VEGF-A121a binding to Neuropilins - A concept revisited
- PMID: 29095088
- PMCID: PMC6149436
- DOI: 10.1080/19336918.2017.1372878
VEGF-A121a binding to Neuropilins - A concept revisited
Abstract
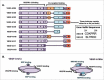
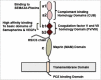
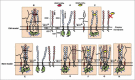
All known splice isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) can bind to the receptor tyrosine kinases VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2. We focus here on VEGF-A121a and VEGF-A165a, two of the most abundant VEGF-A splice isoforms in human tissue 1 , and their ability to bind the Neuropilin co-receptors NRP1 and NRP2. The Neuropilins are key vascular, immune, and nervous system receptors on endothelial cells, neuronal axons, and regulatory T cells respectively. They serve as co-receptors for the Plexins in Semaphorin binding on neuronal and vascular endothelial cells, and for the VEGFRs in VEGF binding on vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells, and thus regulate the initiation and coordination of cell signaling by Semaphorins and VEGFs. 2 There is conflicting evidence in the literature as to whether only heparin-binding VEGF-A isoforms - that is, isoforms with domains encoded by exons 6 and/or 7 plus 8a - bind to Neuropilins on endothelial cells. While it is clear that VEGF-A165a binds to both NRP1 and NRP2, published studies do not all agree on the ability of VEGF-A121a to bind NRPs. Here, we review and attempt to reconcile evidence for and against VEGF-A121a binding to Neuropilins. This evidence suggests that, in vitro, VEGF-A121a can bind to both NRP1 and NRP2 via domains encoded by exons 5 and 8a; in the case of NRP1, VEGF-A121a binds with lower affinity than VEGF-A165a. In in vitro cell culture experiments, both NRP1 and NRP2 can enhance VEGF-A121a-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2 and downstream signaling including proliferation. However, unlike VEGFA-165a, experiments have shown that VEGF-A121a does not 'bridge' VEGFR2 and NRP1, i.e. it does not bind both receptors simultaneously at their extracellular domain. Thus, the mechanism by which Neuropilins potentiate VEGF-A121a-mediated VEGFR2 signaling may be different from that for VEGF-A165a. We suggest such an alternate mechanism: interactions between NRP1 and VEGFR2 transmembrane (TM) and intracellular (IC) domains.
Keywords: HSPG; Neuropilin; VEGF; VEGFR2; activation; binding; transmembrane domain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The interaction of Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 with tyrosine-kinase receptors for VEGF.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:81-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0119-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12613545 Review.
-
Immunolocalization and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) and neuropilins (NRPs) on keratinocytes in human epidermis.Mol Med. 2006 Jul-Aug;12(7-8):127-36. doi: 10.2119/2006-00024.Man. Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 17088944 Free PMC article.
-
A mutated soluble neuropilin-2 B domain antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor bioactivity and inhibits tumor progression.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Aug;8(8):1063-73. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0157. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20651020 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the receptor binding profiles of the vascular endothelial growth factors on their angiogenic features.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1840(1):454-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24112971
-
The role of neuropilin in vascular and tumor biology.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:33-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0119-0_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12613541 Review.
Cited by
-
NRP1 interacts with endoglin and VEGFR2 to modulate VEGF signaling and endothelial cell sprouting.Commun Biol. 2024 Jan 19;7(1):112. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-05798-2. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38242992 Free PMC article.
-
A Structural Overview of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Pharmacological Ligands: From Macromolecules to Designed Peptidomimetics.Molecules. 2021 Nov 9;26(22):6759. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226759. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34833851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pro-Tumoral Activity of Heparan Sulfate 3-O-Sulfotransferase 3B (HS3ST3B) in Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells Is Dependent on the Expression of Neuropilin-1.Molecules. 2018 Oct 22;23(10):2718. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102718. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30360368 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activity through Alternative Splicing of Ligands and Receptors in the VEGF-A/VEGFR Axis.Cells. 2019 Mar 28;8(4):288. doi: 10.3390/cells8040288. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30925751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A and VEGFR-1 Change during Preimplantation in Heifers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 15;21(2):544. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020544. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31952188 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
