The Tiam1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor is auto-inhibited by its pleckstrin homology coiled-coil extension domain
- PMID: 28882897
- PMCID: PMC5663878
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.799114
The Tiam1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor is auto-inhibited by its pleckstrin homology coiled-coil extension domain
Abstract
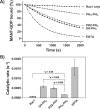
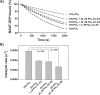
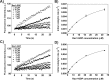
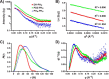
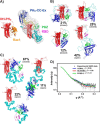
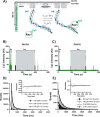
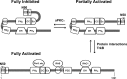
T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 1 (Tiam1) is a Dbl-family guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that specifically activates the Rho-family GTPase Rac1 in response to upstream signals, thereby regulating cellular processes including cell adhesion and migration. Tiam1 contains multiple domains, including an N-terminal pleckstrin homology coiled-coiled extension (PHn-CC-Ex) and catalytic Dbl homology and C-terminal pleckstrin homology (DH-PHc) domain. Previous studies indicate that larger fragments of Tiam1, such as the region encompassing the N-terminal to C-terminal pleckstrin homology domains (PHn-PHc), are auto-inhibited. However, the domains in this region responsible for inhibition remain unknown. Here, we show that the PHn-CC-Ex domain inhibits Tiam1 GEF activity by directly interacting with the catalytic DH-PHc domain, preventing Rac1 binding and activation. Enzyme kinetics experiments suggested that Tiam1 is auto-inhibited through occlusion of the catalytic site rather than by allostery. Small angle X-ray scattering and ensemble modeling yielded models of the PHn-PHc fragment that indicate it is in equilibrium between "open" and "closed" conformational states. Finally, single-molecule experiments support a model in which conformational sampling between the open and closed states of Tiam1 contributes to Rac1 dissociation. Our results highlight the role of the PHn-CC-Ex domain in Tiam1 GEF regulation and suggest a combinatorial model for GEF inhibition and activation of the Rac1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1); Tiam1; auto-inhibition; enzyme kinetics; guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF); in vitro GEF assays; inhibition mechanism; single-molecule total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy; small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS).
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-resolution structure of the Tiam1 PHn-CC-Ex domain.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013 Jul;69(Pt 7):744-52. doi: 10.1107/S1744309113014206. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013. PMID: 23832200 Free PMC article.
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
-
CD44 interaction with tiam1 promotes Rac1 signaling and hyaluronic acid-mediated breast tumor cell migration.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jan 21;275(3):1829-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.3.1829. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10636882
-
Crystal structure of Rac1 in complex with the guanine nucleotide exchange region of Tiam1.Nature. 2000 Dec 7;408(6813):682-8. doi: 10.1038/35047014. Nature. 2000. PMID: 11130063
-
New Mechanisms Underlying Oncogenesis in Dbl Family Rho Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors.Mol Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 16;106(3):117-128. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.124.000904. Mol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38902036 Review.
Cited by
-
GPCRs that Rhoar the Guanine nucleotide exchange factors.Small GTPases. 2022 Jan;13(1):84-99. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2021.1896963. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Small GTPases. 2022. PMID: 33849392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoactivatable Nanobody Conjugate Dimerizer Temporally Resolves Tiam1-Rac1 Signaling Axis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Mar;11(11):e2307549. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307549. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38225743 Free PMC article.
-
Par3 is essential for the establishment of planar cell polarity of inner ear hair cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 12;116(11):4999-5008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816333116. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30814219 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal domain of the adaptor protein p140Cap interacts with Tiam1 and controls Tiam1/Rac1 axis.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 1;10(12):4308-4324. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33415001 Free PMC article.
-
Tiam1 is Critical for Glutamatergic Synapse Structure and Function in the Hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2019 Nov 20;39(47):9306-9315. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1566-19.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 9. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31597723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hodge R. G., and Ridley A. J. (2016) Regulating Rho GTPases and their regulators. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 17, 496–510 - PubMed
-
- Chen X., and Macara I. G. (2005) Par-3 controls tight junction assembly through the Rac exchange factor Tiam1. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 262–269 - PubMed
-
- Jaffe A. B., and Hall A. (2005) Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 247–269 - PubMed
-
- Nishimura T., Yamaguchi T., Kato K., Yoshizawa M., Nabeshima Y., Ohno S., Hoshino M., and Kaibuchi K. (2005) PAR-6-PAR-3 mediates Cdc42-induced Rac activation through the Rac GEFs STEF/Tiam1. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 270–277 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

