Expression and function of Abcg4 in the mouse blood-brain barrier: role in restricting the brain entry of amyloid-β peptide
- PMID: 29042617
- PMCID: PMC5645361
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13750-0
Expression and function of Abcg4 in the mouse blood-brain barrier: role in restricting the brain entry of amyloid-β peptide
Abstract
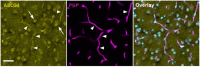
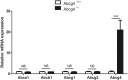
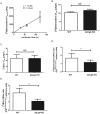
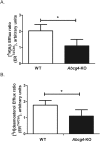
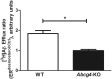
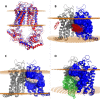
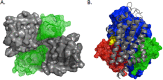
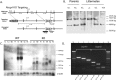
ABCG4 is an ATP-binding cassette transmembrane protein which has been shown, in vitro, to participate in the cellular efflux of desmosterol and amyloid-β peptide (Aβ). ABCG4 is highly expressed in the brain, but its localization and function at the blood-brain barrier (BBB) level remain unknown. We demonstrate by qRT-PCR and confocal imaging that mouse Abcg4 is expressed in the brain capillary endothelial cells. Modelling studies of the Abcg4 dimer suggested that desmosterol showed thermodynamically favorable binding at the putative sterol-binding site, and this was greater than for cholesterol. Additionally, unbiased docking also showed Aβ binding at this site. Using a novel Abcg4-deficient mouse model, we show that Abcg4 was able to export Aβ and desmosterol at the BBB level and these processes could be inhibited by probucol and L-thyroxine. Our assay also showed that desmosterol antagonized the export of Aβ, presumably as both bind at the sterol-binding site on Abcg4. We show for the first time that Abcg4 may function in vivo to export Aβ at the BBB, in a process that can be antagonized by its putative natural ligand, desmosterol (and possibly cholesterol).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ABCG2- and ABCG4-mediated efflux of amyloid-β peptide 1-40 at the mouse blood-brain barrier.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;30(1):155-66. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-112189. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22391220
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters G1 and G4 mediate cholesterol and desmosterol efflux to HDL and regulate sterol accumulation in the brain.FASEB J. 2008 Apr;22(4):1073-82. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9944com. Epub 2007 Nov 26. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18039927
-
Age-Dependent Regulation of the Blood-Brain Barrier Influx/Efflux Equilibrium of Amyloid-β Peptide in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease (3xTg-AD).J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49(2):287-300. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150350. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 26484906
-
Alzheimer's disease: neuroprogesterone, epoxycholesterol, and ABC transporters as determinants of neurodesmosterol tissue levels and its role in amyloid protein processing.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;35(3):441-50. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130044. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 23455994 Review.
-
Human ABC transporters ABCG2 (BCRP) and ABCG4.Xenobiotica. 2008 Jul;38(7-8):863-88. doi: 10.1080/00498250801986944. Xenobiotica. 2008. PMID: 18668433 Review.
Cited by
-
Alteration in the Function and Expression of SLC and ABC Transporters in the Neurovascular Unit in Alzheimer's Disease and the Clinical Significance.Aging Dis. 2020 Mar 9;11(2):390-404. doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.0519. eCollection 2020 Apr. Aging Dis. 2020. PMID: 32257549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rebuilding insight into the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease through new blood-brain barrier models.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Sep 1;19(9):1954-1960. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390978. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38227521 Free PMC article.
-
The concerted amyloid-beta clearance of LRP1 and ABCB1/P-gp across the blood-brain barrier is linked by PICALM.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Oct;73:21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 30041013 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Distribution of Drugs: Brain Morphology, Delivery Routes, and Species Differences.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;273:97-120. doi: 10.1007/164_2020_402. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33474672
-
ABCG5 and ABCG8: more than a defense against xenosterols.J Lipid Res. 2018 Jul;59(7):1103-1113. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R084244. Epub 2018 May 4. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 29728459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bernacki J, Dobrowolska A, Nierwińska K, Małecki A. Physiology and pharmacological role of the blood-brain barrier. Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60:600–622. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

