Swallowing difficulties with medication intake assessed with a novel self-report questionnaire in patients with systemic sclerosis - a cross-sectional population study
- PMID: 29033556
- PMCID: PMC5630072
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S142653
Swallowing difficulties with medication intake assessed with a novel self-report questionnaire in patients with systemic sclerosis - a cross-sectional population study
Abstract
Objectives: To assess subjective swallowing difficulties (SD) with medication intake and their practical consequences in patients suffering from systemic sclerosis (SSc) with a novel self-report questionnaire.
Design and setting: Based on a systematic literature review, we developed a self-report questionnaire and got it approved by an expert panel. Subsequently, we sent the questionnaire by post mail to SSc patients of the European Center for the Rehabilitation of Scleroderma Rheinfelden, Switzerland.
Participants: Patients were eligible if they were diagnosed with SSc, treated at the center, and were of age ≥18 years at the study start.
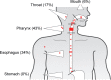
Main outcome measures: Prevalence and pattern of SD with oral medication intake, including localization and intensity of complaints.
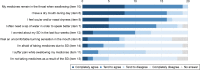
Results: The questionnaire consisted of 30 items divided into five sections Complaints, Intensity, Localization, Coping strategies, and Adherence. Of the 64 SSc patients eligible in 2014, 43 (67%) returned the questionnaire. Twenty patients reported SD with medication intake (prevalence 47%), either currently (11; 26%) or in the past that had been overcome (9; 21%). Self-reported SD were localized mostly in the larynx (43%) and esophagus (34%). They were of moderate (45%) or strong to unbearable intensity (25%). Modification of the dosage form was reported in 40% of cases with SD. Adherence was poor for 20 (47%) patients and was not associated with SD (p=0.148).
Conclusion: Our novel self-report questionnaire is able to assess the pattern of complaints linked to medication intake, that is, localization and intensity. It may serve as a guide for health care professionals in selecting the most suitable therapy option, enabling tailored counseling to reduce inappropriate medication modifications.
Keywords: coping behavior; deglutition disorders; medication intake; self-report questionnaire; swallowing difficulties; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work and declare no support from any organization for the submitted work, no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years, and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Translation to English, cross-cultural adaptation, and pilot testing of the self-report questionnaire on swallowing difficulties with medication intake and coping strategies (SWAMECO) for adults with polypharmacy.BMJ Open. 2020 Aug 16;10(8):e036761. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-036761. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32801198 Free PMC article.
-
Difficulties in swallowing oral medications in Jordan.Int J Clin Pharm. 2017 Apr;39(2):373-379. doi: 10.1007/s11096-017-0449-z. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Int J Clin Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28281225
-
Therapy satisfaction and health literacy are key factors to improve medication adherence in systemic sclerosis.Scand J Rheumatol. 2023 Jul;52(4):395-402. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2022.2111771. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Scand J Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36124810
-
Systematic review of systemic sclerosis-specific instruments for the EULAR Outcome Measures Library: An evolutional database model of validated patient-reported outcomes.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2017 Apr;46(5):609-614. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2017. PMID: 27839740 Review.
-
Analysis of the validation status of quality of life and functional disability measures in pulmonary arterial hypertension related to systemic sclerosis: results of a systematic literature analysis by the Expert Panel on Outcomes Measures in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension related to Systemic Sclerosis (EPOSS).J Rheumatol. 2011 Nov;38(11):2419-27. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.110344. Epub 2011 Oct 1. J Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21965635 Review.
Cited by
-
Community pharmacy Medicines Use Review: current challenges.Integr Pharm Res Pract. 2018 Jul 9;7:83-92. doi: 10.2147/IPRP.S148765. eCollection 2017. Integr Pharm Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30023339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A qualitative study of imaginary pills and open-label placebos in test anxiety.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 1;18(9):e0291004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291004. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37656757 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Managing gastrointestinal complications in patients with systemic sclerosis.Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2020 Dec;18:531-544. doi: 10.1007/s11938-020-00314-x. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 34305387 Free PMC article.
-
Patient preferences for systemic sclerosis treatment: A descriptive study within an Italian cohort.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2021 Jun;6(2):165-169. doi: 10.1177/2397198320971984. Epub 2020 Dec 3. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 35386742 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and addressing pill aversion in adults without physiological-related dysphagia: A narrative review.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Dec;88(12):5128-5148. doi: 10.1111/bcp.15463. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35849849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aitichou M, Skalli S, Faudel A, et al. Crushing pills, an easy practice of an old problem? Evaluation of crushing practices in a geriatric long term care unit. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy. 2012;34(1):244–245.
-
- Andersen O, Zweidorff OK, Hjelde T, Rødland EA. Problems when swallowing tablets. A questionnaire study from general practice. Tidsskrift for den Norske Laegeforening. 1995;115(8):947–949. - PubMed
-
- Baker R, Tsou VM, Tung J, et al. Clinical results from a randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging study of pantoprazole in children aged 1 through 5 years with symptomatic histologic or erosive esophagitis. Clinical Pediatrics. 2010;49(9):852–865. - PubMed
-
- Dabade TS, Kane SV, Howden CW, et al. T1066 Proton Pump Inhibitor Compliance Does Not Impact GERD Symptom Resolution. Gastroenterology. 136(5):A-492.
-
- Fallon A, Sloane P, Coffey M, Craig A. An analysis of the impact of xerostomia on the quality of life of head and neck cancer patients receiving radiotherapy. Radiotherapy and Oncology. 2011;99:S319.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

