The receptor for activated protein kinase C promotes cell growth, invasion and migration in cervical cancer
- PMID: 29048616
- PMCID: PMC5642390
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4137
The receptor for activated protein kinase C promotes cell growth, invasion and migration in cervical cancer
Abstract
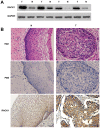
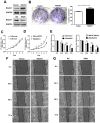
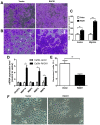
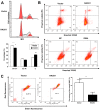
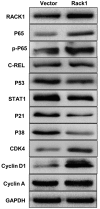
Cervical cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in women all over the world. However, the exact etiology of cervical cancer remains unclear. The receptor for activated protein kinase C (RACK1) is reported to be involved in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Besides, the prognostic value of RACK1 in several kinds of tumors has been identified. However, there are limited studies on the functional role of RACK1 in cervical cancer. In this study, we tested the expression level of RACK1 by immunohistochemistry and western blot technologies and find that it is upregulated in cervical cancer. Colony formation and CCK8 assays indicate that RACK1 promotes cell proliferation in CaSki cervical cancer cells. While the silence of RACK1 decreases the cell proliferation in CCK8 analysis. β-galactosidase staining suggests that RACK1 decreases cell senescence in cervical cancer cells. Invasion and migration assay show that RACK1 promotes the invasion and migration of cervical cancer cells. Also, when RACK1 was silenced, it exerts the opposite result. Furthermore, the mRNA expression levels of MMP‑3, MMP‑9 and MMP‑10 were upregulated in RACK1‑overexpressed CaSki cells by qPCR analysis. RACK1 also induces S phase accumulation in cell cycle analysis and suppresses cell apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. Flow cytometry analysis of mitochondria functions suggests that RACK1 increases the mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) levels to prevent mitochondrial apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. To explore the possible mechanism of RACK1, we tested and found that RACK1 upregulates the expression of NF-κB, cyclin D1 and CDK4 and downregulates the expression of p53, p38, p21 and STAT1 in cervical cancer cells. These results suggest that RACK1 promotes cell growth and invasion and inhibits the senescence and apoptosis in cervical cancer cells probably by affecting the p53 pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RACK1 promotes the invasive activities and lymph node metastasis of cervical cancer via galectin-1.Cancer Lett. 2020 Jan 28;469:287-300. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31705928
-
RACK1 promotes the occurrence and progression of cervical carcinoma.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 Feb;38(4):e25012. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25012. Epub 2024 Feb 2. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 38305509 Free PMC article.
-
PHB2 promotes tumorigenesis via RACK1 in non-small cell lung cancer.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(7):3150-3166. doi: 10.7150/thno.52848. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537079 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for RACK1 in cancer cell migration and invasion.Cell Signal. 2017 Jul;35:250-255. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Cell Signal. 2017. PMID: 28336233 Review.
-
The cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase 4D5 (PDE4D5)/receptor for activated C-kinase 1 (RACK1) signalling complex as a sensor of the extracellular nano-environment.Cell Signal. 2017 Jul;35:282-289. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Cell Signal. 2017. PMID: 28069443 Review.
Cited by
-
Long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by sponging miR-892b to up-regulate LPAR1 expression.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(2):1437-1450. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14823. Epub 2019 Dec 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31851778 Free PMC article.
-
SMAGP a novel biomarker of cervical cancer development and progression.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Oct 15;11:6925-6935. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S175808. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30410350 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Malignant Transformation of Balb/c-3T3 Cells Induced by Long-Term Exposure to 1800 MHz Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Radiation (RF-EMR).Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Jan 18;9(2):43. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9020043. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35200397 Free PMC article.
-
Species-specific FMRP regulation of RACK1 is critical for prenatal cortical development.Neuron. 2023 Dec 20;111(24):3988-4005.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.09.014. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Neuron. 2023. PMID: 37820724 Free PMC article.
-
YWHAH activates the HMGA1/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by positively regulating Fra-1 to affect the proliferation of gastric cancer cells.Oncol Res. 2023 Jun 27;31(4):615-630. doi: 10.32604/or.2023.029698. eCollection 2023. Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 37415737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chatzistamatiou K, Moysiadis T, Moschaki V, Panteleris N, Agorastos T. Comparison of cytology, HPV DNA testing and HPV 16/18 genotyping alone or combined targeting to the more balanced methodology for cervical cancer screening. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;142:120–127. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.04.027. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

