Vascular endothelial growth receptor 1 acts as a stress-associated protein in the therapeutic response to thalidomide
- PMID: 29075340
- PMCID: PMC5647747
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5028
Vascular endothelial growth receptor 1 acts as a stress-associated protein in the therapeutic response to thalidomide
Abstract
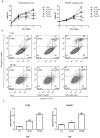
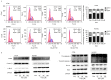
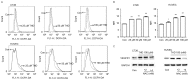
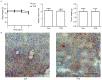
Thalidomide (THD) exhibits antitumor effects in several types of cancer. However, the failure of THD to inhibit tumor growth has also been observed in a number of murine models in vivo. The mechanism involved in the therapeutic failure of THD remains unclear. The present study demonstrated that, accompanied by growth-arresting and apoptosis-inducing effects (P<0.05), THD upregulated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1) expression levels in CT26 murine colorectal carcinoma cell lines. This in vitro phenomenon was also observed in various other cell lines, including human umbilical vein endothelial cells, SW480, SW620 and HCT116. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were increased compared with those in the untreated control when cells were exposed to THD (P<0.05). Furthermore, results suggested that ROS suppression may have provoked the induction of VEGFR1 expression to some extent. In addition, the results revealed that THD failed to inhibit CT26 tumor growth in vivo and the expression of VEGFR1 protein was elevated by THD treatment compared with the control group in the murine colorectal tumor model (P<0.05). The results of further experiments suggested that VEGFR1 was elevated in response to various stress-associated situations, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy and thermotherapy, which indicate that it may act as a stress-associated protein. The present findings provide a foundation for the future study of VEGFR1-targeted therapy to enhance the efficacy of current therapies.
Keywords: CT26; human umbilical vein endothelial cells; reactive oxygen species; stress response; thalidomide; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of thalidomide on growth and VEGF-A expression in SW480 colon cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Mar;15(3):3313-3320. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7645. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29435073 Free PMC article.
-
[Study of thalidomide on the growth and angiogenesis of ovary cancer SKOV3 transplanted subcutaneously in nude mice].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2005 Mar;40(3):186-9. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15840315 Chinese.
-
Thalidomide (THD) alleviates radiation induced lung fibrosis (RILF) via down-regulation of TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway in an Nrf2-dependent manner.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Dec;129:446-453. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.10.423. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 30339882
-
Effect of thalidomide in combination with gemcitabine on human pancreatic carcinoma SW-1990 cell lines in vitro and in vivo.Oncol Lett. 2015 May;9(5):2353-2360. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3064. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26137070 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism-based testing strategy using in vitro approaches for identification of thyroid hormone disrupting chemicals.Toxicol In Vitro. 2013 Jun;27(4):1320-46. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2013.02.012. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Toxicol In Vitro. 2013. PMID: 23453986 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
