Needle syringe programmes and opioid substitution therapy for preventing hepatitis C transmission in people who inject drugs
- PMID: 28922449
- PMCID: PMC5621373
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012021.pub2
Needle syringe programmes and opioid substitution therapy for preventing hepatitis C transmission in people who inject drugs
Abstract
Background: Needle syringe programmes and opioid substitution therapy for preventing hepatitis C transmission in people who inject drugsNeedle syringe programmes (NSP) and opioid substitution therapy (OST) are the primary interventions to reduce hepatitis C (HCV) transmission in people who inject drugs. There is good evidence for the effectiveness of NSP and OST in reducing injecting risk behaviour and increasing evidence for the effectiveness of OST and NSP in reducing HIV acquisition risk, but the evidence on the effectiveness of NSP and OST for preventing HCV acquisition is weak.
Objectives: To assess the effects of needle syringe programmes and opioid substitution therapy, alone or in combination, for preventing acquisition of HCV in people who inject drugs.
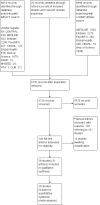
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Drug and Alcohol Register, CENTRAL, the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE), the Health Technology Assessment Database (HTA), the NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHSEED), MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, Global Health, CINAHL, and the Web of Science up to 16 November 2015. We updated this search in March 2017, but we have not incorporated these results into the review yet. Where observational studies did not report any outcome measure, we asked authors to provide unpublished data. We searched publications of key international agencies and conference abstracts. We reviewed reference lists of all included articles and topic-related systematic reviews for eligible papers.
Selection criteria: We included prospective and retrospective cohort studies, cross-sectional surveys, case-control studies and randomised controlled trials that measured exposure to NSP and/or OST against no intervention or a reduced exposure and reported HCV incidence as an outcome in people who inject drugs. We defined interventions as current OST (within previous 6 months), lifetime use of OST and high NSP coverage (regular attendance at an NSP or all injections covered by a new needle/syringe) or low NSP coverage (irregular attendance at an NSP or less than 100% of injections covered by a new needle/syringe) compared with no intervention or reduced exposure.
Data collection and analysis: We followed the standard Cochrane methodological procedures incorporating new methods for classifying risk of bias for observational studies. We described study methods against the following 'Risk of bias' domains: confounding, selection bias, measurement of interventions, departures from intervention, missing data, measurement of outcomes, selection of reported results; and we assigned a judgment (low, moderate, serious, critical, unclear) for each criterion.
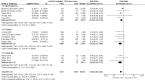
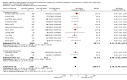
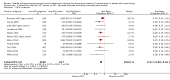
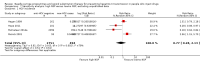
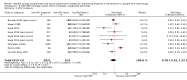
Main results: We identified 28 studies (21 published, 7 unpublished): 13 from North America, 5 from the UK, 4 from continental Europe, 5 from Australia and 1 from China, comprising 1817 incident HCV infections and 8806.95 person-years of follow-up. HCV incidence ranged from 0.09 cases to 42 cases per 100 person-years across the studies. We judged only two studies to be at moderate overall risk of bias, while 17 were at serious risk and 7 were at critical risk; for two unpublished datasets there was insufficient information to assess bias. As none of the intervention effects were generated from RCT evidence, we typically categorised quality as low. We found evidence that current OST reduces the risk of HCV acquisition by 50% (risk ratio (RR) 0.50, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.40 to 0.63, I2 = 0%, 12 studies across all regions, N = 6361), but the quality of the evidence was low. The intervention effect remained significant in sensitivity analyses that excluded unpublished datasets and papers judged to be at critical risk of bias. We found evidence of differential impact by proportion of female participants in the sample, but not geographical region of study, the main drug used, or history of homelessness or imprisonment among study samples.Overall, we found very low-quality evidence that high NSP coverage did not reduce risk of HCV acquisition (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.61) with high heterogeneity (I2 = 77%) based on five studies from North America and Europe involving 3530 participants. After stratification by region, high NSP coverage in Europe was associated with a 76% reduction in HCV acquisition risk (RR 0.24, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.62) with less heterogeneity (I2 =0%). We found low-quality evidence of the impact of combined high coverage of NSP and OST, from three studies involving 3241 participants, resulting in a 74% reduction in the risk of HCV acquisition (RR 0.26 95% CI 0.07 to 0.89).
Authors' conclusions: OST is associated with a reduction in the risk of HCV acquisition, which is strengthened in studies that assess the combination of OST and NSP. There was greater heterogeneity between studies and weaker evidence for the impact of NSP on HCV acquisition. High NSP coverage was associated with a reduction in the risk of HCV acquisition in studies in Europe.
Conflict of interest statement
Lucy Platt: none known.
Jennifer Reed: none known.
Silvia Minozzi: none known.
Peter Vickerman: received research grant funding off Gilead for doing work unrelated to this project.
Holly Hagan: none known.
Clare French: none known.
Ashly Jordan: none known.
Louisa Degenhardt: I have received untied educational grants from Reckitt Benckiser for the postmarketing surveillance of buprenorphine‐naloxone tablets and soluble film (2006 to 2013), the development of an opioid‐related behaviour scale (2010), and from Mundipharma for the conduct of postmarketing surveillance studies following the introduction of a new formulation of oxycodone in Australia. All such studies' design, conduct and interpretation of findings are the work of the investigators; the funders had no role in these. They had no knowledge of this work.
Vivian Hope: none known.
Sharon Hutchinson: outside the submitted work, received honoraria from pharma (Abbvie and Gilead) for speaking at conferences/meetings on the epidemiology and treatment of HCV infection.
Lisa Maher: none known.
Norah Palmateer: none known.
Avril Taylor: the Scottish Government funded the Needle Exchange Surveillance Initiative. Some of the data from this is used in the paper under consideration.
Julie Bruneau: outside the submitted work, received honoraria from pharma (Merck and Gilead) as advisor on the treatment of HCV infection among people who inject drugs.
Matthew Hickman: none known.
Figures














Update of
-
Effectiveness of needle/syringe programmes and opiate substitution therapy in preventing HCV transmission among people who inject drugs.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2016(1):CD012021. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012021. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9:CD012021. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012021.pub2. PMID: 27127417 Free PMC article. Updated.
Similar articles
-
Needle and syringe programmes and opioid substitution therapy for preventing HCV transmission among people who inject drugs: findings from a Cochrane Review and meta-analysis.Addiction. 2018 Mar;113(3):545-563. doi: 10.1111/add.14012. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Addiction. 2018. PMID: 28891267 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and country-level coverage of interventions to prevent and manage HIV and hepatitis C among people who inject drugs: a systematic review.Lancet Glob Health. 2017 Dec;5(12):e1208-e1220. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30373-X. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Lancet Glob Health. 2017. PMID: 29074410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of needle and syringe provision and opiate substitution therapy on the incidence of hepatitis C virus in injecting drug users: pooling of UK evidence.Addiction. 2011 Nov;106(11):1978-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03515.x. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Addiction. 2011. PMID: 21615585
-
Interventions to prevent HIV and Hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: a review of reviews to assess evidence of effectiveness.Int J Drug Policy. 2014 Jan;25(1):34-52. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Int J Drug Policy. 2014. PMID: 23973009 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Routes of Potential Hepatitis C Virus Transmission among People Who Inject Drugs: Secondary Blood Exposures Related to Injection Drug Use.Subst Use Misuse. 2021;56(6):751-757. doi: 10.1080/10826084.2021.1879149. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Subst Use Misuse. 2021. PMID: 33769203 Free PMC article.
-
Uptake and predictors of direct-acting antiviral treatment for hepatitis C among people receiving opioid agonist therapy in Sweden and Norway: a drug utilization study from 2014 to 2017.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020 Jun 30;15(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13011-020-00286-2. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020. PMID: 32605625 Free PMC article.
-
Risky injection practices and HCV awareness in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand: a respondent-driven sampling study of people who inject drugs.BMC Public Health. 2020 Sep 24;20(1):1450. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09549-w. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32972359 Free PMC article.
-
Optimising opioid substitution therapy in the prison environment.Int J Prison Health. 2019 Dec 5;15(4):293-307. doi: 10.1108/IJPH-12-2017-0061. Int J Prison Health. 2019. PMID: 31532339 Free PMC article.
-
Injections and infections: understanding syringe service program utilization in a rural state.Harm Reduct J. 2021 Jul 17;18(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12954-021-00524-1. Harm Reduct J. 2021. PMID: 34273986 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Aitken 2015 [pers comm] {unpublished data only}
-
- Unpublished dataset [personal communication]. Email to: Paul Dietz 1st November 2016.
Bruneau 2015 [pers comm] {unpublished data only}
-
- Unpublished dataset [personal communication]. Email to: Julie Bruneau 1st November 2016.
Craine 2009 {published data only}
-
- Craine N, Hickman M, Parry JV, Smith J, Walker AM, Russell D, et al. Incidence of hepatitis C in drug injectors: the role of homelessness, opiate substitution treatment, equipment sharing, and community size. Epidemiology and Infection 2009;137(9):1255‐65. - PubMed
Crofts 1997 {published data only}
-
- Crofts N, Nigro L, Oman K, Stevenson E, Sherman J. Methadone maintenance and hepatitis C virus infection among injecting drug users. Addiction 1997;92(8):999‐1005. - PubMed
Hagan 1995 {published data only}
Hagan 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hagan H, McGough JP, Thiede H, Weiss NS, Hopkins S, Alexander ER. Syringe exchange and risk of infection with hepatitis B and C viruses. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149(3):203‐13. - PubMed
Holtzman 2009 {published data only}
-
- Holtzman D, Barry V, Ouellet LJ, Jarlais DC, Vlahov D, Golub ET, et al. The influence of needle exchange programs on injection risk behaviors and infection with hepatitis C virus among young injection drug users in select cities in the United States, 1994‐2004. Preventive Medicine 2009;49(1):68‐73. - PubMed
Hope 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hope VD, Hickman M, Ngui SL, Jones S, Telfer M, Bizzarri M, et al. Measuring the incidence, prevalence and genetic relatedness of hepatitis C infections among a community recruited sample of injecting drug users, using dried blood spots. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2011;18(4):262‐70. - PubMed
Hope 2015 [pers comm] {unpublished data only}
-
- Unpublished dataset [personal communication]. Email to: Vivian Hope 1st November 2015.
Judd 2015 [pers comm] {unpublished data only}
-
- Unpublished dataset [personal communication]. Email to: Ali Judd 1st November 2015.
Lucidarme 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bruandet A, Lucidarme D, Decoster A, Ilef D, Harbonnier J, Jacob C, et al. Incidence and risk factors of HCV infection in a cohort of intravenous drug users in the North and East of France [Incidence et facteurs de risque de la seroconversion au virus de l'hepatite C dans une cohorte d'usagers de drogue intraveineux du nord‐est de la France]. Revue d'Epidemiologie et de Sante Publique 2006;54(HS1):1S15‐22. - PubMed
Maher 2015 {unpublished data only}
-
- Unpublished dataset [pers comm]. Email to: Meghan Morris 1st November 2016.
Mehta 2015 [pers comm] {unpublished data only}
-
- Unpublished dataset [personal communication]. Email to: Shruti Mehta 1st November 2015.
Nolan 2014 {published data only}
Page 2015 [pers comm] {unpublished data only}
-
- Unpublished dataset [personal communication]. Email to: Kimberly Page 1st November 2015.
Palmateer 2014a {published data only}
-
- Allen EJ, Palmateer NE, Hutchinson SJ, Cameron S, Goldberg DJ, Taylor A. Association between harm reduction intervention uptake and recent hepatitis C infection among people who inject drugs attending sites that provide sterile injecting equipment in Scotland. International Journal on Drug Policy 2012;23(5):346‐52. - PubMed
-
- Palmateer N, Taylor A, Goldberg DJ, Munro A, Aitken C, Shepherd SJ, et al. Risk of transmission associated with sharing drug injecting paraphernalia: Analysis of recent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection using cross‐sectional survey data. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2014;21(1):25‐32. - PubMed
Patrick 2001 {published data only}
Rezza 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rezza G, Sagliocca L, Zaccarelli M, Nespoli M, Siconolfi M, Baldassarre C. Incidence rate and risk factors for HCV seroconversion among injecting drug users in an area with low HIV seroprevalence. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1996;28(1):27‐9. - PubMed
Roy 2007 {published data only}
-
- Roy E, Alary M, Morissette C, Leclerc P, Boudreau JF, Parent R, et al. High hepatitis C virus prevalence and incidence among Canadian intravenous drug users. International Journal of STD & AIDS 2007;18(1):23‐7. - PubMed
Ruan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ruan Y, Qin G, Yin L, Chen K, Qian H‐Z, Hao C, et al. Incidence of HIV, hepatitis C and hepatitis B viruses among injection drug users in southwestern China: A 3‐year follow‐up study. AIDS 2007;21(Suppl 8):S39‐46. - PubMed
Spittal 2012 {published data only}
Thiede 2000 {published data only}
Thorpe 2002 {published data only}
-
- Thorpe LE, Ouellet LJ, Hershow R, Bailey SL, Williams IT, Williamson J, et al. Risk of hepatitis C virus infection among young adult injection drug users who share injection equipment. American Journal of Epidemiology 2002;155(7):645‐53. - PubMed
Tsui 2014 {published data only}
Vallejo 2015 {published data only}
-
- Vallejo F, Barrio G, Brugal MT, Pulido J, Toro C, Sordo L, et al. High hepatitis C virus prevalence and incidence in a community cohort of young heroin injectors in a context of extensive harm reduction programmes. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health 2015;69(6):599‐603. - PubMed
Van Beek 1998 {published data only}
Van Den Berg 2007 {published data only}
White 2014 {published data only}
-
- White B, Dore GJ, Lloyd AR, Rawlinson WD, Maher L. Opioid substitution therapy protects against hepatitis C virus acquisition in people who inject drugs: the HITS‐c study. Medical Journal of Australia 2014;201(6):326‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aubisson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Aubisson S, Carrieri P, Lovell A‐M, Ben Diane M‐K, Peretti‐Watel P, Spire B. New tools for preventing and evaluating risk practices for hepatitis C transmission among injection drug users: some reflections on injection rooms and the measurement of risk‐taking behaviors [Quels nouveaux outils pour prevenir et evaluer les pratiques a risque chez les injecteurs de drogue face au VHC? Reflexions sur les salles d'injection et les outils de mesure des prises de risques]. Revue d'Epidemiologie et de Sante Publique 2006;54(Spec No 1):1S69‐75. - PubMed
Azim 2005 {published data only}
Bayoumi 2008 {published data only}
Burt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Burt RD, Hagan H, Garfein RS, Sabin K, Weinbaum C, Thiede H. Trends in hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and human immunodeficiency virus prevalence, risk behaviors, and preventive measures among Seattle injection drug users aged 18‐30 years, 1994‐2004. Urban Health 2007;84(3):436‐54. - PMC - PubMed
Buxton 2010 {published data only}
Collins 2009 {published data only}
-
- Collins R, Ewing D, Boggs B, Patterson D. Opiate substitution prescribing in Belfast ‐ two year follow up study. Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine 2009;26(4):183‐6. - PubMed
Cox 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cox GM, Lawless MC, Cassin SP, Geoghegan TW. Syringe exchanges: a public health response to problem drug use. Irish Medical Journal 2000;93(5):143‐6. - PubMed
Crofts 1993 {published data only}
-
- Crofts N, Hopper JL, Bowden DS, Breschkin AM, Milner R, Locarnini SA. Hepatitis C virus infection among a cohort of Victorian injecting drug users. Medical Journal of Australia 1993;159(4):237‐41. - PubMed
Des Jarlais 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jarlais DC, Perlis T, Arasteh K, Torian LV, Hagan H, Beatrice S, et al. Reductions in hepatitis C virus and HIV infections among injecting drug users in New York City, 1990‐2001. AIDS 2005;19:S20‐5. - PubMed
Des Jarlais 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jarlais DC, Arasteh K, Perlis T, Hagan H, Abdul‐Quader A, Heckathorn DD, et al. Convergence of HIV seroprevalence among injecting and non‐injecting drug users in New York City. AIDS 2007;21(2):231‐5. - PubMed
De Vos 2012 {published data only}
-
- Vos AS, Helm JJ, Prins M, Kretzschmar MEE. Decline in incidence of HIV and hepatitis C virus infection among injecting drug users in Amsterdam: Evidence for harm reduction?. Journal of the International AIDS Society 2012;15:78. - PubMed
Dubois‐Arber 2008 {published data only}
-
- Dubois‐Arber F, Balthasar H, Huissoud T, Zobel F, Arnaud S, Samitca S, et al. Trends in drug consumption and risk of transmission of HIV and hepatitis C virus among injecting drug users in Switzerland, 1993‐2006. Euro Surveillance: Bulletin Europeen sur les Maladies Transmissibles = European Communicable Disease Bulletin 2008;13:22. Erratum in: Euro Surveill. 2008 May 29;13(22). pii: 18887. - PubMed
Emmanuelli 2005 {published data only}
-
- Emmanuelli J, Desenclos J‐C. "Harm reduction interventions, behaviours and associated health outcomes in France, 1996‐2003": Corrigendum. Addiction 2006;101(4):616. - PubMed
-
- Emmanuelli J, Desenclos J‐C. Harm reduction interventions, behaviours and associated health outcomes in France, 1996‐2003. Addiction 2005;100(11):1690‐700. - PubMed
Esteban 2003 {published data only}
-
- Esteban J, Gimeno C, Aragones A, Barril J, Cruz Pellin M. Prevalence of infection by HIV and hepatitis C virus in a cohort of patients on methadone treatment [Prevalencia de infeccion por virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana y hepatitis C en una cohorte de pacientes en tratamiento de mantenimiento con metadona]. Medicina Clinica 2003;120(20):765‐7. - PubMed
Falster 2009 {published data only}
Fatseas 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fatseas M, Denis C, Serre F, Dubernet J, Daulouede JP, Auriacombe M. Change in HIV‐HCV risk‐taking behavior and seroprevalence among opiate users seeking treatment over an 11‐year period and harm reduction policy. AIDS and Behavior 2012;16(7):2082‐90. - PubMed
Fhima 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fhima A, Henrion R, Lowenstein W, Charpak Y. Two‐year follow‐up of an opioid‐user cohort treated with high‐dose buprenorphine (Subutex) [Suivi a 2 ans d'une cohorte de patients dependants aux opiaces traites par buprenorphine haut dosage (Subutex)]. Annales De Medecine Interne (Paris) 2001;152(Suppl 3):IS26‐36. - PubMed
Fudala 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fudala PJ, Bridge TP, Herbert S, Williford WO, Chiang CN, Jones K, et al. Office‐based treatment of opiate addiction with a sublingual‐tablet formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;349(10):949‐58. - PubMed
Fuller 2004 {published data only}
Galeazzl 1995 {published data only}
-
- Galeazzl B, Tufano A, Barbierato E, Bortolotti F. Hepatitis C virus infection in Italian intravenous drug users: Epidemiological and clinical aspects. Liver 1995;15(4):209‐12. - PubMed
Gambashidze 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gambashidze N, Sikharulidze Z, Piralishvili G, Gvakharia N. Evaluation of pilot methadone maintenance therapy in Georgia (Caucasus). Georgian Medical News 2008;N/A(160‐1):25‐30. - PubMed
Garfein 1998 {published data only}
-
- Garfein RS, Doherty MC, Monterroso ER, Thomas DL, Nelson KE, Vlahov D. Prevalence and incidence of hepatitis C virus infection among young adult injection drug users. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 1998;18(Suppl 1):S11‐9. - PubMed
Garfein 2007 {published data only}
-
- Garfein RS, Golub ET, Greenberg AE, Hagan H, Hanson DL, Hudson SM, et al. A peer‐education intervention to reduce injection risk behaviors for HIV and hepatitis C virus infection in young injection drug users. AIDS 2007;21(14):1923‐32. - PubMed
Garten 2004 {published data only}
-
- Garten RJ, Lai S, Zhang J, Liu W, Chen J, Vlahov D, et al. Rapid transmission of hepatitis C virus among young injecting heroin users in Southern China. International Journal of Epidemiology 2004;33(1):182‐8. - PubMed
Gervasoni 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gervasoni J‐P, Balthasar H, Huissoud T, Jeannin A, Dubois‐Arber F. A high proportion of users of low‐threshold facilities with needle exchange programmes in Switzerland are currently on methadone treatment: Implications for new approaches in harm reduction and care. International Journal on Drug Policy 2012;23(1):33‐6. - PubMed
Goldberg 1998 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg D, Cameron S, McMenamin J. Hepatitis C virus antibody prevalence among injecting drug users in Glasgow has fallen but remains high. Communicable Disease and Public Health 1998;1(2):95‐7. - PubMed
Goldberg 2001 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg D, Burns S, Taylor A, Cameron S, Hargreaves D, Hutchinson S. Trends in HCV prevalence among injecting drug users in Glasgow and Edinburgh during the era of needle/syringe exchange. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2001;33(6):457‐61. - PubMed
Goswami 2014 {published data only}
-
- Goswami P, Medhi GK, Armstrong G, Setia MS, Mathew S, Thongamba G, et al. An assessment of an HIV prevention intervention among People Who Inject Drugs in the states of Manipur and Nagaland, India. International Journal on Drug Policy 2014;25(5):853‐64. - PubMed
Grebely 2013 {published data only}
-
- Grebely J, Bruggmann P, Backmund M, Dore G J. Prevention and management of hepatitis C virus infection among people who inject drugs: moving the agenda forward. International Symposium on Hepatitis in Substance Users, Brussels, Belgium, 15‐16 September 2011. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2013;57:S29‐S137. - PubMed
Grebely 2014 {published data only}
Guadagnino 1995 {published data only}
-
- Guadagnino V, Zimatore G, Izzi A, Caroleo B, Rocca A, Montesano F, et al. Relevance of intravenous cocaine use in relation to prevalence of HIV, hepatitis B and C virus markers among intravenous drug abusers in southern Italy. Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Immunology 1995;47(1):1‐9. - PubMed
Hagan 2000 {published data only}
Heimer 1999 {published data only}
Higgs 2012 {published data only}
-
- Higgs P, Aitken C, Cogger S, Papanastasiou C, Dietze P. Hepatitis C incidence in the Melbourne injecting drug user cohort study: 2009‐2012. Drug and Alcohol Review 2012;31:33.
Jackson 2014 {published data only}
-
- Jackson JB, Wei L, Liping F, Aramrattana A, Celentano DD, Walshe L, et al. Prevalence and seroincidence of hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection in high risk people who inject drugs in China and Thailand. Hepatitis Research and Treatment 2014;2014:296958. [DOI: 10.1155/2014/296958] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Javanbakht 2014 {published data only}
Judd 2005 {published data only}
Kwon 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kwon JA, Iversen J, Maher L, Law MG, Wilson DP. The impact of needle and syringe programs on HIV and HCV transmissions in injecting drug users in Australia: a model‐based analysis. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2009;51(4):462‐9. - PubMed
Lai 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lai S, Liu W, Chen J, Yang J, Li Z‐J, Li R‐J, et al. Changes in HIV‐1 incidence in heroin users in Guangxi Province, China. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2001;26(4):365‐70. - PubMed
Larney 2015 {published data only}
-
- Larney S, Grebely J, Falster M, Swart A, Amin J, Degenhardt L, et al. Opioid substitution therapy is associated with increased detection of hepatitis C virus infection: a 15‐year observational cohort study. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2015;148:213‐6. - PubMed
Mansson 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mansson AS, Moestrup T, Nordenfelt E, Widell A. Continued transmission of hepatitis B and C viruses, but no transmission of human immunodeficiency virus among intravenous drug users participating in a syringe/needle exchange program. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2000;32(3):253‐8. - PubMed
Mikolajczyk 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mikolajczyk R, Prins M, Wiesing L, Kretzschmar M. Trajectories of injecting behaviour in the Amsterdam Cohort Study among drug users. European Journal of Epidemiology 2013;28:S13‐4. - PubMed
Moshkovich 2000 {published data only}
-
- Moshkovich GF, Pikovskaia ED, Fedotova NV, Shilov DV, Kuznetsov AV, Moiseev AP. The prevention of HIV infection and other blood‐contact diseases among intravenous narcotic users in Nizhniy Novgorod within the framework of the Harm Reduction program [Profilaktika VICh‐infektsii i drugikh gemokontaktnykh zabolevanii sredi potrebitelei vnutrivennykh narkotikov Nizhnego Novgoroda v ramkakh programmy "Snizhenie vreda"]. Zhurnal Mikrobiologii, Epidemiologii, i Immunobiologii 2000, (4):78‐82. - PubMed
Muga 2006 {published data only}
-
- Muga R, Sanvisens A, Bolao F, Tor J, Santesmases J, Pujol R, et al. Significant reductions of HIV prevalence but not of hepatitis C virus infections in injection drug users from metropolitan Barcelona: 1987‐2001. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2006;82:S29‐33. - PubMed
Nasir 2011 {published data only}
Page 2009 {published data only}
Page 2013 {published data only}
-
- Page K, Osburn W, Evans J, Hahn J, Cox A, Busch M. Controlling hepatitis C virus (HCV): reinfection and intercalation and clearance of viremia in highly exposed young injectors. Journal of Hepatology 2011;54:S463.
Palmateer 2014b {published data only}
-
- Palmateer N, Hutchinson S, McAllister G, Munro A, Cameron S, Goldberg D, et al. Risk of transmission associated with sharing drug injecting paraphernalia: analysis of recent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection using cross‐sectional survey data. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2014;21(1):25‐32. - PubMed
Paquette 2010 {published data only}
-
- Paquette C, Roy E, Petit G, Boivin J‐F. Predictors of crack cocaine initiation among Montreal street youth: a first look at the phenomenon. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2010;110(1‐2):85‐91. - PubMed
Parrino 2003 {published data only}
-
- Parrino MW. Drug Court Fact Sheet: methadone maintenance and other pharmacotherapeutic interventions in the treatment of opioid dependence. Journal of Maintenance in the Addictions 2003;2:85‐93.
Pedrana 2009 {published data only}
-
- Pedrana A, Aitken C, Higgs P, Spelman T, Bowden S, Bharadwaj M, et al. High incidence of hepatitis C virus resolution and reinfection in a cohort of injecting drugs users. Drug and Alcohol Review 2009;28:A50‐1.
Peles 2011 {published data only}
-
- Peles E, Schreiber S, Rados V, Adelson M. Low risk for hepatitis C seroconversion in methadone maintenance treatment. Journal of Addiction Medicine 2011;5(3):214‐20. - PubMed
Pollack 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pollack HA. Cost‐effectiveness of harm reduction in preventing hepatitis C among injection drug users. Medical Decision Making 2001;21(5):357‐67. - PubMed
Pratt 2002 {published data only}
Robotin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Robotin MC, Copland J, Tallis G, Coleman D, Giele C, Carter L, et al. Surveillance for newly acquired hepatitis C in Australia. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2004;19:283‐8. - PubMed
Rohrig 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rohrig S, Grob PJ. Infection with hepatitis viruses HAV, HBV and HCV as well as with AIDS virus HIV in drug addicts of the Zurich street scene‐‐a prevalence study [Infektionen mit den Hepatitisviren HAV, HBV und HCV sowie mit dem Aidsvirus HIV bei Drogenabhangigen der Gassenszene Zurichs‐‐eine Pravalenzstudie]. Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift 1990;120(17):621‐9. - PubMed
Roux 2012 {published data only}
Roux 2014 {published data only}
Roy 2009 {published data only}
-
- Roy E, Boudreau J‐F, Boivin J‐F. Hepatitis C virus incidence among young street‐involved IDUs in relation to injection experience. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2009;102(1‐3):158‐61. - PubMed
Roy 2012 {published data only}
-
- Roy E, Arruda N, Leclerc P, Haley N, Bruneau J, Boivin J‐F. Injection of drug residue as a potential risk factor for HCV acquisition among Montreal young injection drug users. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2012;126:246‐50. - PubMed
Ruan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ruan Y, Liang S, Zhu J, Li X, Pan SW, Liu Q, et al. Evaluation of harm reduction programs on seroincidence of HIV, hepatitis B and C, and syphilis among intravenous drug users in Southwest China. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2013;40(4):323‐8. - PubMed
Samo 2013 {published data only}
Sanders‐Buell 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sanders‐Buell E, Rutvisuttinunt W, Todd CS, Nasir A, Bradfield A, Lei E, et al. Hepatitis C genotype distribution and homology among geographically disparate injecting drug users in Afghanistan. Journal of Medical Virology 2013;85(7):1170‐9. - PubMed
Seal 2004 {published data only}
-
- Seal KH, Monto A, Dove L, Vittinghoff E, Shen H, Tracy D, et al. Determinants of hepatitis C viral RNA levels among a cohort of injection drug users with and without human immunodeficiency virus coinfection. Hepatology 2004;40:403A.
-
- Selvey LA, Denton M, Plant AJ. Incidence and prevalence of hepatitis C among clients of a Brisbane methadone clinic: Factors influencing hepatitis C serostatus. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health 1997;21(1):102‐4. - PubMed
Selvey 1997 {published data only}
-
- Selvey LA, Denton M, Plant AJ. Incidence and prevalence of hepatitis C among clients of a Brisbane methadone clinic: Factors influencing hepatitis C serostatus. Australia and New Zealand Journal of Public Health 1997;21(1):102‐104. - PubMed
Sendi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sendi P, Hoffmann M, Bucher HC, Erb P, Haller P, Gyr N, et al. Intravenous opiate maintenance in a cohort of injecting drug addicts. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2003;69(2):183‐8. - PubMed
Shannon 2010 {published data only}
Shi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shi J, Zhao LY, Epstein DH, Zhao CZ, Shuai YL, Yan B, et al. The effect of methadone maintenance on illicit opioid use, human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus infection, health status, employment, and criminal activity among heroin abusers during 6 months of treatment in China. Journal of Addiction Medicine 2007;1(4):186‐90. - PubMed
Solomon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Solomon SS, Celentano DD, Srikrishnan AK, Vasudevan CK, Murugavel KG, Iqbal SH, et al. Low incidences of human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus infection and declining risk behaviors in a cohort of injection drug users in Chennai, India. American Journal of Epidemiology 2010;172(11):1259‐67. - PMC - PubMed
Spencer 1997 {published data only}
-
- Spencer JD, Latt N, Beeby PJ, Collins E, Saunders JB, McCaughan GW, et al. Transmission of hepatitis C virus to infants of human immunodeficiency virus‐negative intravenous drug‐using mothers: rate of infection and assessment of risk factors for transmission. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 1997;4(6):395‐409. - PubMed
Steffen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Steffen T, Blattler R, Gutzwiller F, Zwahlen M. HIV and hepatitis virus infections among injecting drug users in a medically controlled heroin prescription programme. European Journal of Public Health 2001;11(4):425‐30. - PubMed
Stein 2009 {published data only}
Stephens 2011 {published data only}
-
- Stephens BP, Tait J, Dillon JF. Is it worth testing unstable drug users for hepatitis C?. Hepatology 2011;54:844A.
Stephens 2013 {published data only}
-
- Stephens BP, Tait J, Evans M, Dillon JF. The natural history of the acquisition of HCV in chaotic PWID. Hepatology 2013;58:1103A.
Strathdee 1997 {published data only}
-
- Strathdee SA, Patrick DM, Currie SL, Cornelisse PGA, Rekart ML, Montaner JSG, et al. Needle exchange is not enough: Lessons from the Vancouver injecting drug use study. AIDS 1997;11:F59‐65. - PubMed
Sullivan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sullivan LE, Chawarski M, O'Connor PG, Schottenfeld RS, Fiellin DA. The practice of office‐based buprenorphine treatment of opioid dependence: Is it associated with new patients entering into treatment?. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2005;79(1):113‐6. - PubMed
Sylvestre 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sylvestre D. Hepatitis C treatment in drug users: perception versus evidence. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2006;18(2):129‐30. - PubMed
Tait 2013a {published data only}
Tait 2013b {published data only}
-
- Tait J, Stephens BP, Evans M, Cleary S, Dillon JF. People who inject drugs (PWID): difficult to get into services, easy to cure. Hepatology 2013;58:1102A‐3A.
Todd 2015 {published data only}
-
- Todd CS, Nasir A, Stanekzai MR, Fiekert K, Sipsma HL, Vlahov D, et al. Hepatitis C and HIV incidence and harm reduction program use in a conflict setting: an observational cohort of injecting drug users in Kabul, Afghanistan. Harm Reduction Journal 2015;12(1):Article Number: 22. [DOI: 10.1186/s12954-015-0056-z] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Tracy 2014 {published data only}
-
- Tracy D, Hahn JA, Fuller Lewis C, Evans J, Briceno A, Morris MD, et al. Higher risk of incident hepatitis C virus among young women who inject drugs compared with young men in association with sexual relationships: a prospective analysis from the UFO Study cohort. BMJ Open 2014;4(5):e004988. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-004988] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Tsirogianni 2013 {published data only}
-
- Tsirogianni E, Kokkonis G, Tziokgas K, Tsekoura P, Stafilidou M, Sotiriadou K, et al. Incidence of new HCV infection or reinfection after successful anti‐HCV therapy among people who inject drugs attending a substitution treatment programme in northern Greece. Suchtmedizin in Forschung und Praxis 2013;15(4):260.
Tsui 2009 {published data only}
Valdez 2011 {published data only}
Van Ameijden 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ameijden EJ, Hoek JA, Mientjes GH, Coutinho RA. A longitudinal study on the incidence and transmission patterns of HIV, HBV and HCV infection among drug users in Amsterdam. European Journal of Epidemiology 1993;9(3):255‐62. - PubMed
Van den Hoek 1990 {published data only}
-
- Hoek JAR, Haastrecht HJA, Goudsmit J, Wolf F, Coutinho RA. Prevalence, incidence, and risk factors of hepatitis C virus infection among drug users in Amsterdam. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1990;162(4):823‐6. - PubMed
Van den Laar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Laar TJW, Molenkamp R, Berg C, Schinkel J, Beld MGHM, Prins M, et al. Frequent HCV reinfection and superinfection in a cohort of injecting drug users in Amsterdam. Journal of Hepatology 2009;51(4):667‐74. - PubMed
Van den Laar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Laar TJ, Rondy M, Bruisten SM, Prins M, Ballegooijen M. Long term follow‐up of injecting drug users suggests protective immunity against HCV reinfection and superinfection with a similar genotype. Journal of Hepatology 2010;52:S262‐3.
Van Santen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Santen DK, Vos AS, Helm JJ, Grady BPX, Kretzschmar MEE, Stolte IG, et al. Temporal trends in mortality rates among drug users in Amsterdam compared to the general Dutch population differ by hepatitis C and HIV (co)infection status. Suchtmedizin in Forschung und Praxis 2013;15(4):235.
Villano 1997 {published data only}
Wand 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wand H, Spiegelman D, Law M, Jalaludin B, Kaldor J, Maher L. Estimating population attributable risk for hepatitis C seroconversion in injecting drug users in Australia: Implications for prevention policy and planning. Addiction 2009;104(12):2049‐56. - PubMed
Wang 2014 {published data only}
Widell 2009 {published data only}
-
- Widell A, Alanko M, Flamholc L, Jacobssen H, Molnegren V, Bjorkman P. Continued heavy transmission of HCV in a needle exchange program that is associated with minimal transmission of HIV. A nine year longitudinal cohort study. Journal of Hepatology 2009;50:S161.
Winkelstein 2013 {published data only}
-
- Winkelstein ER, Edlin BR, Szott K, Shu MA, McKnight C, DesJarlais DC, et al. The SWAN Project: integrating research and service with a cohort of young people who use drugs at risk for hepatitis C in New York City. Suchtmedizin in Forschung und Praxis 2013;15:238.
Woody 2008 {published data only}
Yang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yang J, Oviedo‐Joekes E, Christian KWM, Li K, Louie M, Schechter M, et al. The Cedar Project: methadone maintenance treatment among young Aboriginal people who use opioids in two Canadian cities. Drug and Alcohol Review 2011;30(6):645‐51. - PubMed
Yen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yen Y F, Yen M Y, Su L W, Li L H, Chuang P, Jiang X R, et al. Prevalences and associated risk factors of HCV/HIV co‐infection and HCV mono‐infection among injecting drug users in a methadone maintenance treatment program in Taipei, Taiwan. BMC Public Health 2012;12:1066. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-1066] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Zhao 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zhao M, Wang QY, Lu GH, Xu P, Xu H, McCoy CB. Risk behaviors and HIV/AIDS prevention education among IDUs in drug treatment in Shanghai. Urban Health 2005;82:iv84‐91. - PubMed
Zhou 2015 {published data only}
Zou 2015 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Bruneau 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bruneau J, Asward DJ, Zang G, Roy E. Effect of combined harm reduction strategies on HCV incidence among people who inject drugs in Montreal, Canada. Journal of Hepatology 2016;64(2):S462.
Chun 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chun H, Li Z, Yuhua R, Yu Z, Zongliang F, Lu Y, et al. On the impact of community‐based methadone maintenance treatment among drug addicts. Journal of Preventive Medicine Information 2006;22:251–5.
Duan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Duan S, Han J, Tang RH, Yang YC, Xiang LF, Ye RH, et al. Study on the incidence and risk factors of HCV infection among heroin addicts who were on methadone maintenance treatment in Dehong prefecture,Yunnan province. Zhonghua Liuxingbing Xue Zazhi [Chinese Journal of Epidemiology] 2013;34(6):552‐6. - PubMed
He 2003 {published data only}
-
- He YX, Ruan YH, Teng T, Hao QN, Qin GM, Wu JL, et al. Community‐based survey of drug use and sexual behavior among female injection drug users. Zhongguo Aizibing Xingbing [Chinese Journal of AIDS & STD] 2003;9:343–6.
He 2004 {published data only}
-
- He YX, Teng T, Ruan YH, Zhou F, Liu SZ, Liu G, et al. A survey of drug abuse and behaviors among injection drug users in Liangshan of Sichuan Province. Zhongguo Yaowu Lanyong Fangzhi Zazhi [Chinese Journal of Drug Abuse Prevention andTreatment] 2004;10:80–3.
Mathei 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mathei C, Bourgeois S, Blach S, Brixko C, Mulkay KP, Razavi H, et al. Mitigating the burden of hepatitis C virus among people who inject drugs in Belgium. Acta Gastro‐Enterologica Belgica 2016;79(2):227‐32. - PubMed
O'Keefe 2016 {published data only}
Ray Saraswati 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ray Saraswati L, Saran A, Sebastian MP, Sharma V, Madan I, Thior I, et al. HIV, Hepatitis B and C among people who inject drugs: high prevalence of HIV and Hepatitis C RNA positive infections observed in Delhi, India. BMC Public Health 2015;15:726. [DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-2003-z] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Siedentopf 2002 {published data only}
-
- Siedentopf J‐P, Nagel M, Buscher U. Possibilities of drug addiction treatment during pregnancy [Moglichkeiten der suchttherapie in der schwangerschaft]. Suchtmedizin in Forschung und Praxis 2002;4:162‐3.
Wada 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wada K. HCV infection among narcotics/methamphetamine abusers. Nippon Rinsho 2004;62(Suppl 7):326‐9. - PubMed
Additional references
Amato 2013
Aspinall 2014
-
- Aspinall EJ, Nambiar D, Goldberg DJ, Hickman M, Weir A, Velzen E, et al. Are needle and syringe programmes associated with a reduction in HIV transmission among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. International Journal of Epidemiology 2014;43(1):235‐48. - PubMed
Bluthenthal 2007
Bourgois 2004
Degenhardt 2010
-
- Degenhardt L, Mathers B, Vickerman P, Rhodes T, Latkin C, Hickman M. Prevention of HIV infection for people who inject drugs: why individual, structural, and combination approaches are needed. Lancet 2010;376(9737):285‐301. - PubMed
Esmaeli 2016
Faggiano 2003
Gibson 1999
-
- Gibson DR, Flynn NM, McCarthy JJ. Effectiveness of methadone treatment in reducing HIV risk behavior and HIV seroconversion among injecting drug users. Aids 1999;13(14):1807‐18. - PubMed
Gibson 2001
-
- Gibson DR, Flynn NM, Perales D. Effectiveness of syringe exchange programs in reducing HIV risk behavior and HIV seroconversion among injecting drug users. AIDS 2001;15(11):1329‐41. - PubMed
Gower 2014
-
- Gower E, Estes C, Blach S, Razavi‐Shearer K, Razavi H. Global epidemiology and genotype distribution of the hepatitis C virus infection. Journal of Hepatology 2014;61(1 Suppl):S45‐57. - PubMed
Gowing 2011
GRADE 2004
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:383‐94. - PubMed
Hagan 2011
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Hope 2010
-
- Hope VD, Hickman M, Ngui SL, Jones S, Telfer M, Bizzarri M, et al. Incidence of HCV infection in PWID as measured via repeat testing such as detection of HCV RNA positive among HCV antibody negative results or antibody avidity. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2010;18:262‐70. - PubMed
Iversen 2015
Jones 2008
-
- Jones L, Pickering L, Sumnall H, Mcveigh J, Bellis MA. A review of the effectiveness and cost‐effectiveness of needle and syringe programmes for injecting drug users. Liverpool: Centre for Public Health, Liverpool John Moores University, 2008.
Kaplan 1992
-
- Kaplan EH, Heimer R. A model‐based estimate of HIV infectivity via needle sharing. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 1992;5(11):1116‐8. - PubMed
MacArthur 2012
Mathers 2008
-
- Mathers BM, Degenhardt L, Phillips B, Wiessing L, Hickman M, Strathdee SA, et al. Global epidemiology of injecting drug use and HIV among people who inject drugs: a systematic review. Lancet 2008;372(9651):1733‐45. - PubMed
Mathers 2012
-
- Mathers BM, Degenhardt L, Ali H, Wiessing L, Hickman M, Mattick RP, et al. HIV prevention, treatment, and care services for people who inject drugs: a systematic review of global, regional, and national coverage. Lancet 2010;375(9719):1014‐28. - PubMed
Miller 2004
-
- Miller CL, Wood E, Spittal PM, Li K, Frankish JC, Braitstein P, et al. The future face of coinfection: prevalence and incidence of HIV and hepatitis C virus coinfection among young injection drug users. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2004;36(2):743‐9. - PubMed
Mohd Hanafiah 2013
-
- Mohd Hanafiah K, Groeger J, Flaxman AD, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: new estimates of age‐specific antibody to HCV seroprevalence. Hepatology 2013;57(4):1333‐42. - PubMed
Palmateer 2010
-
- Palmateer N, Kimber J, Hickman M, Hutchinson S, Rhodes T, Goldberg D. Evidence for the effectiveness of sterile injecting equipment provision in preventing hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus transmission among injecting drug users: a review of reviews. Addiction 2010;105(5):844‐59. - PubMed
Perz 2006
-
- Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA, Hutin YJ, Bell BP. The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide. Journal of Hepatology 2006;45(4):529‐38. - PubMed
Platt 2016
-
- Platt L, Easterbrook P, Gower E, McDonald B, Sabin K, McGowan C, et al. Prevalence and burden of HCV co‐infection in people living with HIV: a global systematic review and meta‐analysis. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2016;16(7):797‐808. - PubMed
Platt 2016a
-
- Platt L, Reed J, Minozzi S, Vickerman P, Hagan H, French C, Jordan A, Degenhardt L, Hope V, Hutchinson S, Maher L, Palmateer N, Taylor A, Hickman M. Effectiveness of needle/syringe programmes and opiate substitution therapy in preventing HCV transmission among people who inject drugs. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 12 Januray 2016;1. - PMC - PubMed
Pouget 2012
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schünemann 2006
-
- Schünemann HJ, Jaeschke R, Cook D, Bria W, El‐Solh A, Ernst A, et al. An official ATS statement: grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in ATS guidelines and recommendations. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006;174(5):605‐14. - PubMed
Sterne 2013
-
- Sterne J, Higgins J, Reeves B. Extending the risk of bias tool to allow for assessment of non‐randomised studies, clust‐randomised trials and cross‐over trials:a Cochrane methods innovation fund project (Workshop), 21st Cochrane Colloquium Abstract Book. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2013.
Strathdee 2010
Tilson 2007
-
- Tilson H, Aramrattana A, Bozzette SA. Preventing HIV Infection among Injecting Drug Users in High‐risk Countries: An Assessment of the Evidence. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine, 2007.
Turner 2011
-
- Turner KM, Hutchinson S, Vickerman P, Hope V, Craine N, Palmateer N, et al. The impact of needle and syringe provision and opiate substitution therapy on the incidence of hepatitis C virus in injecting drug users: pooling of UK evidence. Addiction 2011;106(11):1978‐88. - PubMed
UNAIDS 2014
-
- UNAIDS. Global Statistics. Fact Sheet. UNAIDS, 2014.
Vickerman 2012
-
- Vickerman P, Martin N, Turner K, Hickman M. Can needle and syringe programmes and opiate substitution therapy achieve substantial reductions in hepatitis C virus prevalence? Model projections for different epidemic settings. Addiction 2012;107(11):1984‐95. - PubMed
Vickerman 2014
-
- Vickerman P, Platt L, Jolley E, Rhodes T, Kazatchkine MD, Latypov A. Controlling HIV among people who inject drugs in Eastern Europe and Central Asia: insights from modeling. International Journal on Drug Policy 2014;25(6):1163‐73. - PubMed
Vorma 2013
-
- Vorma H, Sokero P, Aaltonen M, Turtiainen S, Hughes LA, Savolainen J. Participation in opioid substitution treatment reduces the rate of criminal convictions: evidence from a community study. Addictive Behaviors 2013;38(7):2316‐6. - PubMed
WHO 2004
-
- World Health Organization, United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime & UNAIDS. Substitution maintenance therapy in the management of opiod dependence and HIV/AIDS prevention: position paper. World Health Organization, 2004.
Wiessing 2009
Wodak 2004
-
- Wodak A, Cooney A. Effectiveness of sterile needle and syringe programming in reducing HIV/AIDS among injecting drug users. Evidence for Action Technical Papers. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2004.
Wood 2007
-
- Wood E, Lloyd‐Smith E, Li K, Strathdee S, Tyndall M, Montaner J, et al. Frequent needle exchange use and HIV incidence in Vancouver, Canada. American Journal of Medicine 2007;120(2):172‐9. - PubMed
Zhang 1998
-
- Zhang J, Yu KF. What's the relative risk? A method of correcting the odds ratio in cohort studies of common outcomes. JAMA 1998;280(19):1960‐1. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Platt 2016b
-
- Platt L, Reed J, Minozzi S, Vickerman P, Hagan H, French C, et al. Effectiveness of needle/syringe programmes and opiate substitution therapy in preventing HCV transmission among people who inject drugs. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 12 January, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858; CD012021.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

