L-Carnitine Attenuates Cardiac Dysfunction by Ischemic Insults Through Akt Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 28973678
- PMCID: PMC5837463
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx193
L-Carnitine Attenuates Cardiac Dysfunction by Ischemic Insults Through Akt Signaling Pathway
Erratum in
-
L-Carnitine Attenuates Cardiac Dysfunction by Ischemic Insults Through Akt Signaling Pathway.Toxicol Sci. 2017 Dec 1;160(2):429. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx211. Toxicol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29186614 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
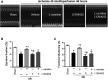
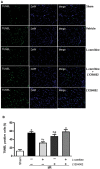
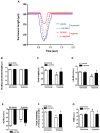
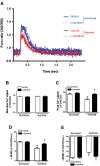
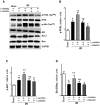
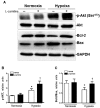
We aim to investigate the cardioprotective effects of L-carnitine (LC) on cardiac function during ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) and contractile function of single cardiomyocyte. C57BL/6 J mice were randomly assigned to 5 groups: sham group; vehicle group, LC preconditioning group, LC preconditioning + LY294002 (a PI3K/Akt signaling pathway inhibitor) group (LC + LY), and LY294002 group (LY). The sham group was exposed to the open heart operation but not I/R, the other groups received 45 min ischemia/48 h reperfusion. At the end of reperfusion, echocardiography was performed on every mouse. In order to determine whether LC's cardioprotection could act directly at the level of cardiomyocytes, we also tested its effects on isolated cardiomyocytes under hypoxia condition. The expressions of p-PI3K, PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, Bax and Bcl-2 proteins were detected by immunoblotting. The results showed that LC preconditioning remarkably improved cardiac function after I/R, but the cardioprotective effect of LC was significantly weakened after the application of LY294002. We also found that LC could directly improve the contractile function of cardiomyocytes under hypoxia condition. The immunoblotting results showed that LC administration restrained myocardial apoptosis as evidenced by decreasing the level of Bax expression, increasing the levels of phosphorylation of Akt, PI3K, and Bcl-2 protein expression, but these were blocked by LYC94002. Thus, the cardioprotective effects of LC against myocardial ischemic damage and its effect on single cardiomyocyte under hypoxia may be associated with the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Keywords: Akt; L-carnitine; myocardial ischemia reperfusion.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Panax notoginseng saponins inhibit ischemia-induced apoptosis by activating PI3K/Akt pathway in cardiomyocytes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 1;137(1):263-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21619920
-
[Protective effect against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injuries induced by hyperoside preconditioning and its relationship with PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in rats].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Jan;40(1):118-23. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25993800 Chinese.
-
Sevoflurane postconditioning attenuates cardiomyocytes hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via PI3K/AKT pathway mediated HIF-1α to regulate the mitochondrial dynamic balance.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 May 29;24(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03868-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38811893 Free PMC article.
-
The cardioprotection of the insulin-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2014 Dec;14(6):433-42. doi: 10.1007/s40256-014-0089-9. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25160498 Review.
-
Circulating blood cells and extracellular vesicles in acute cardioprotection.Cardiovasc Res. 2019 Jun 1;115(7):1156-1166. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy314. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30590395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
L-Carnitine: An Antioxidant Remedy for the Survival of Cardiomyocytes under Hyperglycemic Condition.J Diabetes Res. 2018 Dec 9;2018:4028297. doi: 10.1155/2018/4028297. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 30622968 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Diseases: Nutraceutical Interventions Related to Caloric Restriction.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 21;22(15):7772. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157772. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
L-carnitine treatment attenuates renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction.Korean J Intern Med. 2021 Mar;36(Suppl 1):S180-S195. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2019.413. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Korean J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 32942841 Free PMC article.
-
Dichloroacetate Ameliorates Cardiac Dysfunction Caused by Ischemic Insults Through AMPK Signal Pathway-Not Only Shifts Metabolism.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Feb 1;167(2):604-617. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy272. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30371859 Free PMC article.
-
Potential protective effects of L-carnitine against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Mar;31(12):18813-18825. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32212-5. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38349499
References
-
- Abe E., Fujiki M., Nagai Y., Shiqi K., Kubo T., Ishii K., Abe T., Kobayashi H. (2010). The phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway mediates geranylgeranylacetone-induced neuroprotection against cerebral infarction in rats. Brain Res. 1330, 151–157. - PubMed
-
- Cantley L. C. (2002). The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296, 1655–1657. - PubMed
-
- Chao H. H., Liu J. C., Hong H. J., Lin J. W., Chen C. H., Cheng T. H. (2011). L-carnitine reduces doxorubicin-induced apoptosis through a prostacyclin-mediated pathway in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Cardiol. 146, 145–152. - PubMed
-
- Chen S., Li J., Liu H., Zeng J., Yang G., Wang J., Lu W., Yu N., Huang Z., Xu H., et al. (2014a). Esophagogastrostomy plus gastrojejunostomy: A novel reconstruction procedure after curative resection for proximal gastric cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 18, 497–504. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

