A comprehensive data mining study shows that most nuclear receptors act as newly proposed homeostasis-associated molecular pattern receptors
- PMID: 29065888
- PMCID: PMC5655880
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-017-0526-8
A comprehensive data mining study shows that most nuclear receptors act as newly proposed homeostasis-associated molecular pattern receptors
Abstract
Background: Nuclear receptors (NRs) can regulate gene expression; therefore, they are classified as transcription factors. Despite the extensive research carried out on NRs, still several issues including (1) the expression profile of NRs in human tissues, (2) how the NR expression is modulated during atherosclerosis and metabolic diseases, and (3) the overview of the role of NRs in inflammatory conditions are not fully understood.
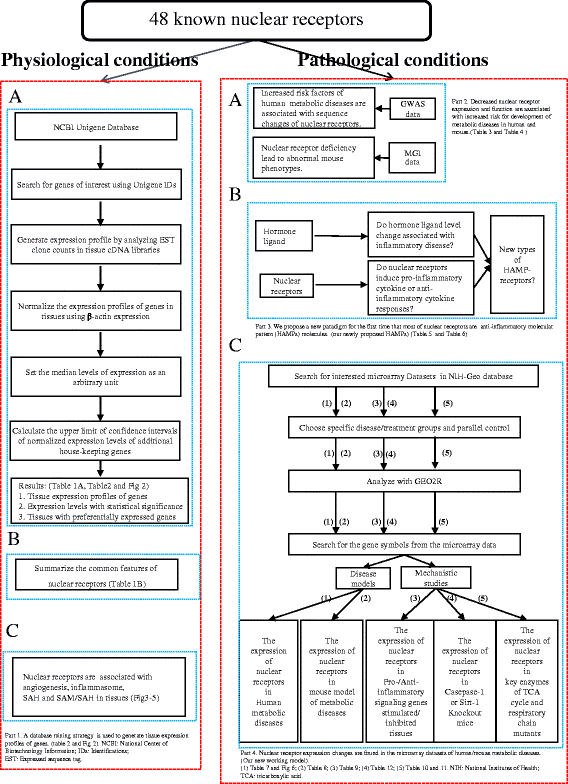
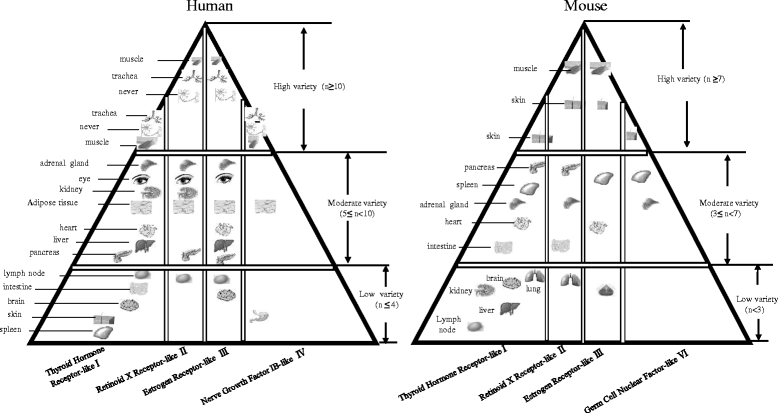
Methods: To determine whether and how the expression of NRs are regulated in physiological/pathological conditions, we took an experimental database analysis to determine expression of all 48 known NRs in 21 human and 17 murine tissues as well as in pathological conditions.
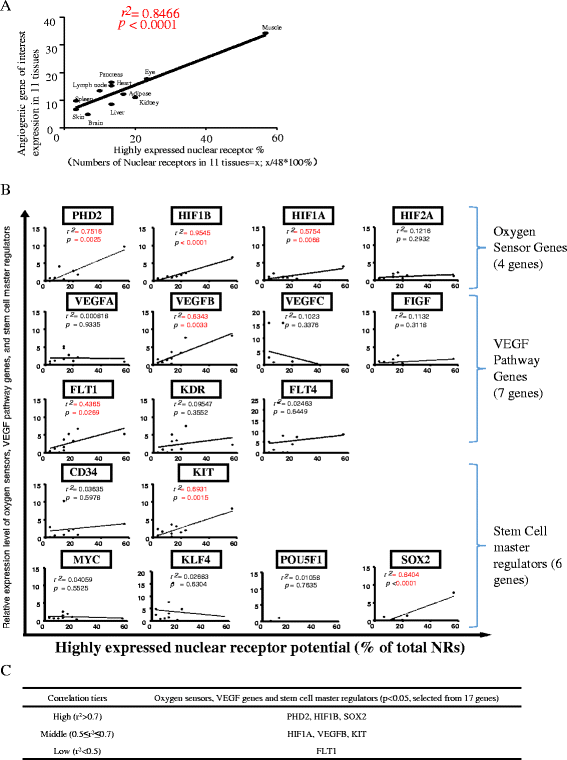
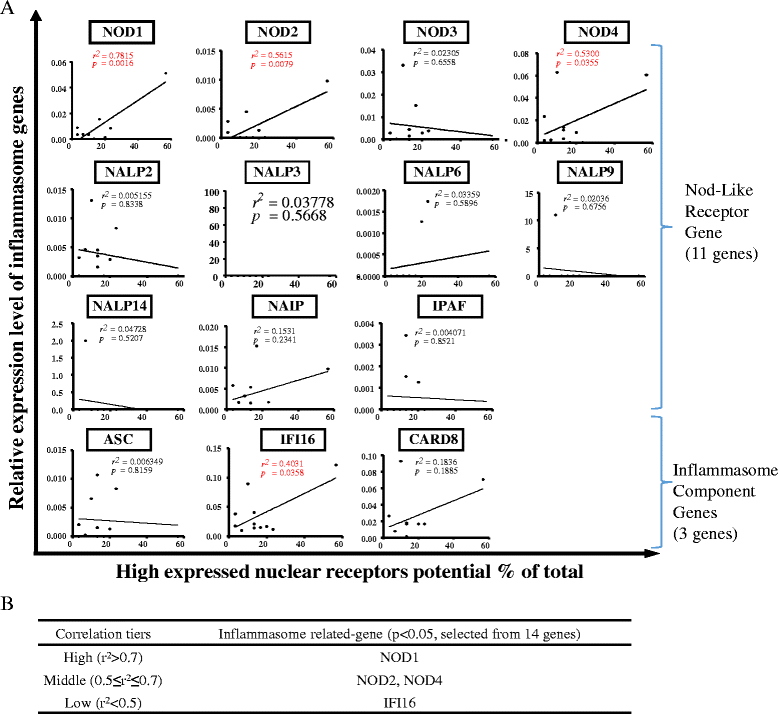
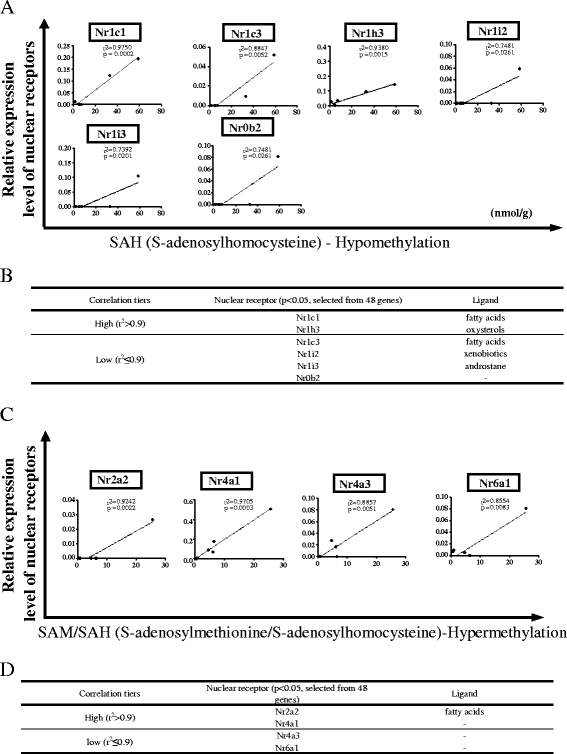
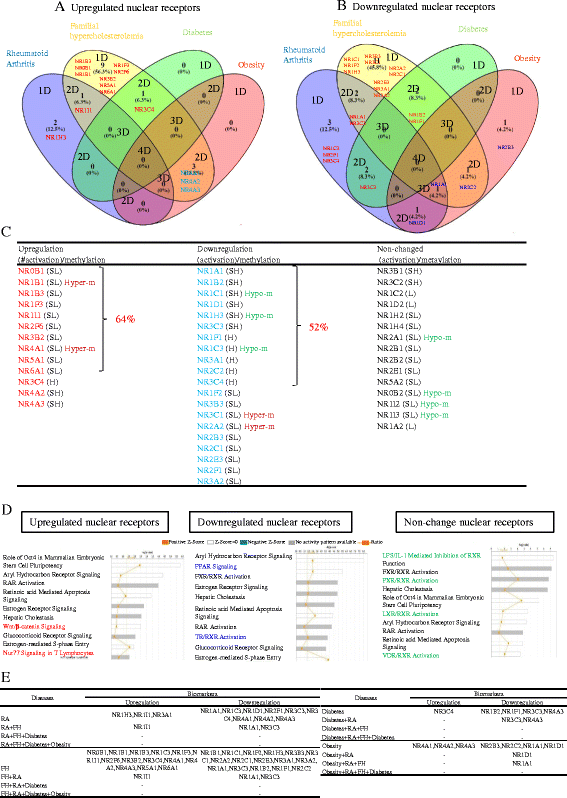
Results: We made the following significant findings: (1) NRs are differentially expressed in tissues, which may be under regulation by oxygen sensors, angiogenesis pathway, stem cell master regulators, inflammasomes, and tissue hypo-/hypermethylation indexes; (2) NR sequence mutations are associated with increased risks for development of cancers and metabolic, cardiovascular, and autoimmune diseases; (3) NRs have less tendency to be upregulated than downregulated in cancers, and autoimmune and metabolic diseases, which may be regulated by inflammation pathways and mitochondrial energy enzymes; and (4) the innate immune sensor inflammasome/caspase-1 pathway regulates the expression of most NRs.
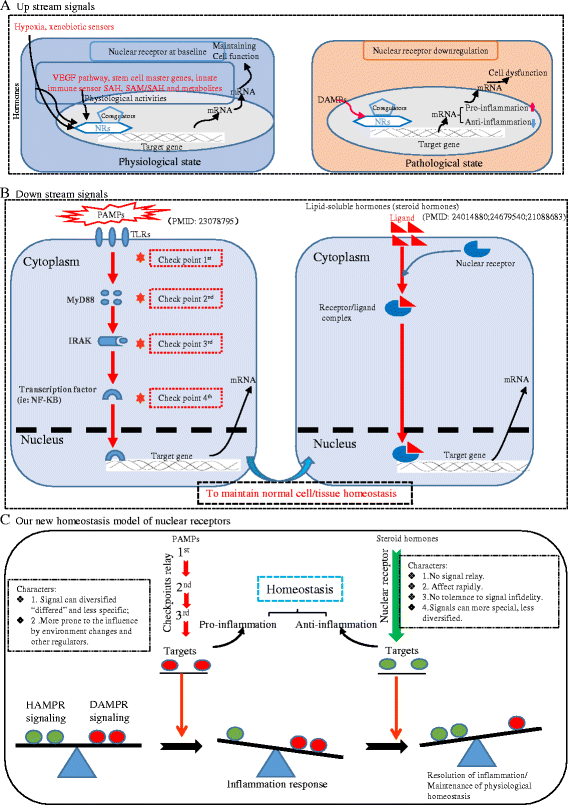
Conclusions: Based on our findings, we propose a new paradigm that most nuclear receptors are anti-inflammatory homeostasis-associated molecular pattern receptors (HAMPRs). Our results have provided a novel insight on NRs as therapeutic targets in metabolic diseases, inflammations, and malignancies.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Homeostasis-associated molecular pattern receptors; Metabolic disease; Nuclear receptors (NRs).
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular pathways involved in the transport of nuclear receptors from the nucleus to cytoplasm.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Apr;178:36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.10.020. Epub 2017 Oct 26. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29107180 Review.
-
Distinct nuclear receptor expression in stroma adjacent to breast tumors.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Nov;142(1):211-23. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2716-6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 24122391
-
Cell signaling and nuclear receptors: new opportunities for molecular pharmaceuticals in liver disease.Mol Pharm. 2008 Jan-Feb;5(1):17-34. doi: 10.1021/mp700098c. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Mol Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18159925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tackling exosome and nuclear receptor interaction: an emerging paradigm in the treatment of chronic diseases.Mil Med Res. 2024 Sep 26;11(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00564-1. Mil Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39327610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel extracellular and nuclear caspase-1 and inflammasomes propagate inflammation and regulate gene expression: a comprehensive database mining study.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Nov 14;9(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0351-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27842563 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A novel generation 1928zT2 CAR T cells induce remission in extramedullary relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Feb 20;11(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0572-x. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29458388 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Innate immunity of vascular smooth muscle cells contributes to two-wave inflammation in atherosclerosis, twin-peak inflammation in aortic aneurysms and trans-differentiation potential into 25 cell types.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 24;14:1348238. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1348238. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38327764 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Oestrogen Receptor Alpha (ERα) in Oral Lichen Planus - A Precancerous Inflammatory Disease in Middle-Aged Females.Indian J Dermatol. 2023 Jul-Aug;68(4):405-409. doi: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_122_23. Indian J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37822373 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis for novel miRNAs markers and ceRNA network in diabetic retinopathy.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 16;13:874885. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.874885. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36186470 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for estrogen receptor expression in human cancer.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2018 Sep 19;7:24. doi: 10.1186/s40164-018-0116-7. eCollection 2018. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30250760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang X, Li YF, Nanayakkara G, Shao Y, Liang B, Cole L, Yang WY, Li X, Cueto R, Yu J, et al. Lysophospholipid receptors, as novel conditional danger receptors and homeostatic receptors modulate inflammation—novel paradigm and therapeutic potential. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2016;9(4):343–359. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

