Salmonella exploits the host endolysosomal tethering factor HOPS complex to promote its intravacuolar replication
- PMID: 29084291
- PMCID: PMC5679646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006700
Salmonella exploits the host endolysosomal tethering factor HOPS complex to promote its intravacuolar replication
Abstract
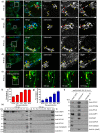
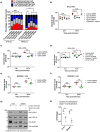
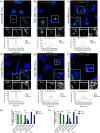
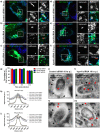
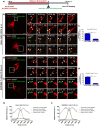
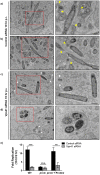
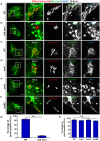
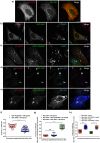
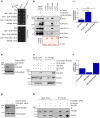
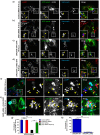
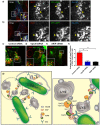
Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium extensively remodels the host late endocytic compartments to establish its vacuolar niche within the host cells conducive for its replication, also known as the Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV). By maintaining a prolonged interaction with late endosomes and lysosomes of the host cells in the form of interconnected network of tubules (Salmonella-induced filaments or SIFs), Salmonella gains access to both membrane and fluid-phase cargo from these compartments. This is essential for maintaining SCV membrane integrity and for bacterial intravacuolar nutrition. Here, we have identified the multisubunit lysosomal tethering factor-HOPS (HOmotypic fusion and Protein Sorting) complex as a crucial host factor facilitating delivery of late endosomal and lysosomal content to SCVs, providing membrane for SIF formation, and nutrients for intravacuolar bacterial replication. Accordingly, depletion of HOPS subunits significantly reduced the bacterial load in non-phagocytic and phagocytic cells as well as in a mouse model of Salmonella infection. We found that Salmonella effector SifA in complex with its binding partner; SKIP, interacts with HOPS subunit Vps39 and mediates recruitment of this tethering factor to SCV compartments. The lysosomal small GTPase Arl8b that binds to, and promotes membrane localization of Vps41 (and other HOPS subunits) was also required for HOPS recruitment to SCVs and SIFs. Our findings suggest that Salmonella recruits the host late endosomal and lysosomal membrane fusion machinery to its vacuolar niche for access to host membrane and nutrients, ensuring its intracellular survival and replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A trafficome-wide RNAi screen reveals deployment of early and late secretory host proteins and the entire late endo-/lysosomal vesicle fusion machinery by intracellular Salmonella.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Jul 13;16(7):e1008220. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008220. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32658937 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella enterica Remodels the Host Cell Endosomal System for Efficient Intravacuolar Nutrition.Cell Host Microbe. 2017 Mar 8;21(3):390-402. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Cell Host Microbe. 2017. PMID: 28238623
-
The small GTPase Arl8b regulates assembly of the mammalian HOPS complex on lysosomes.J Cell Sci. 2015 May 1;128(9):1746-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.162651. Epub 2015 Apr 23. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 25908847 Free PMC article.
-
How to do business with lysosomes: Salmonella leads the way.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2019 Feb;47:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2018.10.003. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30391777 Review.
-
Dynamic modification of microtubule-dependent transport by effector proteins of intracellular Salmonella enterica.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;90(11):897-902. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 Jul 30. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21803443 Review.
Cited by
-
DENND6A links Arl8b to a Rab34/RILP/dynein complex, regulating lysosomal positioning and autophagy.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 31;15(1):919. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44957-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38296963 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosome-Mediated Plasma Membrane Repair Is Dependent on the Small GTPase Arl8b and Determines Cell Death Type in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection.J Immunol. 2018 May 1;200(9):3160-3169. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700829. Epub 2018 Mar 28. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29592961 Free PMC article.
-
SifA SUMOylation governs Salmonella Typhimurium intracellular survival via modulation of lysosomal function.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Sep 29;19(9):e1011686. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011686. eCollection 2023 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37773952 Free PMC article.
-
ARL11 regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage activation by promoting mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 22;293(25):9892-9909. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000727. Epub 2018 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29618517 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of endolysosome fusion increases exosome secretion.J Cell Biol. 2023 Jun 5;222(6):e202209084. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202209084. Epub 2023 May 22. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37213076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LaRock DL, Chaudhary A, Miller SI (2015) Salmonellae interactions with host processes. Nat Rev Microbiol 13: 191–205. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3420 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liss V, Hensel M (2015) Take the tube: remodelling of the endosomal system by intracellular Salmonella enterica. Cell Microbiol 17: 639–647. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12441 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Figueira R, Holden DW (2012) Functions of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI-2) type III secretion system effectors. Microbiology 158: 1147–1161. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.058115-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bujny MV, Ewels PA, Humphrey S, Attar N, Jepson MA, et al. (2008) Sorting nexin-1 defines an early phase of Salmonella-containing vacuole-remodeling during Salmonella infection. J Cell Sci 121: 2027–2036. doi: 10.1242/jcs.018432 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Steele-Mortimer O, Meresse S, Gorvel JP, Toh BH, Finlay BB (1999) Biogenesis of Salmonella typhimurium-containing vacuoles in epithelial cells involves interactions with the early endocytic pathway. Cell Microbiol 1: 33–49. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

