Genomic imprinting of Xist by maternal H3K27me3
- PMID: 29089420
- PMCID: PMC5710138
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.304113.117
Genomic imprinting of Xist by maternal H3K27me3
Abstract
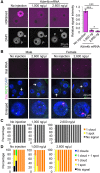
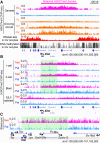
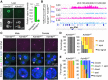
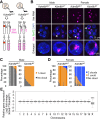
Maternal imprinting at the Xist gene is essential to achieve paternal allele-specific imprinted X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) in female mammals. However, the mechanism underlying Xist imprinting is unclear. Here we show that the Xist locus is coated with a broad H3K27me3 domain that is established during oocyte growth and persists through preimplantation development in mice. Loss of maternal H3K27me3 induces maternal Xist expression and maternal XCI in preimplantation embryos. Our study thus identifies maternal H3K27me3 as the imprinting mark of Xist.
Keywords: H3K27me3; X-chromosome inactivation; genomic imprinting; mouse early development.
© 2017 Inoue et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Manipulation of Xist Imprinting in Mouse Preimplantation Embryos.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1861:47-53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8766-5_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30218358
-
Antagonist Xist and Tsix co-transcription during mouse oogenesis and maternal Xist expression during pre-implantation development calls into question the nature of the maternal imprint on the X chromosome.Epigenetics. 2015;10(10):931-42. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1081327. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26267271 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Eed knockout causes loss of H3K27me3 imprinting and random X inactivation in the extraembryonic cells.Genes Dev. 2018 Dec 1;32(23-24):1525-1536. doi: 10.1101/gad.318675.118. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 30463900 Free PMC article.
-
What makes the maternal X chromosome resistant to undergoing imprinted X inactivation?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Nov 5;372(1733):20160365. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0365. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28947661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal H3K27me3-dependent autosomal and X chromosome imprinting.Nat Rev Genet. 2020 Sep;21(9):555-571. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-0245-9. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Nat Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32514155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orchestrating Asymmetric Expression: Mechanisms behind Xist Regulation.Epigenomes. 2024 Feb 1;8(1):6. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes8010006. Epigenomes. 2024. PMID: 38390897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stepwise de novo establishment of inactive X chromosome architecture in early development.Nat Genet. 2024 Oct;56(10):2185-2198. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01897-2. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 39256583
-
The Evolutionary Advantage in Mammals of the Complementary Monoallelic Expression Mechanism of Genomic Imprinting and Its Emergence From a Defense Against the Insertion Into the Host Genome.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 3;13:832983. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.832983. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35309133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse epigenetic mechanisms maintain parental imprints within the embryonic and extraembryonic lineages.Dev Cell. 2021 Nov 8;56(21):2995-3005.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.10.010. Dev Cell. 2021. PMID: 34752748 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient embryonic homozygous gene conversion via RAD51-enhanced interhomolog repair.Cell. 2021 Jun 10;184(12):3267-3280.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.035. Epub 2021 May 26. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34043941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augui S, Nora EP, Heard E. 2011. Regulation of X-chromosome inactivation by the X-inactivation centre. Nat Genet 12: 429–442. - PubMed
-
- Brind'Amour J, Liu S, Hudson M, Chen C, Karimi MM, Lorincz MC. 2015. An ultra-low-input native ChIP-seq protocol for genome-wide profiling of rare cell populations. Nat Commun 6: 6033. - PubMed
-
- Chiba H, Hirasawa R, Kaneda M, Amakawa Y, Li E, Sado T, Sasaki H. 2008. De novoDNA methylation independent establishment of maternal imprint on X chromosome in mouse oocytes. Genesis 46: 768–774. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
