The hallmarks of mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 28893420
- PMCID: PMC5667560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.05.034
The hallmarks of mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
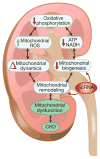
Recent advances have led to a greater appreciation of how mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to diverse acute and chronic pathologies. Indeed, mitochondria have received increasing attention as a therapeutic target in a variety of diseases because they serve as key regulatory hubs uniquely situated at crossroads between multiple cellular processes. This review provides an overview of the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease, with special emphasis on its role in the development of diabetic nephropathy. We examine the current understanding of the molecular mechanisms that cause mitochondrial dysfunction in the kidney and describe the impact of mitochondrial damage on kidney function. The new concept that mitochondrial shape and structure are closely linked with its function in the kidneys is discussed. Furthermore, the mechanisms that translate cellular cues and demands into mitochondrial remodeling and cellular damage, including the role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs, are examined with the final goal of identifying mitochondrial targets to improve treatment of patients with chronic kidney diseases.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; chronic kidney disease; diabetes; diabetic nephropathy; mitochondria; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2017 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic kidney disease.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Sep;496:108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.07.005. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31276635 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Diabetic Kidney.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;982:553-562. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55330-6_28. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28551806 Review.
-
The long noncoding RNA Tug1 connects metabolic changes with kidney disease in podocytes.J Clin Invest. 2016 Nov 1;126(11):4072-4075. doi: 10.1172/JCI90828. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27760046 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathophysiology of renal diseases.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Feb 15;306(4):F367-78. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00571.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24305473 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Diabetic Nephropathy: Nontraditional Therapeutic Opportunities.J Diabetes Res. 2021 Dec 9;2021:1010268. doi: 10.1155/2021/1010268. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 34926696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant protects against chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced renal injury in rats.BMC Nephrol. 2021 Apr 26;22(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02362-6. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33902473 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in kidney disease: Implications for vascular growth factors.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(22):12910-12919. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15999. Epub 2020 Oct 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33067928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Acute to Chronic: Unraveling the Pathophysiological Mechanisms of the Progression from Acute Kidney Injury to Acute Kidney Disease to Chronic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 1;25(3):1755. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031755. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex Differences of Cardiolipin in Tissue Distribution Based on Targeted Lipidomic Analysis by UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS.Molecules. 2022 Oct 18;27(20):6988. doi: 10.3390/molecules27206988. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296581 Free PMC article.
-
Food as medicine: targeting the uraemic phenotype in chronic kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Mar;17(3):153-171. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-00345-8. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 32963366 Review.
References
-
- Wirthensohn G, Guder WG. Renal substrate metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1986;66:469–497. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 2005;54:1615–1625. - PubMed
-
- Tubbs E, Rieusset J. Metabolic signaling functions of ER-mitochondria contact sites: role in metabolic diseases. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017;58:R87–R106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

