Alcohol Misuse Link to POEMS Syndrome in a Patient
- PMID: 28946631
- PMCID: PMC5664068
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers9100129
Alcohol Misuse Link to POEMS Syndrome in a Patient
Abstract
Previously called Crow-Fukase syndrome, POEMS syndrome is characterized by poly-neuropathy, osteo-sclerotic myeloma, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal plasma cell disorder, and skin changes. Extremely elevated levels of serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are characteristic of the syndrome. Chronic hepatitis B (HBV) and C (HCV) infections can also be present in POEMS. The pathogenesis of the syndrome is not well understood. The link between chronic alcohol consumption and this malignant condition has not been reported until now. In addition, no previous study has evaluated the influence of cytokine and chemokines or viruses in the severity and evolution of POEMS.
Objectives: (1) to describe a heavy-alcohol user, who was diagnosed with POEMS; (2) to demonstrate the utility of quantitative measurement of serum levels of VEGF in the diagnosis of POEMS and the monitoring of therapeutic interventions; (3) to demonstrate that overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines is a characteristic of POEMS.
Methods: We describe a case of a POEMS patient presenting HCV and who is a heavy drinker; we compare the serum levels of cytokines and chemokines between the POEMS patient with 80 patients with HCV, 12 healthy controls, and 80 individuals with alcoholic liver disease (ALD). We quantified (ELISA pg/mL) the levels of VEGF, Interferon gamma (IFN-γ), Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF-α), Regulated-upon-Activation Normal-T-cell-Expressed and presumably-Secreted (RANTES), and Nuclear Factor kappa-B (NFκB).
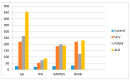
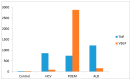
Results: In POEMS patients, VEGF levels were elevated versus control or other diseases, TNFα levels were higher versus control, but lower when compared with HCV or ALD patients. VEGF levels in POEMS patients decreased with therapeutic intervention.
Conclusions: Chronic alcohol misuse can be a strong risk factor to rare malignancies such as POEMS syndrome. Extreme elevation of VEGF levels is diagnostic for POEMS syndrome, and should be followed to assess response to therapy. In addition, other comorbidities should be considered individually to ensure personalized therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: POEMS; RANTES; TNF-alpha; VEGF; alcohol; biomarkers; malignancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. J. Neary and S.E. Goodwin are the treating physicians of the patient, L.B. Cohen clinically diagnosed and treated the patients from the control groups and M.G. Neuman designed the study and performed all the laboratory analyses of the entire study. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overproduction of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor is causative in Crow-Fukase (POEMS) syndrome.Muscle Nerve. 1998 Nov;21(11):1390-7. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199811)21:11<1390::aid-mus5>3.0.co;2-4. Muscle Nerve. 1998. PMID: 9771661
-
[Electrophysiologic aspects of Crow-Fukase (POEMS) syndrome--significance in early diagnosis and insights into the pathophysiology].Brain Nerve. 2008 Jun;60(6):595-601. Brain Nerve. 2008. PMID: 18567354 Review. Japanese.
-
Overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines imbalanced by their antagonists in POEMS syndrome.Blood. 1996 Feb 15;87(4):1458-65. Blood. 1996. PMID: 8608236
-
[Crow-Fukase (POEMS) syndrome].Brain Nerve. 2010 Apr;62(4):395-400. Brain Nerve. 2010. PMID: 20420180 Review. Japanese.
-
[Crow-Fukase (POEMS) syndrome: pathophysiology and treatments].Nihon Rinsho. 2013 May;71(5):865-9. Nihon Rinsho. 2013. PMID: 23777096 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Alcoholic-Hepatitis, Links to Brain and Microbiome: Mechanisms, Clinical and Experimental Research.Biomedicines. 2020 Mar 18;8(3):63. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8030063. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32197424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Missed diagnosis of POEMS syndrome with onset of progressive fatigue and numbness: a case report.J Int Med Res. 2021 Feb;49(2):300060520986706. doi: 10.1177/0300060520986706. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33530791 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular, Viral and Clinical Features of Alcohol- and Non-Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Mar 16;44(3):1294-1315. doi: 10.3390/cimb44030087. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35723310 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of paraproteinemic demyelinating neuropathies. Report of a Joint Task Force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society-first revision. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2010;15:185. - PubMed
-
- Kawagashira Y., Koike H., Tomita M., Morozumi S., Iijima M., Nakamura T., Katsuno M., Tanaka F., Sobue G. Morphological progression of myelin abnormalities in IgM-monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein neuropathy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010;69:1143–1157. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181fa44af. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

