Regulation of cancer epigenomes with a histone-binding synthetic transcription factor
- PMID: 28919981
- PMCID: PMC5600530
- DOI: 10.1038/s41525-016-0002-3
Regulation of cancer epigenomes with a histone-binding synthetic transcription factor
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Regulation of cancer epigenomes with a histonebinding synthetic transcription factor.NPJ Genom Med. 2017 Sep 5;2:27. doi: 10.1038/s41525-017-0029-0. eCollection 2017. NPJ Genom Med. 2017. PMID: 29263837 Free PMC article.
Abstract
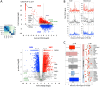
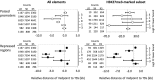
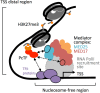
Chromatin proteins have expanded the mammalian synthetic biology toolbox by enabling control of active and silenced states at endogenous genes. Others have reported synthetic proteins that bind DNA and regulate genes by altering chromatin marks, such as histone modifications. Previously, we reported the first synthetic transcriptional activator, the "Polycomb-based transcription factor" (PcTF) that reads histone modifications through a protein-protein interaction between the polycomb chromodomain motif and trimethylated lysine 27 of histone H3 (H3K27me3). Here, we describe the genome-wide behavior of the polycomb-based transcription factor fusion protein. Transcriptome and chromatin profiling revealed several polycomb-based transcription factor-sensitive promoter regions marked by distal H3K27me3 and proximal fusion protein binding. These results illuminate a mechanism in which polycomb-based transcription factor interactions bridge epigenomic marks with the transcription initiation complex at target genes. In three cancer-derived human cell lines tested here, some target genes encode developmental regulators and tumor suppressors. Thus, the polycomb-based transcription factor represents a powerful new fusion protein-based method for cancer research and treatment where silencing marks are translated into direct gene activation.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
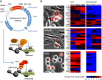
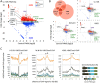
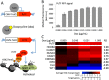
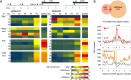
Similar articles
-
Tandem Histone-Binding Domains Enhance the Activity of a Synthetic Chromatin Effector.ACS Synth Biol. 2018 Mar 16;7(3):842-852. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00281. Epub 2018 Feb 23. ACS Synth Biol. 2018. PMID: 29429329 Free PMC article.
-
The synthetic histone-binding regulator protein PcTF activates interferon genes in breast cancer cells.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Sep 25;12(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12918-018-0608-4. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 30253781 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic reversal of epigenetic silencing.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 5;286(31):27176-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C111.229567. Epub 2011 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21669865 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb group protein-mediated histone modifications during cell differentiation.Epigenomics. 2015;7(1):75-84. doi: 10.2217/epi.14.61. Epigenomics. 2015. PMID: 25687468 Review.
-
LHP1 Could Act as an Activator and a Repressor of Transcription in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Nov 28;8:2041. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02041. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29234344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design, Construction, and Validation of Histone-Binding Effectors in Vitro and in Cells.Biochemistry. 2018 Aug 7;57(31):4707-4716. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00327. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29791133 Free PMC article.
-
The sound of silence: Transgene silencing in mammalian cell engineering.Cell Syst. 2022 Dec 21;13(12):950-973. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2022.11.005. Cell Syst. 2022. PMID: 36549273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic Reader-Actuators Targeted to Polycomb-Silenced Genes Block Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Proliferation and Invasion.GEN Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 1;2(4):301-316. doi: 10.1089/genbio.2023.0020. Epub 2023 Aug 17. GEN Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37928406 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the marks: reader-effectors as drivers of epigenetics and chromatin engineering.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 May;47(5):417-432. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.03.002. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35427480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tandem Histone-Binding Domains Enhance the Activity of a Synthetic Chromatin Effector.ACS Synth Biol. 2018 Mar 16;7(3):842-852. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00281. Epub 2018 Feb 23. ACS Synth Biol. 2018. PMID: 29429329 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

