Dihydrocapsaicin Attenuates Blood Brain Barrier and Cerebral Damage in Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion via Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory
- PMID: 28874782
- PMCID: PMC5585260
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11181-5
Dihydrocapsaicin Attenuates Blood Brain Barrier and Cerebral Damage in Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion via Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory
Abstract
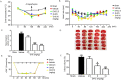
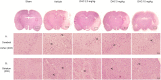
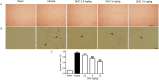
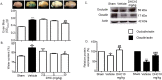
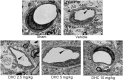
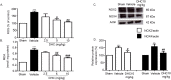
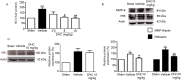
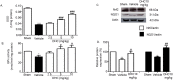
This study investigated the effect of dihydrocapsaicin (DHC) on cerebral and blood brain barrier (BBB) damage in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) models. The models were induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 2 h followed by reperfusion. The rats were divided into five groups: sham, or control group; vehicle group; and 2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, and 10 mg/kg BW DHC-treated I/R groups. After 24 h of reperfusion, we found that DHC significantly reduced the area of infarction, morphology changes in the neuronal cells including apoptotic cell death, and also decreased the BBB damage via reducing Evan Blue leakage, water content, and ultrastructure changes, in addition to increasing the tight junction (TJ) protein expression. DHC also activated nuclear-related factor-2 (Nrf2) which involves antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and significantly decreased oxidative stress and inflammation via down-regulated reactive oxygen species (ROS), NADPH oxidase (NOX2, NOX4), nuclear factor kappa-beta (NF-ĸB), and nitric oxide (NO), including matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9) levels. DHC protected the cerebral and the BBB from I/R injury via attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Therefore, this study offers to aid future development for protection against cerebral I/R injury in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin by down-regulating NF-kB and elevating Nrf2, reduces brain edema and neurological dysfunction after cerebral I/R.Microvasc Res. 2016 Jul;106:117-27. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2015.12.008. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Microvasc Res. 2016. PMID: 26686249
-
Isoquercetin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury via Nrf2-mediated inhibition of the NOX4/ROS/NF-κB pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Mar 25;284:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29454613
-
DCA Protects against Oxidation Injury Attributed to Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion by Regulating Glycolysis through PDK2-PDH-Nrf2 Axis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 19;2021:5173035. doi: 10.1155/2021/5173035. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34712383 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Ganoderic Acid against Focal Ischemic Stroke Induced by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in the Rats via Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2024 Oct;518(1):361-371. doi: 10.1134/S1607672924600313. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39023671
-
Morin protects the blood-brain barrier integrity against cerebral ischemia reperfusion through anti-inflammatory actions in rats.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 7;10(1):13379. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70214-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32770144 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Apelin-13 prevents the effects of oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion on bEnd.3 cells by inhibiting AKT-mTOR signaling.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Jan;248(2):146-156. doi: 10.1177/15353702221139186. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 36573455 Free PMC article.
-
The Nrf2 Pathway in Ischemic Stroke: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Aug 18;26(16):5001. doi: 10.3390/molecules26165001. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA LOC366613 alleviates the cerebral ischemic injury via regulating the miR-532-5p/phosphatase and tensin homolog axis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):2511-2522. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1930966. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34251959 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo protective effects of 6‑gingerol in cerebral ischemia involve preservation of antioxidant defenses and activation of anti‑apoptotic pathways.Biomed Rep. 2024 Apr 4;20(6):85. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1773. eCollection 2024 Jun. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 38665422 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane Protects Piglet Brains from Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury.Dev Neurosci. 2020;42(2-4):124-134. doi: 10.1159/000511888. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Dev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33302269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holm, L. Focal ischemic reperfusion stroke model in rats and the role of galanin. Linkoping University Medical Dissertations, (2011).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

