Loss of miR-141/200c ameliorates hepatic steatosis and inflammation by reprogramming multiple signaling pathways in NASH
- PMID: 29093267
- PMCID: PMC5752284
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.96094
Loss of miR-141/200c ameliorates hepatic steatosis and inflammation by reprogramming multiple signaling pathways in NASH
Abstract
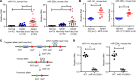
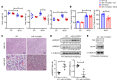
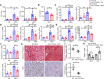
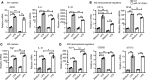
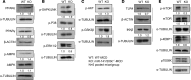
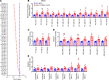
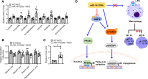
Accumulation of lipid droplets and inflammatory cell infiltration is the hallmark of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The roles of noncoding RNAs in NASH are less known. We aim to elucidate the function of miR-141/200c in diet-induced NASH. WT and miR-141/200c-/- mice were fed a methionine and choline deficient (MCD) diet for 2 weeks to assess markers of steatosis, liver injury, and inflammation. Hepatic miR-141 and miR-200c RNA levels were highly induced in human patients with NASH fatty liver and in WT MCD mice. miR-141/200c-/- MCD mice had reduced liver weights and triglyceride (TG) levels, which was associated with increased microsomal TG transfer protein (MTTP) and PPARα but reduced SREBP1c and FAS expression. Inflammation was attenuated and F4/80 macrophage activation was suppressed in miR-141/200c-/- mice, as evidenced by decreased serum aminotransferases and IL-6 and reduced hepatic proinflammatory, neutrophil, and profibrotic genes. Treatment with LPS in BM-derived macrophages isolated from miR-200c/141-/- mice polarized macrophages toward the M2 antiinflammatory state by increasing Arg1 and IL-10 levels while decreasing the M1 marker iNOS. In addition, elevated phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK), p-AKT, and p-GSK3β and diminished TLR4 and p-mTOR/p-4EBP1 proteins were observed. Lipidomics and metabolomics revealed alterations of TG and phosphatidylcholine (PC) lipid species by miR-141/200c deficiency. In summary, miR-141/200c deficiency diminished NASH-associated hepatic steatosis and inflammation by reprogramming lipid and inflammation signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibrinogen-like protein 2 aggravates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via interaction with TLR4, eliciting inflammation in macrophages and inducing hepatic lipid metabolism disorder.Theranostics. 2020 Aug 1;10(21):9702-9720. doi: 10.7150/thno.44297. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32863955 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in non-obese mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Feb 28;22(8):2512-23. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2512. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26937139 Free PMC article.
-
Methionine restriction prevents the progression of hepatic steatosis in leptin-deficient obese mice.Metabolism. 2013 Nov;62(11):1651-61. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23928105
-
Peroxisomal footprint in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Ann Hepatol. 2020 Sep-Oct;19(5):466-471. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Ann Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31870746 Review.
-
The role of neutrophils in innate immunity-driven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: lessons learned and future promise.Hepatol Int. 2020 Sep;14(5):652-666. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10081-7. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Hepatol Int. 2020. PMID: 32880077 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage Polarization and Its Role in Liver Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 14;12:803037. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.803037. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34970275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ironing Out the Details: How Iron Orchestrates Macrophage Polarization.Front Immunol. 2021 May 12;12:669566. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.669566. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated mir-141 in obesity: Insights into the interplay with sirtuin 1 and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Obes Sci Pract. 2024 Sep 27;10(5):e70007. doi: 10.1002/osp4.70007. eCollection 2024 Oct. Obes Sci Pract. 2024. PMID: 39345780 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Macrophages: Regulators of Activation and Function.J Immunol. 2023 Feb 15;210(4):359-368. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200467. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36724439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise-mediated macrophage polarization modulates the targeted therapeutic effect of NAFLD: a review.Phys Act Nutr. 2023 Sep;27(3):10-16. doi: 10.20463/pan.2023.0023. Epub 2023 Sep 30. Phys Act Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37946441 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

