Tumor size and proliferative marker geminin rather than Ki67 expression levels significantly associated with maximum uptake of 18F-deoxyglucose levels on positron emission tomography for breast cancers
- PMID: 28886153
- PMCID: PMC5590948
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184508
Tumor size and proliferative marker geminin rather than Ki67 expression levels significantly associated with maximum uptake of 18F-deoxyglucose levels on positron emission tomography for breast cancers
Abstract
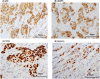
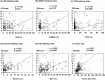
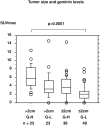
It has been well established that maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) for 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG PET/CT) is clinically useful for evaluating treatment efficacy as well as predicting prognosis of breast cancer patients. Although SUVmax reflects increased glucose uptake and metabolism possibly induced by activation of growth factor signaling or TP53 dysfunction, tumor characteristics of SUVmax-high breast cancers remain to be elucidated. For the present study, we used immunohistochemical staining to investigate expressions of phospho-ribosomal protein S6 (pS6, downstream molecule of phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of the rapamycin/S6K pathway) and phosphor-p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (pMAPK). Expression levels of TP53 and proliferative marker geminin as well as Ki67 were also examined by means of immunostaining in 163 invasive breast cancers. Cutoff values were set at 10% for pS6, 20% for pMAPK and TP53, and 4% for geminin. The SUVmax levels were significantly higher in the pS6-positive (p = 0.0173), TP53-positive (p = 0.0207) and geminin-high cancers (p<0.0001), but there was no significant association between pMAPK expression levels and SUVmax levels. Multivariable analysis showed that a high geminin level (odds ratio: 6.497, 95% confidence interval: 2.427-19.202, p = 0.0001) and large tumor size (6.438, 2.224-20.946, p = 0.0005) were significantly and independently associated with SUVmax-high. Univariable but not multivariable analysis indicated that Ki67-high significantly correlated with SUVmax-high. Twenty of 23 (87.0%) breast cancers with tumor size >2cm and geminin-high showed SUVmax-high, while only 6 of 49 (12.2%) breast cancers ≤2cm in size and with low geminin levels were SUVmax-high. In conclusion, we could determine that breast cancers with a large tumor and a geminin-high rather than Ki67-high proliferative marker were significantly associated with high levels of SUVmax. These findings may signify that SUVmax reflects tumor characteristics with high proliferative activity but not activation of mTOR/S6K and MAPK pathways or increased glucose metabolism due to dysfunction of TP53.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of mTOR/S6K But Not MAPK Pathways Might Be Associated With High Ki-67, ER(+), and HER2(-) Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2015 Jun;15(3):197-203. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Clin Breast Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25600244
-
Prognostic significance of geminin expression levels in Ki67-high subset of estrogen receptor-positive and HER2-negative breast cancers.Breast Cancer. 2016 Mar;23(2):224-30. doi: 10.1007/s12282-014-0556-9. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Breast Cancer. 2016. PMID: 25082658
-
Prognostic significance of preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT for breast cancer subtypes.Breast. 2016 Dec;30:5-12. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.08.003. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Breast. 2016. PMID: 27569020
-
Association between partial-volume corrected SUVmax and Oncotype DX recurrence score in early-stage, ER-positive/HER2-negative invasive breast cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016 Aug;43(9):1574-84. doi: 10.1007/s00259-016-3418-1. Epub 2016 May 21. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27209424
-
Biostatistics and tumor marker studies in breast cancer: design, analysis and interpretation issues.Int J Biol Markers. 2003 Jan-Mar;18(1):40-8. doi: 10.1177/172460080301800107. Int J Biol Markers. 2003. PMID: 12699062 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Clinical Utility of Pre-Therapeutic [18F]FDG PET/CT Imaging for Predicting Outcomes in Breast Cancer.J Clin Med. 2023 Aug 24;12(17):5487. doi: 10.3390/jcm12175487. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37685551 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Accuracy of FUCCI Cell Cycle In Vivo Fluorescent Imaging to Assess Tumor Proliferation in Preclinical Oncology Models.Mol Imaging Biol. 2022 Dec;24(6):898-908. doi: 10.1007/s11307-022-01739-9. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Mol Imaging Biol. 2022. PMID: 35650411
-
Relationship between 18F-FDG PET/CT Semi-Quantitative Parameters and International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Classification in Lung Adenocarcinomas.Korean J Radiol. 2022 Jan;23(1):112-123. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2021.0455. Korean J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34983098 Free PMC article.
-
Total metabolic tumor volume and spleen metabolism on baseline [18F]-FDG PET/CT as independent prognostic biomarkers of recurrence in resected breast cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Oct;48(11):3560-3570. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05322-2. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33774685
-
Associations Between PET Parameters and Expression of Ki-67 in Breast Cancer.Transl Oncol. 2019 Feb;12(2):375-380. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30522044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee JH. Radionuclide methods for breast cancer staging. Semin Nucl Med. 2013;43(4):294–8. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2013.04.001 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garami Z, Hascsi Z, Varga J, Dinya T, Tanyi M, Garai I, et al. The value of 18-FDG PET/CT in early-stage breast cancer compared to traditional diagnostic modalities with an emphasis on changes in disease stage designation and treatment plan. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012;38(1):31–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2011.09.002 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kadoya T, Aogi K, Kiyoto S, Masumoto N, Sugawara Y, Okada M. Role of maximum standardized uptake value in fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography predicts malignancy grade and prognosis of operable breast cancer: a multi-institute study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;141(2):269–75. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2687-7 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahn SG, Park JT, Lee HM, Lee HW, Jeon TJ, Han K, et al. Standardized uptake value of (1)(8)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for prediction of tumor recurrence in breast cancer beyond tumor burden. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16(6):502 doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0502-y ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang JS, Lee J, Kim HJ, Kim KH, Yun M, Kim SI, et al. (18)F-FDG/PET May Help to Identify a Subgroup of Patients with T1-T2 Breast Cancer and 1–3 Positive Lymph Nodes Who Are at a High Risk of Recurrence after Mastectomy. Cancer Res Treat. 2016;48(2):508–17. doi: 10.4143/crt.2015.172 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

