Two-tailed RT-qPCR: a novel method for highly accurate miRNA quantification
- PMID: 28911110
- PMCID: PMC5587787
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx588
Two-tailed RT-qPCR: a novel method for highly accurate miRNA quantification
Abstract
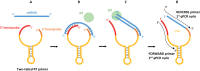
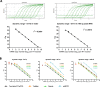
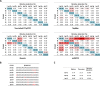
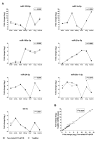
MicroRNAs are a class of small non-coding RNAs that serve as important regulators of gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. They are stable in body fluids and pose great potential to serve as biomarkers. Here, we present a highly specific, sensitive and cost-effective system to quantify miRNA expression based on two-step RT-qPCR with SYBR-green detection chemistry called Two-tailed RT-qPCR. It takes advantage of novel, target-specific primers for reverse transcription composed of two hemiprobes complementary to two different parts of the targeted miRNA, connected by a hairpin structure. The introduction of a second probe ensures high sensitivity and enables discrimination of highly homologous miRNAs irrespectively of the position of the mismatched nucleotide. Two-tailed RT-qPCR has a dynamic range of seven logs and a sensitivity sufficient to detect down to ten target miRNA molecules. It is capable to capture the full isomiR repertoire, leading to accurate representation of the complete miRNA content in a sample. The reverse transcription step can be multiplexed and the miRNA profiles measured with Two-tailed RT-qPCR show excellent correlation with the industry standard TaqMan miRNA assays (r2 = 0.985). Moreover, Two-tailed RT-qPCR allows for rapid testing with a total analysis time of less than 2.5 hours.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Linear-hairpin variable primer RT-qPCR for MicroRNA.Chem Sci. 2018 Dec 4;10(7):2034-2043. doi: 10.1039/c8sc04621b. eCollection 2019 Feb 21. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 30842860 Free PMC article.
-
Stem-loop RT-qPCR for microRNA expression profiling.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;822:33-52. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-427-8_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22144190
-
MicroRNA detection in prostate tumors by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR).J Vis Exp. 2012 May 16;(63):e3874. doi: 10.3791/3874. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22643910 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA.Methods. 2008 Jan;44(1):31-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.09.006. Methods. 2008. PMID: 18158130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA Quantification Method Using Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction in Conjunction with C q Method.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1706:257-265. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7471-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29423803 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and optimization of parameters for accurate quantification of RNA by RT-dPCR.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 Sep;416(23):5049-5058. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05447-x. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39046502
-
Research progress in molecular biology related quantitative methods of MicroRNA.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Jul 15;12(7):3198-3211. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32774694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of miR-21 in Osteoblasts-Osteoclasts Coupling In Vitro.Cells. 2020 Feb 19;9(2):479. doi: 10.3390/cells9020479. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32093031 Free PMC article.
-
Linear-hairpin variable primer RT-qPCR for MicroRNA.Chem Sci. 2018 Dec 4;10(7):2034-2043. doi: 10.1039/c8sc04621b. eCollection 2019 Feb 21. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 30842860 Free PMC article.
-
Research Tools for the Functional Genomics of Plant miRNAs During Zygotic and Somatic Embryogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 14;21(14):4969. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144969. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32674459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huntzinger E., Izaurralde E.. Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011; 12:99–110. - PubMed
-
- Kim V.N., Han J., Siomi M.C.. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009; 10:126–139. - PubMed
-
- Winter J., Jung S., Keller S., Gregory R.I., Diederichs S.. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009; 11:228–234. - PubMed
-
- Krol J., Loedige I., Filipowicz W.. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010; 11:597–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

