Cell-specific gain modulation by synaptically released zinc in cortical circuits of audition
- PMID: 28887876
- PMCID: PMC5876454
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.29893
Cell-specific gain modulation by synaptically released zinc in cortical circuits of audition
Abstract
In many excitatory synapses, mobile zinc is found within glutamatergic vesicles and is coreleased with glutamate. Ex vivo studies established that synaptically released (synaptic) zinc inhibits excitatory neurotransmission at lower frequencies of synaptic activity but enhances steady state synaptic responses during higher frequencies of activity. However, it remains unknown how synaptic zinc affects neuronal processing in vivo. Here, we imaged the sound-evoked neuronal activity of the primary auditory cortex in awake mice. We discovered that synaptic zinc enhanced the gain of sound-evoked responses in CaMKII-expressing principal neurons, but it reduced the gain of parvalbumin- and somatostatin-expressing interneurons. This modulation was sound intensity-dependent and, in part, NMDA receptor-independent. By establishing a previously unknown link between synaptic zinc and gain control of auditory cortical processing, our findings advance understanding about cortical synaptic mechanisms and create a new framework for approaching and interpreting the role of the auditory cortex in sound processing.
Keywords: auditory cortex; cortical gain; interneurons; mouse; neuroscience; principal neurons; sound processing; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures
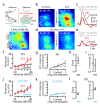
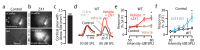
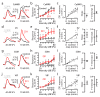
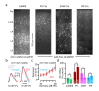
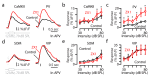
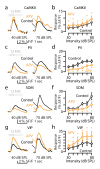
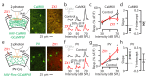
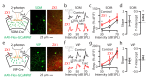
Comment in
-
A new role for zinc in the brain.Elife. 2017 Oct 6;6:e31816. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31816. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28985179 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Fine Control of Sound Frequency Tuning and Frequency Discrimination Acuity by Synaptic Zinc Signaling in Mouse Auditory Cortex.J Neurosci. 2019 Jan 30;39(5):854-865. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1339-18.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 30. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30504277 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Zinc Enhances Inhibition Mediated by Somatostatin, but not Parvalbumin, Cells in Mouse Auditory Cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2020 Jun 1;30(7):3895-3909. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa005. Cereb Cortex. 2020. PMID: 32090251 Free PMC article.
-
Context-Dependent Modulation of Excitatory Synaptic Strength by Synaptically Released Zinc.eNeuro. 2017 Mar 3;4(1):ENEURO.0011-17.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0011-17.2017. eCollection 2017 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 28275718 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc at glutamatergic synapses.Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):126-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.061. Epub 2008 Feb 15. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18353558 Review.
-
Synaptic interactions and inhibitory regulation in auditory cortex.Biol Psychol. 2016 Apr;116:4-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 7. Biol Psychol. 2016. PMID: 26555718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Superiority of SpiroZin2 Versus FluoZin-3 for monitoring vesicular Zn2+ allows tracking of lysosomal Zn2+ pools.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 9;8(1):15034. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33102-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30302024 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulatory Mechanisms Underlying Contrast Gain Control in Mouse Auditory Cortex.J Neurosci. 2022 Jul 13;42(28):5564-5579. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2054-21.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 3. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35998293 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Transcriptional Changes in AMPA and GABAA Receptor Genes Support Compensatory Plasticity Following Unilateral Hearing Loss.Neuroscience. 2019 May 21;407:108-119. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.08.023. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30176318 Free PMC article.
-
Fine Control of Sound Frequency Tuning and Frequency Discrimination Acuity by Synaptic Zinc Signaling in Mouse Auditory Cortex.J Neurosci. 2019 Jan 30;39(5):854-865. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1339-18.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 30. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30504277 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type-specific plasticity of inhibitory interneurons in the rehabilitation of auditory cortex after peripheral damage.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 13;14(1):4170. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39732-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37443148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carlén M, Meletis K, Siegle JH, Cardin JA, Futai K, Vierling-Claassen D, Rühlmann C, Jones SR, Deisseroth K, Sheng M, Moore CI, Tsai LH. A critical role for NMDA receptors in parvalbumin interneurons for gamma rhythm induction and behavior. Molecular Psychiatry. 2012;17:537–548. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.31. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

