretion as well as protection against diabetes. Since we recently identified thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) as an upstream regulator of miR-204, we also assessed whether in vivo deletion of TXNIP could mimic that of miR-204. Indeed, it also enhanced islet GLP1R expression and GLP1R agonist-induced insulin secretion and glucose tolerance. Thus, the present studies show for the first time that GLP1R is under the control of a microRNA, miR-204, and uncover a previously unappreciated link between TXNIP and incretin action.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhanced Glucose Control Following Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Does Not Require a β-Cell Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor.Diabetes. 2018 Aug;67(8):1504-1511. doi: 10.2337/db18-0081. Epub 2018 May 14. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29759973 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained expression of GLP-1 receptor differentially modulates β-cell functions in diabetic and nondiabetic mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Feb 26;471(1):68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.177. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26854076 Free PMC article.
-
GLP1R Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms rs3765467 and rs10305492 Affect β Cell Insulin Secretory Capacity and Apoptosis Through GLP-1.DNA Cell Biol. 2020 Sep;39(9):1700-1710. doi: 10.1089/dna.2020.5424. Epub 2020 Jul 27. DNA Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32721233
-
Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells.Metabolism. 2014 Jan;63(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140094 Review.
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists: Beta-Cell Protection or Exhaustion?Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jul;27(7):442-445. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.04.009. Epub 2016 May 6. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27160799 Review.
Cited by
-
Major miRNA Involved in Insulin Secretion and Production in Beta-Cells.Int J Gen Med. 2020 Mar 10;13:89-97. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S249011. eCollection 2020. Int J Gen Med. 2020. PMID: 32210605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of mRNAs, miRNAs and lncRNAs in the Longissimus dorsi Muscles between Fat-Type and Lean-Type Pigs.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 13;12(9):1294. doi: 10.3390/biom12091294. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139132 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of miR-373 and miR-204 levels in neuronal exosomes in Alzheimer's disease.Turk J Med Sci. 2022 Oct;52(5):1458-1467. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5484. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Turk J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36422510 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs in the Beta Cell-Friends or Foes?Endocrinology. 2023 Mar 13;164(5):bqad040. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad040. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 36869830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular study of the proliferation process of beta cells derived from pluripotent stem cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1429-1436. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06892-y. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34734370 Review.
References
-
- Guay C, Roggli E, Nesca V, Jacovetti C, Regazzi R. Diabetes mellitus, a microRNA-related disease? Transl Res 2011;157:253–264 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

