A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson's disease risk loci
- PMID: 28892059
- PMCID: PMC5812477
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3955
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson's disease risk loci
Abstract
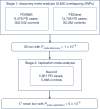
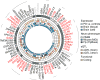
Common variant genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have, to date, identified >24 risk loci for Parkinson's disease (PD). To discover additional loci, we carried out a GWAS comparing 6,476 PD cases with 302,042 controls, followed by a meta-analysis with a recent study of over 13,000 PD cases and 95,000 controls at 9,830 overlapping variants. We then tested 35 loci (P < 1 × 10-6) in a replication cohort of 5,851 cases and 5,866 controls. We identified 17 novel risk loci (P < 5 × 10-8) in a joint analysis of 26,035 cases and 403,190 controls. We used a neurocentric strategy to assign candidate risk genes to the loci. We identified protein-altering or cis-expression quantitative trait locus (cis-eQTL) variants in linkage disequilibrium with the index variant in 29 of the 41 PD loci. These results indicate a key role for autophagy and lysosomal biology in PD risk, and suggest potential new drug targets for PD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the
Figures
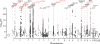
Comment in
-
Novel Parkinson's disease risk loci identified through a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies.Mov Disord. 2018 Jan;33(1):74. doi: 10.1002/mds.27276. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 29266412 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes for Parkinson's disease in an Ashkenazi Jewish population.BMC Med Genet. 2011 Aug 3;12:104. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-12-104. BMC Med Genet. 2011. PMID: 21812969 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson's disease.Nat Genet. 2009 Dec;41(12):1303-7. doi: 10.1038/ng.485. Epub 2009 Nov 15. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19915576
-
Functional genomics elucidates regulatory mechanisms of Parkinson's disease-associated variants.BMC Med. 2022 Feb 16;20(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02264-w. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 35168626 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omic insights into Parkinson's Disease: From genetic associations to functional mechanisms.Neurobiol Dis. 2022 Feb;163:105580. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105580. Epub 2021 Dec 4. Neurobiol Dis. 2022. PMID: 34871738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in understanding genomic markers and pharmacogenetics of Parkinson's disease.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;12(4):433-48. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2016.1158250. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26910127 Review.
Cited by
-
An Introspective Approach: A Lifetime of Parkinson's Disease Research and Not Much to Show for it Yet?Cells. 2021 Feb 28;10(3):513. doi: 10.3390/cells10030513. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33670933 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation as a mediator of genetic and environmental influences on Parkinson's disease susceptibility: Impacts of alpha-Synuclein, physical activity, and pesticide exposure on the epigenome.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 19;13:971298. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.971298. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36061205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics in parkinson's disease: From better disease understanding to machine learning based precision medicine.Front Mol Med. 2022 Oct 3;2:933383. doi: 10.3389/fmmed.2022.933383. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 39086979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accurate MS-based Rab10 Phosphorylation Stoichiometry Determination as Readout for LRRK2 Activity in Parkinson's Disease.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Sep;19(9):1546-1560. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.002055. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32601174 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative polyadenylation transcriptome-wide association study identifies APA-linked susceptibility genes in brain disorders.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 3;14(1):583. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36311-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36737438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corti O, Lesage S, Brice A. What genetics tells us about the causes and mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease. Physiol. Rev. 2011;91:1161–1218. - PubMed
-
- Verstraeten A, Theuns J, Van Broeckhoven C. Progress in unraveling the genetic etiology of Parkinson disease in a genomic era. Trends Genet. 2015;31:140–149. - PubMed
-
- Nussbaum RL, Ellis CE. Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1356–1364. - PubMed
-
- Shulman JM, De Jager PL, Feany MB. Parkinson’s disease: genetics and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011;6:193–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

