Curcumin Ameliorates Neuroinflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Memory Deficits in p25 Transgenic Mouse Model that Bears Hallmarks of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 29036814
- PMCID: PMC8092919
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-170093
Curcumin Ameliorates Neuroinflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Memory Deficits in p25 Transgenic Mouse Model that Bears Hallmarks of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
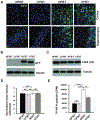
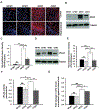
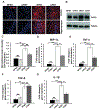
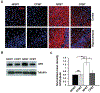
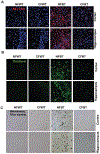
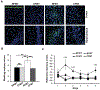
Several studies have indicated that neuroinflammation is indeed associated with neurodegenerative disease pathology. However, failures of recent clinical trials of anti-inflammatory agents in neurodegenerative disorders have emphasized the need to better understand the complexity of the neuroinflammatory process in order to unravel its link with neurodegeneration. Deregulation of Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) activity by production of its hyperactivator p25 is involved in the formation of tau and amyloid pathology reminiscent of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Recent studies show an association between p25/Cdk5 hyperactivation and robust neuroinflammation. In addition, we recently reported the novel link between the p25/Cdk5 hyperactivation-induced inflammatory responses and neurodegenerative changes using a transgenic mouse that overexpresses p25 (p25Tg). In this study, we aimed to understand the effects of early intervention with a potent natural anti-inflammatory agent, curcumin, on p25-mediated neuroinflammation and the progression of neurodegeneration in p25Tg mice. The results from this study showed that curcumin effectively counteracted the p25-mediated glial activation and pro-inflammatory chemokines/cytokines production in p25Tg mice. Moreover, this curcumin-mediated suppression of neuroinflammation reduced the progression of p25-induced tau/amyloid pathology and in turn ameliorated the p25-induced cognitive impairments. It is widely acknowledged that to treat AD, one must target the early-stage of pathological changes to protect neurons from irreversible damage. In line with this, our results demonstrated that early intervention of inflammation could reduce the progression of AD-like pathological outcomes. Moreover, our data provide a rationale for the potential use of curcuminoids in the treatment of inflammation associated neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Amyloid; Cdk5; curcumin; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; p25; tau.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cdk5/p25-induced cytosolic PLA2-mediated lysophosphatidylcholine production regulates neuroinflammation and triggers neurodegeneration.J Neurosci. 2012 Jan 18;32(3):1020-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5177-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22262900 Free PMC article.
-
SLOH, a carbazole-based fluorophore, mitigates neuropathology and behavioral impairment in the triple-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Mar 15;131:351-363. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29309769
-
Cdk5 Inhibitory Peptide Prevents Loss of Neurons and Alleviates Behavioral Changes in p25 Transgenic Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;74(4):1231-1242. doi: 10.3233/JAD-191098. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32144987
-
Involvement of inflammation in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis and therapeutic potential of anti-inflammatory agents.Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Dec;38(12):2106-19. doi: 10.1007/s12272-015-0648-x. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Arch Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 26289122 Review.
-
Neuroprotective and Neurological/Cognitive Enhancement Effects of Curcumin after Brain Ischemia Injury with Alzheimer's Disease Phenotype.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 12;19(12):4002. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124002. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30545070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomaterials-based anti-inflammatory treatment strategies for Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Jan;19(1):100-115. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.374137. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37488851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotection: Targeting Multiple Pathways by Naturally Occurring Phytochemicals.Biomedicines. 2020 Aug 12;8(8):284. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8080284. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32806490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compounds that extend longevity are protective in neurodegenerative diseases and provide a novel treatment strategy for these devastating disorders.Mech Ageing Dev. 2020 Sep;190:111297. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2020.111297. Epub 2020 Jun 28. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020. PMID: 32610099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benefits of dietary polyphenols in Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Dec 13;14:1019942. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1019942. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36583187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcuma Longa, the "Golden Spice" to Counteract Neuroinflammaging and Cognitive Decline-What Have We Learned and What Needs to Be Done.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 30;13(5):1519. doi: 10.3390/nu13051519. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33946356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nikolic M, Chou MM, Lu W, Mayer BJ, Tsai LH (1998) The p35/Cdk5 kinase is a neuron-specific Rac effector that inhibits Pak1 activity. Nature 395, 194–198. - PubMed
-
- Smith DS, Greer PL, Tsai LH (2001) Cdk5 on the brain. Cell Growth Differ 12, 277–283. - PubMed
-
- Kusakawa G, Saito T, Onuki R, Ishiguro K, Kishimoto T, Hisanaga S (2000) Calpain-dependent proteolytic cleavage of the p35 cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator to p25. J Biol Chem 275, 17166–17172. - PubMed
-
- Lee MS, Kwon YT, Li M, Peng J, Friedlander RM, Tsai LH (2000) Neurotoxicity induces cleavage of p35 to p25 by calpain. Nature 405, 360–364. - PubMed
-
- Patrick GN, Zukerberg L, Nikolic M, de la Monte S, Dikkes P, Tsai LH (1999) Conversion of p35 to p25 deregulates Cdk5 activity and promotes neurodegeneration. Nature 402, 615–622. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

