Divergent Immunomodulation Capacity of Individual Myelin Peptides-Components of Liposomal Therapeutic against Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 29085375
- PMCID: PMC5650689
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01335
Divergent Immunomodulation Capacity of Individual Myelin Peptides-Components of Liposomal Therapeutic against Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
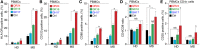
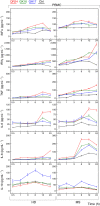
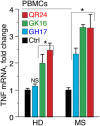
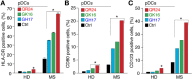
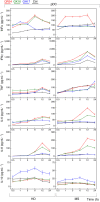
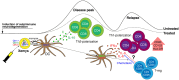
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by demyelination and consequent neuron injury. Although the pathogenesis of MS is largely unknown, a breach in immune self-tolerance to myelin followed by development of autoreactive encephalitogenic T cells is suggested to play the central role. The myelin basic protein (MBP) is believed to be one of the main targets for autoreactive lymphocytes. Recently, immunodominant MBP peptides encapsulated into the mannosylated liposomes, referred as Xemys, were shown to suppress development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a rodent model of MS, and furthermore passed the initial stage of clinical trials. Here, we investigated the role of individual polypeptide components [MBP peptides 46-62 (GH17), 124-139 (GK16), and 147-170 (QR24)] of this liposomal peptide therapeutic in cytokine release and activation of immune cells from MS patients and healthy donors. The overall effects were assessed using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), whereas alterations in antigen-presenting capacities were studied utilizing plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). Among three MBP-immunodominant peptides, QR24 and GK16 activated leukocytes, while GH17 was characterized by an immunosuppressive effect. Peptides QR24 and GK16 upregulated CD4 over CD8 T cells and induced proliferation of CD25+ cells, whereas GH17 decreased the CD4/CD8 T cell ratio and had limited effects on CD25+ T cells. Accordingly, components of liposomal peptide therapeutic differed in upregulation of cytokines upon addition to PBMCs and pDCs. Peptide QR24 was evidently more effective in upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, whereas GH17 significantly increased production of IL-10 through treated cells. Altogether, these data suggest a complexity of action of the liposomal peptide therapeutic that does not seem to involve simple helper T cells (Th)-shift but rather the rebalancing of the immune system.
Keywords: T helper cells; T regulatory cells; cytokines/chemokines; dendritic cells; liposomal peptide therapeutic; multiple sclerosis; myelin basic protein; treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Properties of myelin altered peptide ligand cyclo(87-99)(Ala91,Ala96)MBP87-99 render it a promising drug lead for immunotherapy of multiple sclerosis.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Aug 28;101:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26112377
-
Cytokine secretion profile of myelin basic protein-specific T cells in multiple sclerosis.Mult Scler. 2000 Apr;6(2):69-77. doi: 10.1177/135245850000600203. Mult Scler. 2000. PMID: 10773850
-
Chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with a delayed onset and an atypical clinical course, induced in PL/J mice by myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-derived peptide: preliminary analysis of MOG T cell epitopes.Eur J Immunol. 1995 Apr;25(4):985-93. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250419. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7737302
-
Immunomodulation neuroprotection and remyelination - the fundamental therapeutic effects of glatiramer acetate: a critical review.J Autoimmun. 2014 Nov;54:81-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 Jun 14. J Autoimmun. 2014. PMID: 24934599 Review.
-
The Diversity of Encephalitogenic CD4+ T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis and Its Animal Models.J Clin Med. 2019 Jan 19;8(1):120. doi: 10.3390/jcm8010120. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 30669462 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple Sclerosis: Focus on Extracellular and Artificial Vesicles, Nanoparticles as Potential Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 18;22(16):8866. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168866. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Extracellular Vesicles to Dendritic Cells and Macrophages.Acta Naturae. 2021 Jul-Sep;13(3):114-121. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.11478. Acta Naturae. 2021. PMID: 34707904 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Fibronectin to Overcome Remyelination Failure in Multiple Sclerosis: The Need for Brain- and Lesion-Targeted Drug Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 29;23(15):8418. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158418. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MHC Class II Presentation in Autoimmunity.Cells. 2023 Jan 14;12(2):314. doi: 10.3390/cells12020314. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Drug Delivery in Lipid-like Nanocages and Extracellular Vesicles.Acta Naturae. 2019 Apr-Jun;11(2):28-41. doi: 10.32607/20758251-2019-11-2-28-41. Acta Naturae. 2019. PMID: 31413877 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

