EGFR T790M: revealing the secrets of a gatekeeper
- PMID: 29070957
- PMCID: PMC5640399
- DOI: 10.2147/LCTT.S117944
EGFR T790M: revealing the secrets of a gatekeeper
Abstract
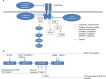
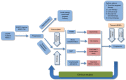
Non-small-cell lung cancers that harbor activating mutations in the EGFR gene represent an important molecularly defined subset of lung cancer. Despite dramatic initial responses with first- and second-generation EGFR-directed tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs) against these cancers, the development of a dominant and frequent resistance mechanism through a threonine-methionine amino acid substitution at position 790 (T790M) of EGFR has limited the long-term efficacy of these targeted therapies. This "gatekeeper" EGFR T790M alteration remains the only validated and relevant second-site resistance mutation for EGFR, allowing for focused research to understand and overcome EGFR T790M-mediated resistance. The current review focuses on EGFR T790M by discussing mechanisms of resistance mediated by EGFR T790M, reviewing development of novel third-generation EGFR TKIs targeting EGFR T790M, and highlighting current research on overcoming resistance to third-generation EGFR T790M TKIs.
Keywords: T790M; epidermal growth factor receptor; lung cancer; resistance; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure BH has received consulting fees from Foundation One, Genoptix, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Takeda, Novartis, Astra-Zeneca, Genentech, Pfizer, and Eli-Lilly, and research support from Merck, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Pfizer, Mirati, Takeda, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Novartis, Eli-Lilly, and Genentech. The other authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Audit of Molecular Mechanisms of Primary and Secondary Resistance to Various Generations of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Known Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in a Tertiary Centre.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022 Nov;34(11):e451-e462. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022. PMID: 35810049
-
Acquired resistance to EGFR targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Cancer Treat Rev. 2018 Apr;65:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018. PMID: 29477930 Review.
-
Next-generation EGFR/HER tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations: a review of the evidence.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Sep 6;9:5461-73. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S94745. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27660463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic diagnostic features after failure of initial treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors among non-small-cell lung cancer patients harboring EGFR mutations.BMC Cancer. 2020 Oct 2;20(1):951. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07424-w. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33008313 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Treating EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer beyond First Line.Front Med (Lausanne). 2017 Jan 18;3:76. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2016.00076. eCollection 2016. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28149837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of novel thiazolyl-pyrazolines as dual EGFR and VEGFR-2 inhibitors endowed with in vitro antitumor activity towards non-small lung cancer.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):2265-2282. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2104841. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36000167 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 in Cancer Immunotherapy: Animal Models and Human Clinical Trials.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 11;11(8):921. doi: 10.3390/genes11080921. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32796761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KinaseMD: kinase mutations and drug response database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 8;49(D1):D552-D561. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa945. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33137204 Free PMC article.
-
Ku-DNA binding inhibitors modulate the DNA damage response in response to DNA double-strand breaks.NAR Cancer. 2023 Feb 6;5(1):zcad003. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcad003. eCollection 2023 Mar. NAR Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36755959 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the EGFR-KDD mutation as a possible mechanism of acquired resistance of non-small cell lung cancer to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A case report.Mol Clin Oncol. 2022 Feb;16(2):30. doi: 10.3892/mco.2021.2463. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Mol Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34987800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304(5676):1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21):2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):947–957. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(25):2380–2388. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(3):239–246. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

