In vitro Evaluation of Acyclovir/Chitosan Floating Systems
- PMID: 28883376
- PMCID: PMC5445812
- DOI: 10.3390/ma3125195
In vitro Evaluation of Acyclovir/Chitosan Floating Systems
Abstract
Chitosan (CS) floating lyophilized formulations (L) for gastric drug delivery of acyclovir (ACV) have been developed. The freeze-dried formulations were obtained from acidic aqueous suspensions prepared with different ACV/CS ratios. No changes in ACV crystallinity were observed during X-ray diffraction powder studies as a consequence of the manufacturing process. Considering that fed and fasted states modified the intragastric pH, swelling and in vitro dissolution studies were carried out in different acidic media (0.1 M HCl and progressive pH medium) in order to understand the influence of these physiological states on ACV/CS formulations. Swelling behavior of the floating lyophilized formulations was dependent on CS and ACV proportions within L and on medium nature due to pH dependent CS solubility. Furthermore, no interactions between ACV and CS were detected in solid state according to the X-ray studies. In vitro dissolution of ACV from L was influenced by the swelling behavior. However, it is feasible to optimize the ACV/CS ratios to achieve a desired formulation that releases the total quantity of ACV at a specific time. Moreover, floatability was assessed by buoyancy tests. The results demonstrated that the freeze-drying process achieved effective floating systems capable of remaining within the stomach while the total amount of ACV is released from L.
Keywords: Acyclovir; chitosan; controlled release; floating freeze-dried formulations; swelling behavior.
Figures
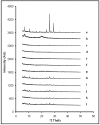
 pH 4) (B).
pH 4) (B).
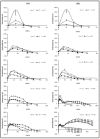
 pH 4).
pH 4).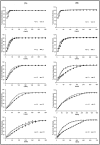
 pH 4) (B).
pH 4) (B).Similar articles
-
Characterization and dissolution study of chitosan freeze-dried systems for drug controlled release.Molecules. 2009 Oct 30;14(11):4370-86. doi: 10.3390/molecules14114370. Molecules. 2009. PMID: 19924071 Free PMC article.
-
Mucoadhesive tablets for controlled release of acyclovir.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012;60(10):1249-57. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c12-00324. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012. PMID: 22863800
-
Development of mucoadhesive floating hollow beads of acyclovir with gastroretentive properties.Pharm Dev Technol. 2014 Aug;19(5):571-6. doi: 10.3109/10837450.2013.813539. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Pharm Dev Technol. 2014. PMID: 23859639
-
Development and evaluation of a monolithic floating drug delivery system for acyclovir.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012;60(2):172-7. doi: 10.1248/cpb.60.172. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012. PMID: 22293475
-
Development and evaluation of alginate-chitosan gastric floating beads loading with oxymatrine solid dispersion.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42(3):456-63. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2015.1088866. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26422447
References
-
- Skaugrud O. Chitosan––New biopolymer for cosmetics and drugs. Drug Cosmetic Ind. 1991;148:24–29.
-
- Ilango R., Jayakar B., Kavimani S. Chitosan as a new pharmaceutical excipient. The East. Pharm. 1998;41:47–49.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

