Partial trisomy chromosome 5 cosegregating with schizophrenia
- PMID: 2895320
- PMCID: PMC3139628
- DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91660-1
Partial trisomy chromosome 5 cosegregating with schizophrenia
Abstract
Schizophrenia was associated with a distinct autosomal abnormality in two related mildly dysmorphic individuals. The finding of cosegregation of schizophrenia and a partial trisomy of chromosome 5 in the family suggests a potential location of a gene or genes linked to schizophrenia.
Figures

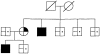
 partial trisomy chromosome 5;
partial trisomy chromosome 5;
 balanced translocation carrier;
balanced translocation carrier;
 normal chromosomes;
normal chromosomes;
 schizophrenia;
schizophrenia;
 no mental illness;
no mental illness;
 physical abnormalities;
physical abnormalities;
 no physical abnormalities.
no physical abnormalities.Similar articles
-
[Familial chromosome translocation (1;5;15) as a cause of partial trisomy 1p].Klin Padiatr. 1987 Jan-Feb;199(1):27-31. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1026754. Klin Padiatr. 1987. PMID: 2435950 German.
-
Physical mapping, linkage analysis of a putative schizophrenia locus on chromosome 5q.Schizophr Bull. 1989;15(3):441-52. doi: 10.1093/schbul/15.3.441. Schizophr Bull. 1989. PMID: 2814374
-
Association of schizophrenia and partial trisomy of chromosome 5p. A case report.Schizophr Res. 1992 Jul;7(2):191-6. doi: 10.1016/0920-9964(92)90050-f. Schizophr Res. 1992. PMID: 1515381
-
Trisomy 6q22 leads to 6qter due to maternal 6;21 translocation. Case report review of the literature.Ann Genet. 1983;26(4):243-6. Ann Genet. 1983. PMID: 6364954 Review.
-
Chromosome abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndromes.Semin Oncol. 1992 Feb;19(1):25-33. Semin Oncol. 1992. PMID: 1736367 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The molecular genetics of schizophrenia.BMJ. 1992 Sep 19;305(6855):664-5. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6855.664. BMJ. 1992. PMID: 1393109 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Genetics of event-related brain potentials in response to a semantic priming paradigm in families with a history of alcoholism.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Jan;68(1):128-135. doi: 10.1086/316936. Epub 2000 Dec 1. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11102287 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular genetics of schizophrenia: an overview and forward view.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1991;240(3):169-73. doi: 10.1007/BF02190759. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1991. PMID: 1827603 Review. No abstract available.
-
Exclusion of a schizophrenia susceptibility gene from the chromosome 5q11-q13 region: new data and a reanalysis of previous reports.Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Sep;47(3):524-35. Am J Hum Genet. 1990. PMID: 2393025 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2008 Apr;10(2):140-7. doi: 10.1007/s11920-008-0025-2. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2008. PMID: 18474207 Review.
References
-
- Robins LN, Helzer JE, Weissman MM, Orvaschel H, Gruenberg E, Burke JD, Jr, Regier DA. Lifetime prevalence of specific psychiatric disorders in three sites. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984;41:949–58. - PubMed
-
- Bleuler M. The schizophrenic disorders: long-term patient and family studies. New Haven: Yale University Press; 1978.
-
- Gottesman II, Shields J. Schizophrenia: the epigenetic puzzle. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1982.
-
- World Health Organization. ICD 9th revision. Vol. 1. Geneva: WHO; 1978.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1987. revised.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

