Kinesin-2 motors adapt their stepping behavior for processive transport on axonemes and microtubules
- PMID: 28887322
- PMCID: PMC5666610
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.201744097
Kinesin-2 motors adapt their stepping behavior for processive transport on axonemes and microtubules
Abstract
Two structurally distinct filamentous tracks, namely singlet microtubules in the cytoplasm and axonemes in the cilium, serve as railroads for long-range transport processes in vivo In all organisms studied so far, the kinesin-2 family is essential for long-range transport on axonemes. Intriguingly, in higher eukaryotes, kinesin-2 has been adapted to work on microtubules in the cytoplasm as well. Here, we show that heterodimeric kinesin-2 motors distinguish between axonemes and microtubules. Unlike canonical kinesin-1, kinesin-2 takes directional, off-axis steps on microtubules, but it resumes a straight path when walking on the axonemes. The inherent ability of kinesin-2 to side-track on the microtubule lattice restricts the motor to one side of the doublet microtubule in axonemes. The mechanistic features revealed here provide a molecular explanation for the previously observed partitioning of oppositely moving intraflagellar transport trains to the A- and B-tubules of the same doublet microtubule. Our results offer first mechanistic insights into why nature may have co-evolved the heterodimeric kinesin-2 with the ciliary machinery to work on the specialized axonemal surface for two-way traffic.
Keywords: axonemes; heterodimeric kinesin‐2; intraflagellar transport; microtubules.
© 2017 The Authors.
Figures
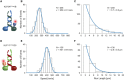
- A–C
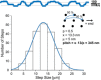
The movement of single KLP3A/B motors fluorescently labeled at the KLP3A subunit was tracked on surface‐attached microtubules at saturating ATP conditions. The velocity (B) and run length data (C) were fit to a Gaussian and single‐exponential distribution, respectively.
- D–F
The corresponding analysis of the KLP11/20 motor fluorescently labeled at the KLP11 subunit moving on surface‐attached axonemes.
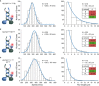
Removal of the random‐coil domain of the KLP3A subunit failed to interfere with the transport parameters of the KLP3A/B motor.
In contrast, removing the corresponding domain of the KLP3B subunit reduced the run length by ˜50% without substantially affecting the velocity of the KLP3A/B motor.
Removal of both random‐coil domains had the same effect as the removal of the KLP3B C‐terminal domain (B).
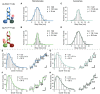
- A, B
The step size distribution centered around ˜13 nm when walking on microtubules. Together with the double‐exponential decay of the dwell times (E, F), these results support a hand‐over‐hand type stepping of the respective motors.
- C, D
Tracking on axonemes increased step size distribution to ˜16 nm which is consistent with protofilament tracking.
- E, F
Double‐exponential decay of the dwell times and raw stepping data with detected steps.
- G, H
Double‐exponential decay of the dwell times again argues for a hand‐over‐hand stepping mechanism on axonemes.
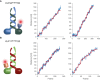
- A, B
Photons from a single fluorophore detected on the CCD are localized and tracked over time. Localization is achieved by fitting a two‐dimensional Gaussian profile to the spot. The Euclidean distance of each location to the position in the first frame is calculated and plotted in blue. Steps in the data are detected by a gliding t‐value algorithm and plotted in red. Frames have a cycle time of 505 ms.
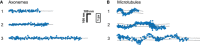
- A, B
On the rotationally symmetric microtubule filaments, the motors show a sinusoidal trajectory, corresponding to a periodic helical path around the symmetry axis of the filament. The axoneme is lacking this symmetry due to the combination of the A‐ and B‐tubules into a doublet microtubule along with the interconnection between the respective doublet tubules. Without a symmetry axis, the periodic path is lost and the motor is restricted to a straight path. The dashed lines underlining the respective trajectories have been obtained from a subpixel detection of filament positions (see Materials and Methods for details). Images of the filaments are shown in Appendix Fig S9, and respective kymographs are shown in Fig EV2.
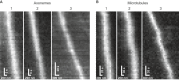
- A, B
The numbers correspond to the runs shown in Fig 4A and B.
Similar articles
-
Measuring rates of intraflagellar transport along Caenorhabditis elegans sensory cilia using fluorescence microscopy.Methods Enzymol. 2013;524:285-304. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397945-2.00016-0. Methods Enzymol. 2013. PMID: 23498746
-
Optimal sidestepping of intraflagellar transport kinesins regulates structure and function of sensory cilia.EMBO J. 2020 Jun 17;39(12):e103955. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019103955. Epub 2020 Apr 27. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 32338401 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport velocity is governed by the number of active KIF17 and KIF3AB motors and their motility properties under load.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 15;114(33):E6830-E6838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708157114. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28761002 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport and the generation of dynamic, structurally and functionally diverse cilia.Trends Cell Biol. 2009 Jul;19(7):306-16. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.04.002. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Trends Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19560357 Review.
-
Kinesin motors and primary cilia.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Oct;39(5):1120-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0391120. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21936775 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Temperature-Dependent Activity of Motor Proteins: Energetics and Their Implications for Collective Behavior.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 26;9:610899. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.610899. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33732692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinesin-2 from C. reinhardtii Is an Atypically Fast and Auto-inhibited Motor that Is Activated by Heterotrimerization for Intraflagellar Transport.Curr Biol. 2020 Mar 23;30(6):1160-1166.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.01.046. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32142698 Free PMC article.
-
The crowding dynamics of the motor protein kinesin-II.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 13;15(2):e0228930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228930. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32053680 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving kinesin stepping: one head at a time.Life Sci Alliance. 2019 Oct 10;2(5):e201900456. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201900456. Print 2019 Oct. Life Sci Alliance. 2019. PMID: 31601622 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution reveals motor activation for intraflagellar transport.Nature. 2018 May;557(7705):387-391. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0105-3. Epub 2018 May 9. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29743676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Block SM, Goldstein LS, Schnapp BJ (1990) Bead movement by single kinesin molecules studied with optical tweezers. Nature 348: 348–352 - PubMed
-
- Mehta AD, Rock RS, Rief M, Spudich JA, Mooseker MS, Cheney RE (1999) Myosin‐V is a processive actin‐based motor. Nature 400: 590–593 - PubMed
-
- Howard J, Hudspeth AJ, Vale RD (1989) Movement of microtubules by single kinesin molecules. Nature 342: 154–158 - PubMed
-
- Svoboda K, Schmidt CF, Schnapp BJ, Block SM (1993) Direct observation of kinesin stepping by optical trapping interferometry. Nature 365: 721–727 - PubMed
-
- Woehlke G, Schliwa M (2000) Walking on two heads: the many talents of kinesin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1: 50–58 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

