IL-12 and IL-15 induce the expression of CXCR6 and CD49a on peripheral natural killer cells
- PMID: 28952190
- PMCID: PMC5818449
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.190
IL-12 and IL-15 induce the expression of CXCR6 and CD49a on peripheral natural killer cells
Abstract
Introduction: Murine hepatic NK cells exhibit adaptive features, with liver-specific adhesion molecules CXCR6 and CD49a acting as surface markers.
Methods: We investigated human liver-resident CXCR6+ and CD49a+ NK cells using RNA sequencing, flow cytometry, and functional analysis. We further assessed the role of cytokines in generating NK cells with these phenotypes from the peripheral blood.
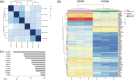
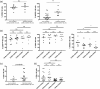
Results: Hepatic CD49a+ NK cells could be induced using cytokines and produce high quantities of IFNγ and TNFα, in contrast to hepatic CXCR6+ NK cells. RNA sequencing of liver-resident CXCR6+ NK cells confirmed a tolerant immature phenotype with reduced expression of markers associated with maturity and cytotoxicity. Liver-resident double-positive CXCR6 + CD49a+ hepatic NK cells are immature but maintain high expression of Th1 cytokines as observed for single-positive CD49a+ NK cells. We show that stimulation with activating cytokines can readily induce upregulation of both CD49a and CXCR6 on NK cells in the peripheral blood. In particular, IL-12 and IL-15 can generate CXCR6 + CD49a+ NK cells in vitro from NK cells isolated from the peripheral blood, with comparable phenotypic and functional features to liver-resident CD49a+ NK cells, including enhanced IFNγ and NKG2C expression.
Conclusion: IL-12 and IL-15 may be key for generating NK cells with a tissue-homing phenotype and strong Th1 cytokine profile in the blood, and links peripheral activation of NK cells with tissue-homing. These findings may have important therapeutic implications for immunotherapy of chronic liver disease.
Keywords: CD49a antigen; chemokine receptor 6 protein; cytokines; human liver; natural killer cells.
© 2017 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CXCR6+ NK Cells in Human Fetal Liver and Spleen Possess Unique Phenotypic and Functional Capabilities.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 19;10:469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00469. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30941128 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive Activation of Natural Killer Cells in Primary Biliary Cholangitis.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 15;10:2633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02633. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31803181 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cell maturation markers in the human liver and expansion of an NKG2C+KIR+ population.Lancet. 2015 Feb 26;385 Suppl 1:S45. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60360-9. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 26312867
-
The role of natural killer cells in autoimmune liver disease: a comprehensive review.J Autoimmun. 2013 Oct;46:55-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 21. J Autoimmun. 2013. PMID: 23880068 Review.
-
Human Circulating and Tissue-Resident CD56(bright) Natural Killer Cell Populations.Front Immunol. 2016 Jun 30;7:262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00262. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27446091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The nuclear export protein XPO1 provides a peptide ligand for natural killer cells.Sci Adv. 2024 Aug 23;10(34):eado6566. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ado6566. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39178254 Free PMC article.
-
29-Color Flow Cytometry: Unraveling Human Liver NK Cell Repertoire Diversity.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 19;10:2692. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02692. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31798596 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cell homing and trafficking in tissues and tumors: from biology to application.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jun 29;7(1):205. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01058-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35768424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of Strategies to Improve Therapy against Tumors Using Natural Killer Cell.J Immunol Res. 2020 Jan 21;2020:8459496. doi: 10.1155/2020/8459496. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32411806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix proteins regulate NK cell function in peripheral tissues.Sci Adv. 2022 Mar 18;8(11):eabk3327. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abk3327. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35294229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Norris, S. , Collins C., Doherty D. G., Smith F., McEntee G., Traynor O., Nolan N., Hegarty J., and O'Farrelly C.. 1998. Resident human hepatic lymphocytes are phenotypically different from circulating lymphocytes. J. Hepatol. 28(1):84–90. - PubMed
-
- Doherty, D. G. , and O'Farrelly C.. 2000. Innate and adaptive lymphoid cells in the human liver. Immunol. Rev. 174:5–20. - PubMed
-
- Khakoo, S. I. , Thio C. L., Martin M. P., Brooks C. R., Gao X., Astemborski J., Cheng J., Goedert J. J., Vlahov D., Hilgartner M., et al. 2004. HLA and NK cell inhibitory receptor genes in resolving hepatitis C virus infection. Science 305(5685):872–874. - PubMed
-
- Knapp, S. , Warshow U., Hegazy D., Brackenbury L., Guha I. N., Fowell A., Little A. M., Alexander G. J., Rosenberg W. M., Cramp M. E., et al. 2010. Consistent beneficial effects of killer cell immunoglobulin‐like receptor 2DL3 and group 1 human leukocyte antigen‐C following exposure to hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 51(4):1168–1175. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vidal‐Castiñeira, J. R. , López‐Vázquez A., Díaz‐Peña R., Alonso‐Arias R., Martínez‐Borra J., Pérez R., Fernández‐Suárez J., Melón S., Prieto J., Rodrigo L., et al. 2010. Effect of killer immunoglobulin‐like receptors in the response to combined treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 84(1):475–481. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

