Biology and Mechanisms of Action of the Vitamin D Hormone
- PMID: 29080638
- PMCID: PMC5762112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.001
Biology and Mechanisms of Action of the Vitamin D Hormone
Abstract
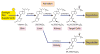
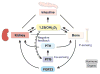
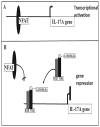
The central role of hormonal 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3] is to regulate calcium and phosphorus homeostasis via actions in intestine, kidney, and bone. These and other actions in many cell types not involved in mineral metabolism are mediated by the vitamin D receptor. Recent studies using genome-wide scale techniques have extended fundamental ideas regarding vitamin D-mediated control of gene expression while simultaneously revealing a series of new concepts. This article summarizes the current view of the biological actions of the vitamin D hormone and focuses on new concepts that drive the understanding of the mechanisms through which vitamin D operates.
Keywords: Calcemic hormones; Genetic linkage; Genome-wide principles; Mineral homeostasis; RANKL; Target genes; Transcription; Transient receptor potential vanilloid type-6 (TRPV6).
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

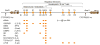
Similar articles
-
Selective biological response by target organs (intestine, kidney, and bone) to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and two analogues.Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 1;53(17):3935-42. Cancer Res. 1993. PMID: 8395333
-
Temporal changes in tissue 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, vitamin D receptor target genes, and calcium and PTH levels after 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment in mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 May 1;304(9):E977-89. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00489.2012. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23482451
-
Mechanism of vitamin D action and its regulation.Am J Kidney Dis. 1998 Oct;32(2 Suppl 2):S13-24. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.1998.v32.pm9808140. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998. PMID: 9808140 Review.
-
The vitamin D hormone and its nuclear receptor: molecular actions and disease states.J Endocrinol. 1997 Sep;154 Suppl:S57-73. J Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9379138 Review.
-
[Classical actions of vitamin D: insights from human genetics and from mouse models on calcium and phosphate homeostasis].Biol Aujourdhui. 2014;208(1):45-53. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2014009. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Biol Aujourdhui. 2014. PMID: 24948018 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Effects of acid on bone.Kidney Int. 2022 Jun;101(6):1160-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.02.032. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 35351460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uterine fibroids - Causes, impact, treatment, and lens to the African perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1045783. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1045783. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36703761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sun Exposure Makes no Discrimination based on Vitamin D Status and VDR-Foki Polymorphisms for Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers Risk in Iranian Subjects: A Case-Control Study.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Jun 1;23(6):1927-1933. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.6.1927. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 35763633 Free PMC article.
-
Titanium Implants and Local Drug Delivery Systems Become Mutual Promoters in Orthopedic Clinics.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Dec 24;12(1):47. doi: 10.3390/nano12010047. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Vitamin D in Cognitive Dysfunction: New Molecular Concepts and Discrepancies between Animal and Human Findings.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 20;13(11):3672. doi: 10.3390/nu13113672. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34835929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Melanby E. An experimental investigation on rickets. Lancet. 1919;1:407–412.
-
- McCollum E, Simmonds N, Becker J, Shipley P. An experimental demonstration of the existence of a vitamin which promotes calcium deposition. J Biol Chem. 1922;1922:293–298. - PubMed
-
- HSHB Fat soluble vitamins. XVII. The induction of growth promoting and calcifying properties in a ration by exposure to ultraviolet light. J Biol Chem. 1924;61:405–422.
-
- Windaus A, Schenck F, von Werden F. Uber das antirachitisch wirksame bestrahlungs-produkt aus 7-dehydrocholesterin. Hoppe-Seyler’s Z Physiol Chem. 1936;241:100–103.
-
- DeLuca HF. Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80(6 Suppl):1689S–1696S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

